Abstract
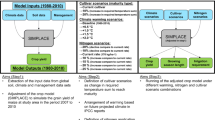
A basic parametric crop yield model (YIELD) that uses climatic and environmental data to calculate yield and associated parameters for grain corn (maize) was applied to a transect through the North American Great Plains. This paper continues our examination of the impact of probable climatic change scenarios on crop evapotranspiration and irrigation requirements (Terjung et al., 1984), This study of grain corn yields showed highest yield for the first (or primary) harvest under full irrigation occurring under a sunny and cold scenario in Austin, TX, sunny and cool in Kansas City, KS, and sunny and warm in Bismarck, ND. Lowest irrigated yield was found with cloudy and hot and very dry climate change scenarios. Under rainfed-only conditions, minima were obtained under the sunny-hot and -warm scenarios and very dry conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bach, W.: 1979, ‘Impact of Increasing Atmospheric CO2 Concentrations on Global Climate: Potential Consequences and Corrective Measures’, Environment International 2, 215–228.
Brouwer, R. and de Wit, C. T.: 1969, ‘A Simulation Model of Plant Growth with Special Attention to Root Growth and Its Consequences’, in: W. J. Whittington (ed.), Root Growth, Butterworths, London, pp. 224–242.
Burt, J. E., Hayes, J. T., O'Rourke, P. A., Terjung, W. H. and Todhunter, P. E.: 1981, ‘A Parametric Cr J.op Water Use Model’, Water Resources Res. 17, 1095–1108.
Burt, J. E., Hayes, J. T., O'Rourke, P. A., Terjung, W. H. and Todhunter, P. E.: 1980, WATER: A Model of Water Requirements for Irrigated and Rainfed Agriculture, Publ. Climatol. 33 (3), C. W. Thornthwaite Assoc. and Cen. for Clim. Res., Elmer, N.J.
Callaway, J. M., Cronin, F. J., Currie, J. W., and Tawil, J.: 1982, An Analysis of Methods and Models for Assessing the Direct and Indirect Economic impacts of CO-Induced Environmental Changes in the Agricultural Sector of the U.S. Economy. Battelle-Pacific Northwest Laboratory, Richland, WA.
Center for Agricultural Meteorology and Climatology: 1983, ‘SAS Data Tape of Nebraska Crop Yields 1945–1982’, courtesy Dr. D. A. Wilhite, CAMaC, Lincoln, Nebraska.
Chang, J.-H.: 1981, ‘Corn Yield in Relation to Photoperiod, Night Temperature, and Solar Radiation’, Agric. Meteorol. 24, 253–262.
Childs, S. W., Gilley, J. R., and Splinter, W. E.: 1977, ‘A Simplified Model of Corn Growth Under Moisture Stress’, Trans. ASAE 20, 858–865.
Clark, W. (ed.): 1982, Carbon Dioxide Review: 1982, Oxford University Press, New York, NY.
De Wit, C. T., Goudriaan, J., van Laar, H. H., Penning de Vries, F. W. T., Rabbinge, R., van Keulen, H., Louwerse, W., Sibma, I., and de Jonge, C.: 1978, Simulation of Assimilation, Respiration, and Transpiration of Crops, John Wiley, New York.
Doorenbos, J. and Kassam, A. H.: 1979, Yield Responses to Water, FAO Irrig. Drain. Pap., 33.
Duncan, W. G., Shaver, D. L., and Williams, W. A.: 1977, ‘Sunlight and Temperature Effects on Corn Growth and Yield’, California Agric. 31(8): 13–14.
Glantz, M. H. and Ausubel, J. H.: 1984, ‘The Ogallala Aquifer and Carbon Dioxide: Comparison and Convergence’, Environmental Conservation 11, 123–131.
Goudriaan, J. and de Ruiter, H. E.: 1983, ‘Plant Growth in Response to CO2 Enrichment, at Two Levels of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Supply. 1. Dry Matter, Leaf Area and Development’, Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 31, 157–169.
