Abstract
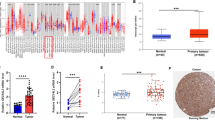
Aberrant expression of miR-10b has been described in many cancers but remains unexplored in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Therefore, we aimed to study the miR-10b expression level in 43 NPC biopsies collected from Tunisian patients and three NPC xenografts. Then, we investigated the correlation between miR-10b expression and its upstream regulators LMP1/Twist1 as well as its adjacent gene HoxD4. We showed that miR-10b was significantly up-regulated in NPC biopsies compared to non-tumor nasopharyngeal tissues (fold change 153; p = 0.004) and associated with advanced clinical stage and young age at diagnosis (p = 0.005 and p = 0.011, respectively). In addition, over-expression of miR-10b was positively associated with the transcription factor Twist1 as well as the EBV oncoprotein LMP1 (fold change 6.32; p = 0.014, fold change 6.58; p = 0.01 respectively). Furthermore, higher level of miR-10b was observed in tumors with simultaneous expression of LMP1 and Twist1, compared to those expressing only Twist1 (fold change 2.49; p = 0.033). Meanwhile, the analysis of the link between miR-10b and its neighbor gene HoxD4 did not show any significant correlation (Fisher test p = 0.205; Mann–Whitney test p = 0.676). This study reports the first evidence of miR-10b over-expression in NPC patients. Furthermore, our findings can support hsa-miR-10b gene regulation through LMP1/Twist1 in NPC malignancy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu MC, Yuan JM. Epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 2002;12(6):421–9.
Boussen H, Bouaouina N, Mokni-Baizig N, Gamoudi A, Chouchane L, Benna F, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Recent data. Pathol Biol. 2005;53(1):45–51.
Wang HY, Sun BY, Zhu ZH, Chang ET, To KF, Hwang JS, et al. Eight-signature classifier for prediction of nasopharyngeal carcinoma survival. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:4516–25.
Chen J, Hu CF, Hou JH, Shao Q, Yan LX, Zhu XF, et al. Epstein–Barr virus encoded latent membrane protein 1 regulates mTOR signaling pathway genes which predict poor prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Transl Med. 2010;8:30.
Dawson CW, Port RJ, Young LS. The role of the EBV-encoded latent membrane proteins LMP1 and LMP2 in the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Semin Cancer Biol. 2012;22:144–53.
Mosialos G, Birkenbach M, Yalamanchili R, VanArsdale T, Ware C, Kieff E. The Epstein–Barr virus transforming protein LMP1 engages signaling proteins for the tumor necrosis factor receptor family. Cell. 1995;80:389–99.
Zhao Y, Wang Y, Zeng S, Hu X. LMP1 expression is positively associated with metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: evidence from a meta-analysis. J Clin Pathol. 2012;65:41–5.
Kondo S, Wakisaka N, Muramatsu M, Zen Y, Endo K, Murono S, et al. Epstein–Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 induces cancer stem/progenitor-like cells in nasopharyngeal epithelial cell lines. J Virol. 2011;85:11255–64.
Bartel DP, Chen CZ. Micromanagers of gene expression: the potentially widespread influence of metazoan microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5(5):396–400.
Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM. Bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell. 2003;113:25–36.
Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF, Bartel DP. MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science. 2004;303:83–6.
Galasso M, Sandhu SK, Volinia S. MicroRNA expression signatures in solid malignancies. Cancer J. 2012;18(3):238–43.
Tran N, McLean T, Zhang X, Zhoao CJ, Thomson JM, O'Brien C, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles in head and neck cancer cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;358:12–7.
Chen HC, Chen GH, Chen YH, Liao WL, Liu CY, Chang KP, et al. MicroRNA deregulation and pathway alterations in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2009;24(6):1002–11.
