Abstract
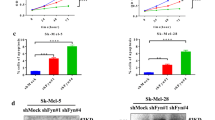
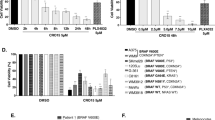
It is vital to develop new therapeutic agents for the treatment of melanoma. In the current study, we studied the potential effect of Compound 13 (C13), a novel α1-selective AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activator, in melanoma cells. We showed that C13 exerted mainly cytostatic, but not cytotoxic activities in melanoma cells. C13 potently inhibited proliferation in melanoma cell lines (A375, OCM-1 and B16), but not in B10BR melanocytes. Meanwhile, the AMPK activator inhibited melanoma cell cycle progression by inducing G1-S arrest. Significantly, we failed to detect significant melanoma cell death or apoptosis after the C13 treatment. For the mechanism study, we showed that C13 activated AMPK and inhibited mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling in melanoma cells through interaction with the α1 subunit. Short hairpin RNA (shRNA)-mediated knockdown of AMPKα1 not only blocked C13-mediated AMPK activation but also abolished its antiproliferative activity against melanoma cells. Together, these results show that C13 inhibits melanoma cell proliferation through activating AMPK signaling. Our data suggest that C13 along with other small molecular AMPK activators may be beneficial for patients with melanoma.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hutchinson L. Skin cancer. Golden age of melanoma therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015;12:1.
Webster RM, Mentzer SE. The malignant melanoma landscape. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13:491–2.
Kingwell K. Anticancer drugs: a new weapon against metastatic melanoma. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13.
Braeuer RR, Watson IR, Wu CJ, Mobley AK, Kamiya T, Shoshan E, et al. Why is melanoma so metastatic? Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014;27:19–36.
Eggermont AM, Robert C. Melanoma: smart therapeutic strategies in immuno-oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014;11:181–2.
Mihaylova MM, Shaw RJ. The ampk signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13:1016–23.
Faubert B, Vincent EE, Poffenberger MC, Jones RG. The amp-activated protein kinase (ampk) and cancer: many faces of a metabolic regulator. Cancer Lett. 2015;356:165–70.
Hardie DG, Ross FA, Hawley SA. Ampk: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:251–62.
Carling D, Thornton C, Woods A, Sanders MJ. Amp-activated protein kinase: new regulation, new roles? Biochem J. 2012;445:11–27.
Hardie DG, Ross FA, Hawley SA. Amp-activated protein kinase: a target for drugs both ancient and modern. Chem Biol. 2012;19:1222–36.
Cerezo M, Tichet M, Abbe P, Ohanna M, Lehraiki A, Rouaud F, et al. Metformin blocks melanoma invasion and metastasis development in ampk/p53-dependent manner. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013;12:1605–15.
Tomic T, Botton T, Cerezo M, Robert G, Luciano F, Puissant A, et al. Metformin inhibits melanoma development through autophagy and apoptosis mechanisms. Cell Death Dis. 2011;2:e199.
Hunter RW, Foretz M, Bultot L, Fullerton MD, Deak M, Ross FA, et al. Mechanism of action of compound-13: an alpha1-selective small molecule activator of ampk. Chem Biol. 2014;21:866–79.
Gomez-Galeno JE, Dang Q, Nguyen TH, Boyer SH, Grote MP, Sun Z, et al. A potent and selective ampk activator that inhibits de novo lipogenesis. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2010;1:478–82.
Lurje G, Lenz HJ. Egfr signaling and drug discovery. Oncology. 2009;77:400–10.
Seshacharyulu P, Ponnusamy MP, Haridas D, Jain M, Ganti AK, Batra SK. Targeting the egfr signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012;16:15–31.
Zhang YM, Zhang ZQ, Liu YY, Zhou X, Shi XH, Jiang Q, et al. Requirement of galphai1/3-gab1 signaling complex for keratinocyte growth factor-induced pi3k-akt-mtorc1 activation. J Investig Dermatol. 2015;135:181–91.
Lv G, Zhu H, Zhou F, Lin Z, Lin G, Li C. Amp-activated protein kinase activation protects gastric epithelial cells from helicobacter pylori-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;453:13–8.
Serini S, Fasano E, Piccioni E, Monego G, Cittadini AR, Celleno L, et al. Dha induces apoptosis and differentiation in human melanoma cells in vitro: involvement of hur-mediated cox-2 mrna stabilization and beta-catenin nuclear translocation. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33:164–73.
Inoki K, Ouyang H, Zhu T, Lindvall C, Wang Y, Zhang X, et al. Tsc2 integrates wnt and energy signals via a coordinated phosphorylation by ampk and gsk3 to regulate cell growth. Cell. 2006;126:955–68.
Inoki K, Zhu T, Guan KL. Tsc2 mediates cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival. Cell. 2003;115:577–90.
Atefi M, von Euw E, Attar N, Ng C, Chu C, Guo D, et al. Reversing melanoma cross-resistance to braf and mek inhibitors by co-targeting the akt/mtor pathway. PLoS One. 2011;6, e28973.
Russo AE, Torrisi E, Bevelacqua Y, Perrotta R, Libra M, McCubrey JA, et al. Melanoma: molecular pathogenesis and emerging target therapies (review). Int J Oncol. 2009;34:1481–9.
Populo H, Soares P, Faustino A, Rocha AS, Silva P, Azevedo F, et al. Mtor pathway activation in cutaneous melanoma is associated with poorer prognosis characteristics. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2011;24:254–7.
Cool B, Zinker B, Chiou W, Kifle L, Cao N, Perham M, et al. Identification and characterization of a small molecule ampk activator that treats key components of type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab. 2006;3:403–16.
Ducommun S, Ford RJ, Bultot L, Deak M, Bertrand L, Kemp BE, et al. Enhanced activation of cellular ampk by dual-small molecule treatment: Aicar and a769662. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014;306:E688–96.
Sun SY. Mtor kinase inhibitors as potential cancer therapeutic drugs. Cancer Lett. 2013;340:1–8.
Rattan R, Giri S, Hartmann LC, Shridhar V. Metformin attenuates ovarian cancer cell growth in an amp-kinase dispensable manner. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15:166–78.
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B, Guan KL. Ampk and mtor regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13:132–41.
Egan DF, Shackelford DB, Mihaylova MM, Gelino S, Kohnz RA, Mair W, et al. Phosphorylation of ulk1 (hatg1) by amp-activated protein kinase connects energy sensing to mitophagy. Science. 2011;331:456–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Jiang, F., Bao, Q. et al. Compound 13, an α1-selective small molecule activator of AMPK, potently inhibits melanoma cell proliferation. Tumor Biol. 37, 1071–1078 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3854-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3854-8