Abstract
Background
Epigenetic processes and miRNAs have been recognized as new targets for anticancer drug design. However, old multi-target drugs such as aspirin may also target epigenetic processes.
Aim
This review aims to provide an overview of our current knowledge on the modulation of epigenetic processes by aspirin and other non steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs) and their implications for cancer treatment and chemoprevention.
Synthesis
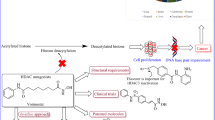
In vitro and in vivo studies, as well as primary patient data, suggest that aspirin and other NSAIDs reverse tumour suppressor gene hypermethylation in cancer tissues. It must be emphasized that, at this point in time, patient data are limited and DNA hypermethylation reversal has been investigated, but not tumour suppressor gene activation. In addition, evidence from experimental and patient data suggests that aspirin and NSAIDs may also reverse global DNA hypomethylation. At the histone level, both induction and inhibition of deacetylases by aspirin have been reported. Also, direct acetylation of histones by aspirin has been reported, while the natural salicylate anacardic acid has been found to inhibit histone acetyltransferase p300 both in vitro and in vivo, and to regulate gene expression through modulation of histone acetylation. Salicylates and other NSAIDs may also down-regulate miRNAs with oncogene-like functions or up-regulate miRNAs with tumour suppressor-like functions. Up till now, clinical trials have been aimed at investigating the effect of salicylates and NSAIDs on a limited number of miRNAs.
Conclusion
So, although the existing evidence is still limited, evidence is accumulating that epigenetic targets may represent nodal targets for the anti-proliferative actions of salicylates and NSAIDs. This, in turn, may have implications for cancer chemoprevention and treatment. Undoubtedly, this notion requires further investigation, but if proved correct, it could lead to the design of less toxic agents that target epigenetic processes as part of existing or novel multi-targeted treatment modalities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Nebert, G. Zhang, E. Vesell, From human genetics and genomics to pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics: past lessons, future directions. Drug Metab Rev 40, 187–224 (2008)
P.K. Lo, S. Sukumar, Epigenomics and breast cancer. Pharmacogenomics 9, 1879–1902 (2008)
J.G. Martínez, J. Pérez-Escuredo, P. Castro-Santos, C.A. Marcos, J.L. Pendás, M.F. Fraga, Hermsen. M.A. Hypomethylation of LINE-1, and not centromeric SAT-α, is associated with centromeric instability in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Oncol 35, 259–67 (2012)
S. Babashah, M. Sadeghizadeh, M.R. Tavirani, S. Farivar, Soleimani. M. Aberrant microRNA expression and its implications in the pathogenesis of leukemias. Cell Oncol 35, 317–34 (2012)
R. Nagadia, P. Pandit, W.B. Coman, J. Cooper-White, C. Punyadeera, miRNAs in head and neck cancer revisited. Cell Oncol 36, 1–7 (2013)
C. Lema, M. Cunningham, MicroRNAs and their implications in toxicological research. Toxicol Lett 198, 100–105 (2010)
P.J. Mishra, P.J. Mishra, D. Barenjee, J.R. Bertino, MiRNSPs or MiR polymorphisms, new players in microRNA mediated regulation of the cell. Cell Cycle 7, 853–858 (2008)