Yu H, Lu J, Zuo L, Yan Q, Yu Z, Li X, et al. Epstein–Barr virus downregulates microRNA 203 through the oncoprotein latent membrane protein 1: a contribution to increased tumor incidence in epithelial cells. J Virol. 2012;86:3088–99.
Anastasiadou E, Boccellato F, Vincenti S, Rosato P, Bozzoni I, Frati L, et al. Epstein–Barr virus encoded LMP1 downregulates TCL1 oncogene through miR-29b. Oncogene. 2010;29:1316–28.
Du ZM, Hu LF, Wang HY, Yan LX, Zeng YX, Shao JY, et al. Upregulation of miR-155 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma is partly driven by LMP1 and LMP2A and downregulates a negative prognostic marker JMJD1A. PLoS One. 2011;6(4):e19137.
Yang GD, Huang TJ, Peng LX, Yang CF, Liu RY, Huang HB, et al. Epstein–Barr Virus_Encoded LMP1 upregulates microRNA-21 to promote the resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by suppressing PDCD4 and Fas-L. Plos One. 2013;8(10):e78355.
Li G, Wu Z, Peng Y, Liu X, Lu J, Wang L, et al. MicroRNA-10b induced by Epstein–Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein-1 promotes the metastasis of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2010;299(1):29–36.
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA. Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature. 2007;449(7163):682–8.
Tian Y, Luo A, Cai Y, Su Q, Ding F, Chen H, et al. MicroRNA-10b promotes migration and invasion through KLF4 in human esophageal cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(11):7986–94.
Sun XJ, Liu H, Zhang P, Zhang XD, Jiang ZW, Jiang CC. miR-10b promotes migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(9):5533–7.
Chai G, Liu N, Ma J, Li H, Oblinger JL, Prahalad AK, et al. MicroRNA-10b regulates tumorigenesis in neurofibromatosis type 1. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:1997–2004.
Gabriely G, Yi M, Narayan RS, Niers JM, Wurdinger T, Imitola J, et al. Human gliomas growth is controlled by microRNA-10b. Cancer Res. 2011;71(10):3563–72.
Mussnich P, D’Angelo D, Leone V, Croce CM, Fusco A. The high mobility group A proteins contribute to thyroid cell transformation by regulating miR-603 and miR-10b expression. Mol Oncol. 2013;7(3):531–42.
Foley NH, Bray I, Watters KM, Das S, Bryan K, Bernas T, et al. microRNAs 10a and 10b are potent inducers of neuroblastoma cell differentiation through targeting of nuclear receptor corepressor 2. Cell Death Differ. 2011;18(7):1089–98.
Fleming ID, Cooper JS, Henson DE, Hutter RV, Kennedy BJ, et al. American Joint Committee on Cancer “cancer staging manual”. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven; 1997. p. pp. 31–9.
Sobin LH and Wittekind CH, Eds. International Union Against Cancer. TNM classification of malignant tumours. Wiley-Liss, New York, 5th edition, 1997. pp. 25–32.
Chan JKC, Pilch BZ, Kuo TT, Wenig BM, Lee AWM. Tumors of the nasopharynx: introduction. In: Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D, editors. Pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours (World Health Organization classification of tumours). Lyon: IARC; 2005. p. 82–4.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔ C T method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8.
Hafez MM, Hassan ZK, Zekri AR, Gaber AA, Al Rejaie SS, Sayed-Ahmed MM, et al. MicroRNAs and metastasis-related gene expression in Egyptian breast cancer patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(2):591–8.
Sasayama T, Nishihara M, Kondoh T, Hosoda K, Kohmura E. MicroRNA-10b is overexpressed in malignant gliomas and associated with tumor invasive factors, uPAR and RhoC. Int J Cancer. 2009;125(6):1407–13.
Gee HE, Camps C, Buffa FM, Patiar S, Winter SC, Betts G, et al. hsa-mir-210 is a marker of tumor hypoxia and a prognostic factor in head and neck cancer. Cancer. 2010;116(9):2148–58.