Hayes, J. T., O'Rourke, P. A., Terjung, W. H., and Todhunter, P. E.: 1982a, ‘A Feasible Crop Yield Model for Worldwide International Food Production’, Int. J. Biomet. 26, 239–257.
Hayes, J. T., O'Rourke, P. A., Terjung, W. H., and Todhunter, P. E.: 1982b, YIELD: A Numerical Crop Yield Model of Irrigated and Rainfed Agriculture, Publ. Climatol. 35, C. W. Thornthwaite Assoc. and Cen. for Clim. Res., Elmer, N.J.
Huda, A. K. S., Ghildyal, B. P. and Tomar, V. S.: 1976, ‘Contribution of Climatic Variables in Predicting Maize Yield Under Monsoon Conditions’, Agric. Meteorol. 17, 33–47.
International Rice Research Institute: 1978, Rice Research and Production in China: an IRRI Team's View, IRRI, LosBanos, Philippines.
Kansas Crop and Livestock Reporting Service: 1982, Historic Crop Estimates by County 1970–1979, Kansas State Board of Agriculture, Topeka, Kansas.
Kansas Crop and Livestock Reporting Service: 1979, Kansas Field Crops from Planting to Harvest, Kansas State Board of Agriculture, Topeka, Kansas.
Katz, R. W.: 1977, ‘Assessing the Impact of Climatic Change on Food Production’, Climatic Change 1, 85–96.
Kundu, S. S., Skogerboe, G. V., and Walker, W. R.: 1982, ‘Using a Crop Growth Simulation Model for Evaluating Irrigation Practices’, Agric. Water Management 5, 253–268.
Lawson, M. P. and Baker, M. E. (eds.): 1981, The Great Plains: Perspective and Prospects, Center for Great Plains Studies, University of Nebraska-Lincoln and University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln, NE.
Mearns, L. O.: 1982, ‘Simulation of the Effect of Climatic Variability on Wheat Yields in Australia’, M. A. Thesis, University of California, Los Angeles.
Mearns, L. O.: 1983, Simulation of the Effect of Climatic Variability on Wheat Yields in Australia, Publications in Climatology, XXXVI (1), C. W. Thornthwaite Assoc. and Center for Climatic Research, University of Delaware, Elmer, N.J.
National Academy of Sciences: 1983, Changing Climate: Report of the Carbon Dioxide Assessment Committee, NAS, Washington, D.C.
National Defense University: 1980, Crop Yields and Climate Change to the Year 2000, Vol. 1, Report on the second phase of a climate impact assessment, NPU, Ft. Lesley J. McNair, Washington, D.C.
National Academy of Sciences: 1976, Climate & Food Climatic Fluctuation and U.S. Agricultural Production, NAS, Washington, D.C.
Neild, R. E., Richman, H. N. and Seeley, M. W.: 1979, ‘Impacts of Different Types of Temperature Change on the Growing Season for Maize’, Agric. Meteorol. 20, 367–374.
Newman, J. E. and others: 1976, Impact of Climatic Fluctuation on Major North American Food Crops, The Institute of Ecology, 1315 16th St., N.W., Wash., D.C. 23 p.
Quinn, M.-L.: 1982, ‘Federal Drought Planning in the Great Plains - A First Look’, Climatic Change 4, 273–296.
Rosenberg, N. J.: 1981, ‘The Increasing CO2 Concentration in the Atmosphere and Its Implication on Agricultural Productivity. I. Effects on Photosynthesis, Transpiration and Water Use Efficiency’, Climatic Change 3, 265–279.
Rosenberg, N. J.: 1982, ‘The Increasing CO2 Concentration in the Atmosphere and Its Implication on Agricultural Productivity. II. Effects Through CO2-Induced Climatic Change’, Climatic Change 4, 239–254.
Russo, J. M. and Knapp, W. W.: 1976, ‘A Numerical Simulation of Plant Growth’, Int. J. Biometeor. 20, 276–285.
Steyeart, L. T.: 1977, ‘Quality of United States Wheat, Corn, and Soybean Crop Statistics’, Dept. Atmospheric Science, University of Missouri, Columbia, Missouri.