P.J. Mishra, J.R. Bertino, MicroRNA polymorphisms: the future of pharmacogenomics, molecular epidemiology and personalized medicine. Pharmacogenomics 10, 399–416 (2009)
E.D. Wiklund, J. Kjems, S.J. Clark, Epigenetic architecture and miRNA: reciprocal regulators. Epigenomics 6, 823–840 (2010)
F.A. Duijkers, R.X. de Menezes, I.J. Goossens-Beumer, D.J. Stumpel, P. Admiraal, R. Pieters, J.P. Meijerink, M.M. van Noesel, Epigenetic drug combination induces genome-wide demethylation and altered gene expression in neuro-ectodermal tumor-derived cell lines. Cell Oncol 36, 351–62 (2013)
J.P. Issa, H.M. Kantarjian, Targeting DNA methylation Clin Cancer Res 15, 3938–46 (2009)
J. García-Quiroz, J. Camacho, Astemizole: an old anti-histamine as a new promising anti-cancer drug. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 11, 307–14 (2011)
C. Zhao, X. Bu, Promoter methylation of tumor-related genes in gastric carcinogenesis. Histol Histopathol 27, 1271–82 (2012)
T.M. Brasky, M.R. Bonner, K.B. Moysich, C.B. Ambrosone, J. Nie, M.H. Tao, S.B. Edge, B.V. Kallakury, H.M. Ochs-Balcom, C. Marian, M. Trevisan, P.G. Shields, J.L. Freudenheim, Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use (NSAID) and breast cancer risk in the western New York exposures and breast cancer (WEB) study. Cancer Causes Control 9, 1503–1512 (2010)
Li, X.; Gao, L.; Cui, Q.; Gary, B.D.; Dyess, D.L.; Taylor, W.; Shevde, L.A.; Samant, R.S.; Dean-Colomb, W.; Piazza, G.A.; Xi, Y. Sulindac inhibits tumor cell invasion by suppressing NF-κB-mediated transcription of microRNAs. Oncogene 31, 4979–4986 (2012)
E. Yiannakopoulou, Modulation of lymphangiogenesis: a New target for aspirin and other Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents? a systematic review. J Clin Pharmacol 52, 1749–54 (2011)
M. Dovizio, A. Bruno, S. Tacconelli, P. Patrignani, Mode of action of aspirin as a chemopreventive agent. Recent Results Cancer Res 191, 39–65 (2013)
J. Worm, P. Guldberg, DNA methylation: an epigenetic pathway to cancer and a promising target for anticancer therapy. J Oral Pathol Med 31, 443–9 (2002)
J. Paluszczak, V. Krajka-Kuźniak, W. Baer-Dubowska, The effect of dietary polyphenols on the epigenetic regulation of gene expression in MCF7 breast cancer cells. Toxicol Lett 192, 119–125 (2010)
J.L. Medina-Franco, T. Caulfield, Advances in the computational development of DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. Drug Discov Today 16, 418–425 (2011)
D. Kuck, N. Singh, F. Lyko, J.L. Medina-Franco, Novel and selective DNA methyltransferase inhibitors: Docking-based virtual screening and experimental evaluation. Bioorg Med Chem 18, 822–829 (2010)
J. Yoo, J.L. Medina Franco, Trimethylaurintricarboxylic acid inhibits human DNA methyltransferase 1: insights from enzymatic and molecular modeling studies. J Mol Model 18, 1583–1589 (2012)
M.R. Pan, H.C. Chang, L.Y. Chuang, W.C. Hung, The nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug NS398 reactivates SPARC expression via promoter demethylation to attenuate invasiveness of lung cancer cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 233, 456–462 (2008)
T. Tahara, T. Shibata, M. Nakamura, H. Yamashita, D. Yoshioka, M. Okubo, N. Maruyama, T. Kamano, Y. Kamiya, H. Fujita, M. Nagasaka, M. Iwata, K. Takahama, M. Watanabe, I. Hirata, T. Arisawa, Chronic aspirin use suppresses CDH1 methylation in human gastric mucosa. Dig Dis Sci 55, 54–9 (2010)