Lin J, Teo S, Lam DH, Jeyaseelan K, Wang S. MicroRNA-10b pleiotropically regulates invasion, angiogenecity and apoptosis of tumor cells resembling mesenchymal subtype of glioblastoma multiforme. Cell Death Dis. 2012;3:e398.
Khabir A, Sellami A, Sakka M, Ghorbel AM, Daoud J, Frikha M, et al. Contrasted frequencies of p53 accumulation in the two age groups of North African nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6(10):3932–6.
Khabir A, Ghorbel A, Daoud J, Frikha M, Drira MM, Laplanche A, et al. Similar BCL-X but different BCL-2 levels in the two age groups of North African nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Cancer Detect Prev. 2003;27(4):250–5.
Karray H, Ayadi W, Fki L, Hammami A, Daoud J, Drira MM, et al. Comparison of three different serological techniques for primary diagnosis and monitoring of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in two age groups from Tunisia. J Med Virol. 2005;75(4):593–602.
Ayadi W, Karray-Hakim H, Feki L, Khabir A, Boudawara T, Ghorbel A, et al. IgA antibodies against the Epstein–Barr nuclear antigen1 as a valuable biomarker for the diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Tunisian patients. J Med Virol. 2009;81(8):1412–21.
Downing NL, Wolden S, Wong P, Petrik DW, Hara W, Le QT. Comparison of treatment results between adult and juvenile nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol, Biol, Phys. 2009;75(4):1064–70.
Sultan I, Casanova M, Ferrari A, Rihani R, Rodriguez-Galindo C. Differential features of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in children and adults: a SEER study. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2010;55(2):279–84.
Nishida N, Yamashita S, Mimori K, Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, et al. miR-10b is a prognostic indicator in colorectal cancer and confers resistance to the chemotherapeutic agent 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer cells. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19(9):3065–71.
Li QJ, Zhou L, Yang F, Wang GX, Zheng H, Wang DS, et al. microRNA-10b promotes migration and invasion through CADM1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Tumor boil. 2012;33(5):1455–65.
Wang YY, Ye ZY, Zhao ZS, Li L, Wang YX, Tao HQ, et al. Clinicopathologic significance of miR-10b expression in gastric carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2013;44(7):1278–85.
Horikawa T, Yang J, Kondo S, Yoshizaki T, Joab I, Furukawa M, et al. Twist and epithelial–mesenchymal transition are induced by the EBV oncoprotein latent membrane protein 1 and are associated with metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007;67(5):1970–8.
Kim K, Lee HC, Park JL, Kim M, Kim SY, Noh SM, et al. Epigenetic regulation of microRNA-10b and targeting of oncogenic MAPRE1 in gastric cancer. Epigenetics. 2011;6(6):740–51.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant of the Tunisian Ministry of High Education and Scientific Research. We wish to thank Pr Adnane Hammami for allowing us to perform the RT-q-PCR experiments in the microbiology laboratory at the School of Medicine of University of Sfax.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. S1
Generating a standard curve to assess reaction efficiency. A Amplification curves and their corresponding melt curves of qPCR reactions using a series of tenfold dilutions of specific cDNA (1, 1/10, 1/100, 1/1000, and 1/10000) of miR-10b (A1) and U6 (A2). B Standard curve with the Ct plotted against the log of the starting quantity of template for each dilution. The equation of the generated curve is shown above the graph. The calculated efficiency was 103 and 101 % for miR10b and U6, respectively (TIFF 2886 kb)
Supplementary Fig. S2
Regulatory network of miR-10b. This schematic representation is created within the open informatic’s site MirOB (http://mirob.interactome.ru/microRNA_databases) (TIFF 4773 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allaya, N., Khabir, A., Sallemi-Boudawara, T. et al. Over-expression of miR-10b in NPC patients: correlation with LMP1 and Twist1. Tumor Biol. 36, 3807–3814 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-3022-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-3022-6