Abstract
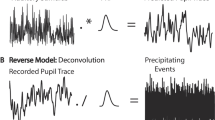
We would like to propose a method of single evoked potential (EP) extraction free from assumptions and based on a novel approach — the wavelet representation of the signal. Wavelets were introduced by Grossman and Morlet in 1984. The method is based on the multiresolution signal decomposition. Wavelets are already used for speech recognition, geophysics investigations and fractal analysis. This method seems to be a useful improvement upon Fourier Transform analysis, since it provides simultaneous information on frequency and time localization of the signal. We would like to introduce wavelet formalism for the first time to brain signal analysis. One of the most important problems in this field is the analysis of evoked potentials. This signal has an amplitude several times smaller than EEG, therefore stimulus-synchronized averaging is commonly used. This method is based on several assumptions. Namely it is postulated that: 1) EP are characterized by a deterministic repeatable pattern, 2) EEG has purely stochastic character, 3) EEG and EP are independent. These assumptions have been challenged e.g. the variability of the EP pattern was demonstrated by John (1973) by means of factor analysis. In view of the works of Sayers et al. (1974) and Başar (1988) EP reflects the reorganization of the spontaneous activity under the influence of a stimulus and it is connected with the redistribution of EEG phases. Several attempts to overcome the limitation of the averaging method have been made. Heintze and Künkel (1984) used an autoregressive moving average (ARMA) model to extract evoked potentials from 2 segments. This was possible under two condiitons: high signal to noise ratio and clear separation of the EEG and EP spectra. These assumptions are not easy to fulfill, though. Cerutti et al. (1987) modeled background EEG activity by means of an AR process and event related brain activity by ARMA. In this way they were able to find a filter extracting single EP. Nevertheless, their method was not quite free of assumptions, since they since they used averaged EP to define their ARMA filter. In the following we shall briefly describe the method of the multiresolution decomposition and we will apply it to the analysis and reconstruction of single evoked potentials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basar E (1988) EEG dynamics and evoked potentials in sensory and cognitive processing by brain. In: Bacar E (ed) Dynamics of sensory and cognitive processing by brain. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 30–55
Cerutti S, Baselli G, Liberati D, Avesi G (1987) Single sweep analysis of visual evoked potentials through a model of parametric identification. Biol Cybern 56:111–120
Daubechies I (1990) The wavelet transform, time-frequency localization and signal analysis. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 36:961–1005
Grossman A, Morlet J (1984) Decomposition of Hardy functions into square integrable wavelets of constant shape. SIAM J Math 15:723–736
Heintze HJ, Kûnkel H (1984) ARMA-filtering of evoked potentials. Meth Inform Med 23:29–36
John ER (1973) Brain evoked potentials. Acquisition and analysis 317–356. In: Thompson RF, Patterson MM (ed) Bioelectric ecording techniques. Academic Press, New York
Mallat SG (1989) A theory of multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intell 11:674–693
Sayers Mc AB, Beagley HA, Menshal WR (1974) The mechanism of auditory evoked EEG responses. Nature 247:481–483
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bartnik, E.A., Blinowska, K.J. & Durka, P.J. Single evoked potential reconstruction by means of wavelet transform. Biol. Cybern. 67, 175–181 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201024
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201024