T. Tahara, T. Shibata, H. Yamashita, M. Nakamura, D. Yoshioka, M. Okubo, I. Hirata, T. Arisawa, Chronic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use suppresses multiple CpG islands hyper methylation (CIHM) of tumor suppressor genes in the human gastric mucosa. Cancer Sci 100, 1192–1197 (2009)
M.L. Slattery, R.K. Wolff, J. Herrick, B.J. Caan, W. Samowitz, Tumor markers and rectal cancer: support for an inflammation-related pathway. Int J Cancer 125, 1698–1704 (2009)
M.L. Slattery, K. Curtin, C. Sweeney, T.R. Levin, J. Potter, R.K. Wolff, H. Albertsen, W.S. Samowitz, Diet and lifestyle factor associations with CpG island methylator phenotype and BRAF mutations in colon cancer. Int J Cancer 120, 656–663 (2007)
E.I. Heath, M.I. Canto, S. Piantadosi, E. Montgomery, W.M. Weinstein, J.G. Herman, A.J. Dannenberg, V.W. Yang, A.O. Shar, E. Hawk, A.A. Forastiere, Chemoprevention for Barrett’s esophagus trial research group. Secondary chemoprevention of Barrett’s esophagus with celecoxib: results of a randomized trial. J. Natl. Cancer Risk 99, 545–557 (2007)
K. Wallace, M.V. Grau, A.J. Levine, L. Shen, R. Hamdan, X. Chen, J. Gui, R.W. Haile, E.L. Barry, D. Ahnen, G. McKeown-Eyssen, J.A. Baron, J.P. Issa, Association between folate levels and CpG Island hypermethylation in normal colorectal mucosa. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 3, 1552–1564 (2010)
J.C. Figueiredo, M.V. Grau, K. Wallace, A.J. Levine, L. Shen, R. Hamdan, X. Chen, R.S. Bresalier, G. McKeown-Eyssen, R.W. Haile, J.A. Baron, J.P. Issa, Global DNA hypomethylation (LINE-1) in the normal colon and lifestyle characteristics and dietary and genetic factors. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 18, 1041–1049 (2009)
L. Tao, W. Wang, P.M. Kramer, R.A. Lubet, V.E. Steele, M.A. Pereira, Modulation of DNA hypomethylation as a surrogate endpoint biomarker for chemoprevention, of colon cancer. Mol Carcinogen 39, 79–842 (2004)
M.A. Pereira, L. Tao, W. Wang, Y. Li, A. Umar, V.E. Steele, Modulation by celecoxib and difluoromethylornithine of the methylation of DNA and the estrogen receptor-alpha gene in rat colon tumors. Carcinogenesis 25, 1917–1923 (2004)
R. Shen, L. Tao, Y. Xu, S. Chang, J. Van Brocklyn, J.X. Gao, Reversibility of aberrant global DNA and estrogen receptor-alpha gene methylation distinguishes colorectal precancer from cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2, 21–23 (2009)
R.M. Eglen, T. Reisine, Screening for compounds that modulate epigenetic regulation of the transcriptome: an overview. J Biomol Screen 16, 1137–1152 (2011)
A. Mai, L. Altucci, Epi-drugs to fight cancer: from chemistry to cancer treatment, the road ahead. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41, 199–213 (2009)
P. Kamble, K. Selvarajan, C. Aluganti Narasimhulu, M. Nandave, S. Parthasarathy, Aspirin may promote mitochondrial biogenesis via the production of hydrogen peroxide and the induction of Sirtuin1/PGC-1α genes. Eur J Pharmacol 699, 55–61 (2013)
F. Di Renzo, G. Cappelletti, M.L. Broccia, E. Giavini, E. Menegola, The inhibition of embryonic histone deacetylases as the possible mechanism accounting for axial skeletal malformations induced by sodium salicylate. Toxicol Sci 104, 397–404 (2008)
J. Sonnemann, I. Hüls, M. Sigler, C.D. Palani, T.T. le Hong, U. Völker, H.K. Kroemer, J.F. Beck, Histone deacetylase inhibitors and aspirin interact synergistically to induce cell death in ovarian cancer cells. Oncol Rep 20, 219–224 (2008)
