Abstract
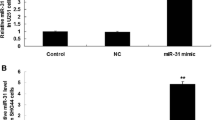
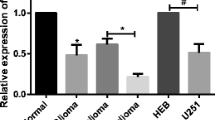
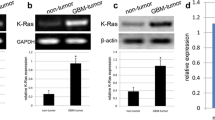
Recently, microRNAs (miRNAs), a kind of small and non-coding RNA, can target the downstream molecules. Increasing evidence demonstrates that miRNAs meditate the onset and progression of a variety of tumors. In the present study, we carried out gene transfection, western blot, and reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) to explore the role of miR-22 in glioblastoma tissues and cell lines. Here, we verified that the expression of miR-22 was downregulated in glioblastoma tissues and cells rather than matched non-tumor tissues and normal human astrocyte (NHA) cells (p < 0.001). By contrast, SIRT1 messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein were upregulated in glioblastoma tissues and cells (p < 0.001). In vitro miR-22 mimics interfered with cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of U87 and U251 cells. Mechanically, the 3′-untranslated regions (3′-UTRs) of SIRT1 were a direct target of miR-22, leading to the decreased expression of SIRT1 protein in U87 and U251 cells. Meanwhile, miR-22 mimics also inhibited the expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP9). In conclusion, miR-22 inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via targeting the 3′-UTR of SIRT1 in the progression of glioblastoma and miR-22-SIRT1 pathway can be recommended as a potential target for treatment of glioblastoma.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300.
Liao A, Shi R, Jiang Y, Tian S, Li P, Song F, et al. SDF-1/CXCR4 axis regulates cell cycle progression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via up-regulation of survivin in glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol. 2014 Nov 25.
Lv Q, Zhang J, Yi Y, Huang Y, Wang Y, Wang Y, et al. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen has an association with prognosis and risks factors of cancer patients: a systematic review. Mol Neurobiol. 2015.
Lv B, Yang X, Lv S, Wang L, Fan K, Shi R, et al. CXCR4 signaling induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by PI3K/AKT and ERK pathways in glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;52(3):1263–8.
Altieri R, Fontanella M, Agnoletti A, Panciani PP, Spena G, Crobeddu E, et al. Role of nitric oxide in glioblastoma therapy: another step to resolve the terrible puzzle? Transl Med UniSa. 2014;12:54–9.
De Paepe A, Vandeneede N, Strens D, Specenier P. The economics of the treatment and follow-up of patients with glioblastoma. Value Health. 2015;18(7):A448.
Kagiya T. MicroRNAs and osteolytic bone metastasis: the roles of microRNAs in tumor-induced osteoclast differentiation. J Clin Med. 2015;4(9):1741–52.
Sanei M, Chen X. Mechanisms of microRNA turnover. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2015;27:199–206.
Luna-Aguirre CM, de la Luz M-FM, Mar-Aguilar F, Garza-Veloz I, Treviño-Alvarado V, Rojas-Martinez A, et al. Circulating microRNA expression profile in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Biomark. 2015;15(3):299–310.
Sampson VB, Yoo S, Kumar A, Vetter NS, Kolb EA. MicroRNAs and potential targets in osteosarcoma: review. Front Pediatr. 2015;3:69.
Kanda M, Kodera Y. Recent advances in the molecular diagnostics of gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(34):9838–52.
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, Castle J, et al. Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 2005;433(7027):769–73.
Lu W, You R, Yuan X, Yang T, Samuel EL, Marcano DC, et al. The microRNA miR-22 inhibits the histone deacetylase HDAC4 to promote TH17 cell-dependent emphysema. Nat Immunol. 2015;16(11):1185–94.
Yang Q, Jiang W, Zhuang C, Geng Z, Hou C, Huang D, et al. MicroRNA-22 downregulation of galectin-9 influences lymphocyte apoptosis and tumor cell proliferation in liver cancer. Oncol Rep. 2015;34(4):1771–8.
Zhou Y, Zhou Z, Zhang W, Hu X, Wei H, Peng J, et al. SIRT1 inhibits adipogenesis and promotes myogenic differentiation in C3H10T1/2 pluripotent cells by regulating Wnt signaling. Cell Biosci. 2015;5:61.
Maiese K. MicroRNAs and SIRT1: a strategy for stem cell renewal and clinical development? J Transl Sci. 2015;1(3):55–7.
Shuang T, Wang M, Zhou Y, Shi C. Over-expression of Sirt1 contributes to chemoresistance and indicates poor prognosis in serous epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). Med Oncol. 2015;32(12):260.
Xiong J, Yu D, Wei N, Fu H, Cai T, Huang Y, et al. An estrogen receptor alpha suppressor, microRNA-22, is downregulated in estrogen receptor alpha-positive human breast cancer cell lines and clinical samples. FEBS J. 2010;277:1684–94.
García I, Vizoso F, Andicoechea A, Fernandez P, Suarez C, García-Muñz JL, et al. C-erbB-2 oncoprotein content in gastric cancer and in adjacent mucosa. Int J Biol Markers. 2000;15(3):231–4.
Dan L, Jian D, Na L, Xiaozhong W. Crosstalk between EGFR and integrin affects invasion and proliferation of gastric cancer cell line, SGC7901. Onco Targets Ther. 2012;5:271–7.
Chen W, Zhong X, Wei Y, Liu Y, Yi Q, Zhang G, et al. TGF-β regulates survivin to affect cell cycle and the expression of EGFR and MMP9 in glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol. 2015.
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, Werb Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell. 2010;141(1):52–67.
Yang X, Lv S, Liu Y, Li D, Shi R, Tang Z, et al. The clinical utility of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in evaluating pathological grade and prognosis of glioma patients: a meta-analysis. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;52(1):38–44.
Kumar B, Koul S, Petersen J, Khandrika L, Hwa JS, Meacham RB, et al. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-driven MAPKAPK2 regulates invasion of bladder cancer by modulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity. Cancer Res. 2010;70(2):832–41.
Yao C, Li P, Song H, Song F, Qu Y, Ma X, et al. CXCL12/CXCR4 axis upregulates twist to induce EMT in human glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol. 2015.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 81502163 and 31370810). We greatly thank Bo Hong in Department of Neurosurgery, Changhai Hospital, Second Military Medical University (Shanghai, 200433, P.R. China) for valuable suggestions and his fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Hanchun Chen and Qiong Lu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Lu, Q., Fei, X. et al. miR-22 inhibits the proliferation, motility, and invasion of human glioblastoma cells by directly targeting SIRT1. Tumor Biol. 37, 6761–6768 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4575-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4575-8