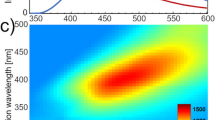
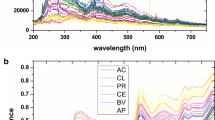
Summary
Use of UV-laser excitation to produce fluorescence spectra for heartwood and sapwood from jack pine (Pinus banksiana), white spruce (Picea glauca) and balsam fir (Abies balsamea) was examined. Spectra were fairly broad without sharp spectral features and overlap of spectra between species was common. Sample to sample and in-sample variation of the recorded fluorescence spectra was observed. The fluorescence spectra obtained from heartwood samples of jack pine showed evidence of photochemical bleaching as a result of the multiple laser pulses needed to produce a complete spectrum. Bleaching may have obscured differences between species. For the mix of species examined no sapwood nor heartwood samples were distinguishable by this technique with the detector used. Use of an optical multichannel analyzer (OMA) could reduce the number of laser pulses needed to obtain an entire spectrum. Under these conditions it would be possible to determine whether the minor differences in spectral features observed for the different species are more pronounced in the first few laser pulses and if they are characteristic of species. Certain aspects of the data suggest that with improved analytical equipment UV-fluorescence might prove to be a useful technique for the identification of certain species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bublitz, W. J.; Meng, T. Y. 1978: The fluorometric behaviour of pulping waste liquors. A valuable tool for lignin and pulping research. Tappi 61(2): 27–30
Dyer, S. T. 1988: Wood fluorescence of indigenous South African trees. IAWA Bull. n.s. 9: 75–87
Hillis, W. E.; Ishikura, N. 1968: The Chromatographic and spectral properties of stilbene derivatives. J. Chromatography 32: 323–336
Krishna, S.; Chowdhury, K. A. 1935: Fluorescence of wood under ultra-violet light. Indian Forester 61: 221–228
Kutscha, N. P.; McOrmond, R. R. 1972: The suitability of using fluorescence microscopy for studying lignification in balsam fir. LSA Experimental Station Technical Bulletin 62
Lamola, A. A.; Hammond, G. S.; Mallory, F. B. 1965: The blue emission from cis-stilbenes. Photochem. Photobiol. 4: 259–263
Malkin, S.; Fischer, E. 1964: Temperature dependence of photoisomerization. III. Direct and sensitized photoisomerization of stilbenes. J. Phys. Chem. 68: 1153–1163
Miller, R. B. 1981: Explanation of coding procedure. IAWA Bull. n.s. 2: 111–145
Miller, R. B.; Baas, P. 1981: Standard list of characters for computerized hardwood identification. IAWA Bull. n.s. 2: 99–110
Stout, S. A.; Bensley, D. F. 1987. Fluorescing macerals from wood precursors. Int. J. of Coal Geology 7: 119–133
Valente, E.; Pardo, L. L. 1957: Fluorescecia de maderas argentinas. Rev. Invest. forestales 1: 47–51
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sum, S.T., Singleton, D.L., Paraskevopoulos, G. et al. Laser-excited fluorescence spectra of eastern SPF wood species. An optical technique for identification and separation of wood species?. Wood Sci.Technol. 25, 405–413 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225233
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225233