K. Deckmann, F. Rörsch, G. Geisslinger, S. Grösch, Dimethylcelecoxib induces an inhibitory complex consisting of HDAC1/NF-κB(p65)RelA leading to transcriptional downregulation of mPGES-1 and EGR1. Cell Signal 24, 460–467 (2012)
H. Yoshioka, T. Watanabe, T.E. Eling, Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene (NAG-1/GDF15) expression is increased by the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A. J Biol Chem 283, 33129–33137 (2008)
S. Marimuthu, R.S. Chivukula, L.F. Alfonso, M. Moridani, F.K. Hagen, G.J. Bhat, Aspirin acetylates multiple cellular proteins in HCT-116 colon cancer cells: Identification of novel targets. Int J Oncol 39, 1273–1283 (2011)
S.B. Jung, C.S. Kim, A. Naqvi, T. Yamamori, I. Mattagajasingh, T.A. Hoffman, M.P. Cole, A. Kumar, J.S. Dericco, B.H. Jeon, K. Irani, Histone deacetylase 3 antagonizes aspirin-stimulated endothelial nitric oxide production by reversing aspirin-induced lysine acetylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circ Res 107, 877–87 (2010)
J. Tan, B. Chen, L. He, Y. Tang, Z. Jiang, G. Yin, J. Wang, X. Jiang, Anacardic acid (6-pentadecylsalicylic acid) induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells through inhibition of androgen receptor and activation of p53 signaling. Chin J Cancer Res 24, 275–83 (2012)
B. Sung, M.K. Pandey, K.S. Ahn, T. Yi, M.M. Chaturvedi, M. Liu, B.B. Aggarwal, Anacardic acid (6-nonadecyl salicylic acid), an inhibitor of histone acetyltransferase, suppresses expression of nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated gene products involved in cell survival, proliferation, invasion, and inflammation through inhibition of the inhibitory subunit of nuclear factor-kappaBalpha kinase, leading to potentiation of apoptosis. Blood 111, 4880–4891 (2008)
Y. Sun, X. Jiang, S. Chen, B.D. Price, Inhibition of histone acetyltransferase activity by anacardic acid sensitizes tumor cells to ionizing radiation. FEBS Lett 580, 4353–4356 (2006)
Y. Kim, K. Kim, D. Park, E. Lee, H. Lee, Y.S. Lee, J. Choe, Y.M. Kim, D. Jeoung, DNA methyl transferase I acts as a negative regulator of allergic skin inflammation. Mol Immunol 53, 1–14 (2013)
A. Koornneef, K. Rindermann, C. Gatz, C.M. Pieterse, Histone modifications do not play a major role in salicylate-mediated suppression of jasmonate-induced PDF1.2 gene expression. Commun Integr Biol 1, 143–5 (2008)
T. Tanaka, A. Kurose, H.D. Halicka, X. Huang, F. Traganos, Z. Darzynkiewicz, Nitrogen oxide-releasing aspirin induces histone H2AX phosphorylation, ATM activation and apoptosis preferentially in S-phase cells: involvement of reactive oxygen species. Cell Cycle 5, 1669–74 (2006)
M. Yanokura, K. Banno, Y. Kobayashi, I. Kisu, A. Ueki, A. Ono, K. Masuda, H. Nomura, A. Hirasawa, N. Susumu, D. Aoki, MicroRNA and endometrial cancer: Roles of small RNAs in human tumors and clinical applications (Review). Oncol Lett 1, 935–940 (2010)
F. Lan, X. Yue, L. Han, Z. Shi, Y. Yang, P. Pu, Z. Yao, C. Kang, Genome-wide identification of TCF7L2/TCF4 target miRNAs reveals a role for miR-21 in Wnt-driven epithelial cancer. Int J Oncol 40, 519–526 (2012)
Y. Chen, W. Liu, T. Chao, Y. Zhang, X. Yan, Y. Gong, B. Qiang, J. Yuan, M. Sun, X. Peng, MicroRNA-21 down-regulates the expression of tumor suppressor PDCD4 in human glioblastoma cell T98G. Cancer Lett 272, 197–205 (2008)