Stillmann, D.: 1986, Texas Statistical Reporting Service, Crop Reporting Branch, Austin, TX. personal communication.
Sudar, R. A., Saxton, K. E., and Spomer, R. G.: 1981, ‘A Predictive Model of Water Stress in Corn and Soybeans’, Trans. ASAE 24, 97–102.
Terjung, W. H., Hayes, J. T., O'Rourke, P. A., Burt, J. E. and Todhunter, P. E.: 1982, ‘Consumptive Water Use Response of Maize to Changes in Environment and Management Practices: Sensitivity Analysis of a Model’, Water Resources Res. 18, 1539–1550.
Terjung, W. H., Ji, H-Y., Hayes, J. T., O'Rourke, P. A., and Todhunter, P. E.: 1983a, ‘Crop Water Requirements for Rainfed and Irrigated Grain Corn in China’, Agric. Water Management 6, 43–64.
Terjung, W. H., Ji, H-Y., Hayes, J. T., O'Rourke, P. A., and Todhunter, P. E.: 1984c, ‘Actual and Potential Yield for Rainfed and Irrigated Maize in China’, Int. J. Biometeor. 28, 115–135.
Terjung, W. H., Hayes, J. T., O'Rourke, P. A., and Todhunter, P. E.: 1984a, ‘Yield Response of Crops to Changes in Environment and Management Practices: Model Sensivitity Analysis. I. Maize’, Int. J. Biometeor. 28, 261–278.
Terjung, W. E., Hayes, J. T., O'Rourke, P. A., and Todhunter, P. E.: 1984b, ‘Yield Response of Crops to Changes in Environment and Management Practices: Model Sensitivity Analysis’ II. Rice, Wheat and Potato, Int. J. Biometeor. 28, 279–292.
Terjung, W. H., Ji, H-Y., Hayes, J. T., O'Rourke, P. A., and Todhunter, P. E.: 1984d, ‘Crop Water Requirements for Rainfed and Irrigated Wheat in China and Korea’, Agric. Water Management 8, 411–427.
Terjung, W. H., Ji, H-Y., Hayes, J. T., O'Rourke, P. A., and Todhunter, P. E.: 1984e, ‘Actual and Potential Yield for Rainfed and Irrigated Wheat in China’, Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 31, 1–23.
Terjung, W. H., Liverman, D. M., Hayes, J. T., and Collaborators: 1984f, ‘Climatic Change and Water Requirements for Grain Corn in the North American Great Plains’, Climatic Change 6, 193–220.
Texas Statistical Reporting Service: 1971–1981, ‘Texas Field Crop Statistics’, Texas State Board of Agriculture, Austin, Texas.
Thompson, L. M.: 1969, ‘Weather and Technology in the Production of Corn in the U.S. Corn Belt’, Agronomy J. 61, 453–456.
Todhunter, P. E.: 1981, ‘A Computer Model Validation of the Simulation of Crop Water Requirements and Irrigation Needs’, M. A. Thesis, University of California, Los Angeles.
U.S. Bureau of the Census, 1984: Statistical Abstract of the United States: 1985 (105th Edition), Washington, D.C.
Walsh, J.: 1980, ‘What to Do When the Well Runs Dry’, Science 210, 754–756.
Wenda, W. I. and Hanks, R. J.: 1981, ‘Corn Yield and Evapotranspiration Under Simulated Drought Conditions’, Irrigation Science 2, 193–204.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
J. T. Hayes is a professor at the Department of Geography and Regional Planning, State University of New York, Albany, NY, U.S.A.
L. O. Mearns is also currently associated with the National Center for Atmospheric Research, funded by the National Science Foundation.
Dr. Liverman is a professor at the Department of Geography, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wis., U.S.A.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liverman, D.M., Terjung, W.H., Hayes, J.T. et al. Climatic change and grain corn yields in the North American Great Plains. Climatic Change 9, 327–347 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00139076
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00139076