F. Meng, R. Henson, H. Wehbe-Janek, K. Ghoshal, S.T. Jacob, T. Patel, MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 133, 647–658 (2007)
Q. Yao, H. Xu, Q.Q. Zhang, H. Zhou, L.H. Qu, MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation and down-regulates the expression of programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) in HeLa cervical carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 388, 539–542 (2009)
Sicard, F.; Gayral, M.; Lulka, H.; Buscail, L.; Cordelier, P. Targeting miR-21 for the Therapy of Pancreatic Cancer. Mol Ther, 2013, doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.35
Y. Saito, H. Suzuki, H. Imaeda, J. Matsuzaki, K. Hirata, H. Tsugawa, S. Hibino, Y. Kanai, H. Saito, T. Hibi, The tumor suppressor microRNA-29c is downregulated and restored by celecoxib in human gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer 132, 1751–1760 (2013)
W.C. Chen, M.S. Lin, Y.L. Ye, H.J. Gao, Z.Y. Song, X.Y. Shen, microRNA expression pattern and its alteration following celecoxib intervention in human colorectal cancer. Exp Ther Med 3, 1039–1048 (2012)
J. Tan, L. Fan, J.J. Mao, B. Chen, L. Zheng, T. Zhang, T. Li, J. Duan, Y. Duan, Z. Jin, W. Kuang, Restoration of miR-34a in p53 deficient cells unexpectedly promotes the cell survival by increasing NFκB activity. J Cell Biochem 113, 2903–8 (2012)
E.D. Eliseeva, V. Valkov, M. Jung, M.O. Jung, Characterization of novel inhibitors of histone acetyltransferases. Mol Cancer Ther 6, 2391–2398 (2007)
A.R. Cyr, F.E. Domann, The redox basis of epigenetic modifications: from mechanisms to functional consequences. Antioxid Redox Signal 15, 551–589 (2011)
R.H. Dowen, M. Pelizzola, R.J. Schmitz, R. Lister, J.M. Dowen, J.R. Nery, J.E. Dixon, J.R. Ecker, Widespread dynamic DNA methylation in response to biotic stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109, E2183–E2191 (2012)
K. Schrör, Pharmacology and cellular/molecular mechanisms of action of aspirin and non-aspirin NSAIDs in colorectal cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 25, 473–484 (2011)
E.C. Yiannakopoulou, E. Tiligada, Protective effect of salicylates against hydrogen peroxide stress in yeast. J Appl Microbiol 106, 903–908 (2009)
M.C. de Andrés, K. Imagawa, K. Hashimoto, A. Gonzalez, H.I. Roach, M.B. Goldring, R.O. Oreffo, Loss of methylation in CpG sites in the NF-κB enhancer elements of inducible nitric oxide synthase is responsible for gene induction in human articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum 65, 732–742 (2013)
Fata, J.E.; Debnath, S.; Jenkins, E.C. Jr; Fournier, M.V. Nongenomic Mechanisms of PTEN Regulation. Int. J. Cell Biol., 2012, 379685
K.K. Wu, Transcription-based COX-2 inhibition: a therapeutic strategy. Thromb Haemost 96, 417–422 (2006)
D.A. Dixon, F.F. Blanco, A. Bruno, P. Patrignani, Mechanistic aspects of COX-2 expression in colorectal neoplasia. Recent Results Cancer Res 191, 7–37 (2013)
S. Fu, R. Kurzrock, Development of curcumin as an epigenetic agent. Cancer 116, 4670–4676 (2010)
Conflict of interest statement
The author has nothing to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yiannakopoulou, E. Targeting epigenetic mechanisms and microRNAs by aspirin and other non steroidal anti-inflammatory agents - implications for cancer treatment and chemoprevention. Cell Oncol. 37, 167–178 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-014-0175-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-014-0175-7