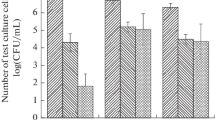
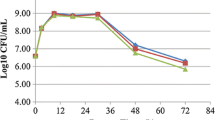
Abstract
An economic liquid growth medium was synthesised for high-rate production of cellular mass, lactic acid and bacteriocin in lactobacilli. Three lactobacilli that are applied extensively in industry—Lactobacillus casei NCIMB 11970, Lactobacillus plantarum NCIMB 8014, Lactobacillus lactis NCIMB 8586—were chosen to test the medium’s efficiency. These bacteria are chemoorganotrophs requiring rich, complex media for optimum growth. Contrary to the current practice of formulating a strain-specific medium, we attempted to prepare a universal broth that would allow easy formulation and optimisation. Man de Rogosa Sharp (MRS) medium, which can support the growth of lactobacilli, was found unsuitable for use in large quantities due to its high cost of preparation and its use of beef extract and peptone from poultry as nitrogen sources, which are not environmentally friendly and have potential health risks. The developed medium supported the growth of all the three bacteria equally, offering good maximum yields and incorporating only the chemical compounds needed, resulting in an improvement in the growth rate of the bacilli of between 50 % and 241 % compared to the same strains grown on MRS. Lactic acid production was between 28.6 and 35.74 g L−1 and bacteriocin production ranged from 110 to 130 IU mL−1.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo-Amer AE (2011) Optimization of bacteriocin production by Lactobacillus acidophilus AA11, a strain isolated from Egyptian cheese. Ann Microbiol 61:445–452
Aktypis A, Tychowski M, Kalantzopoulos G, Aggelis G (2007) Studies on bacteriocin (thermophilin T) production by Streptococcus thermophilus ACA-DC 0040 in batch and fed-batch fermentation modes. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 92:207–220
Avonts L, Van Uyten E, De Vuyst L (2004) Cell growth and bacteriocin production of probiotic Lactobacillus strains in different media. Int Dairy J 14:947–955
Ayres JC, Mundt JO, Saudrine WE (1980) Microbiology of foods. Freeman, San Francisco
Bernadeau M, Vernoux JP, Henri-Dubernet S, Gueguen M (2007) The Lactobacillus genus. Int J Food Microbiol 41:103–125
Board RG (1983) A modern introduction to food microbiology. Blackwell, London
Bober JA, Demicri A (2004) Nisin fermentation by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis using plastic composite supports in biofilm reactors. Agric Eng Int CIGR J Sci Res Dev 6:1–15
Budde BB, Rasch MA (2001) Comparative study on the use of flow cytometry and colony forming units for assessment of the antibacterial effect of bacteriocins. Int J Food Microbiol 63:65–72
Bu’lock JD, Kristiansen B (1978) Basic biotechnology. Academic, London
Carr JG, Cutting CV, Whiting GC (1975) Lactic acid bacteria in beverage and food. Academic, London
Casida LE (1968) Industrial microbiology. Wiley, Chichester
Chen H, Hoover DG (2003) Bacteriocins and their food applications. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 2:83–97
Daoudi M, Bakkas S, Culioli G, Ortalo-Magne A, Piovetti L, Guiry MD (2001) Acyclic diterpenes and sterols from the genera Bifurcaria and Bifurcariopsis (Cystoseiracea, Phaeophyceae). Biochem Syst Ecol 29:973–978
Deegan LH, Cotter PD, Colin H, Ross P (2006) Bacteriocins: biological tools for bio-preservation and shelf-life extension. Int Dairy J 16:1058–1071
Delgado A, Brito D, Feveiro P, Tenreiro R, Peres C (2005) Bioactivity quantification of crude bacteriocin solution. J Microbiol Method 62:121–124
Demain LA, Davies JE (1999) Manual of industrial microbiology and biotechnology. ASM Press, Washington DC
Dembczynski R, Jankowski T (2002) Growth characteristics and acidifying activity of Lactobacillus rhamnosus in alginate/starch liquid core capsules. Enzyme Microb Technol J 31:111–115
Desjardins P, Meghrous J, Lacroix C (2001) Effect of aeration and dilution rate of nisin Z production during continuous fermentation with free and immobilized Lactococcus lactis UL719 in supplemented whey permeate. Int Dairy J 11:943–951
Drosinos EH, Mataragas M, Nasis P, Galiotou M, Metaxopoulos J (2005) Growth and bacteriocin production kinetics of Leuconostoc mesenteroides E131. J Appl Microbiol 99:1314–1323
Drosinos EH, Mataragas M, Metaxopoulos J (2006) Modelling of growth and bacteriocin production by Leuconostoc mesenteroides E131. J Meat Sci 74:690–696
Frazier WC (1978) Food microbiology. McGraw Hill, New York
Fu W, Mathews AP (1999) Lactic acid production from lactoseby Lactobacillus plantarum: kinetic model and effects of pH,substrate, and oxygen. Biochem Eng J 3:163–170
Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Costilow RN, Nester EW, Wood WA, Krieg NR, Phillips GB (1981) Manual of methods for general bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC
Giraffa G, Neviani E, Veneroni A (1990) Use of conductance to detect bacteriocin activity. J Food Prot 53:772–776
Gruger A, Gruger W (1989) Biotechnology: a textbook of industrial microbiology. Sinauer, Sunderland
Guillaume N, Auger I, Beaudoin M, Halle F et al (2004) Improved methods for mutacin detection and production. J Microbiol Methods 59:351–361
Hoefnagel MHN (2002) Metabolic engineering of lactic acid bacteria, the combined approach: kinetic modelling, metabolic control and experimental analysis. J Microbiol 148:1003–1013
Hofvendahl K, Bärbel Hahn-Hägerdal B (2000) Factors affecting the fermentative lactic acid production from renewable resources. Enzyme Microb Technol 26:87–107
Hofvendahl K, Åkerberg C, Zacchi G, Hahn-Hagerdal B (1999) Simultaneous enzymatic wheat starch saccharification and fermentation to lactic acid by Lactococcus lactis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:163–169
Holt JG (1974) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. Williams and Willkins, Baltimore
Hujanen M, Linko Y-Y (1996) Effect of temperature and various nitrogen sources on l (+)-lactic acid production by Lactobacillus casei. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 45:307–313
Jack RW, Tagg JR, Ray B (1995) Bacteriocins of Gram-positive bacteria. Microbiol Rev 3:171–200
Jung I, Lovitt RW (2010a) A comparative study of the growth of lactic acid bacteria in a pilot scale membrane bioreactor. J Chem Tech Biotechnol 85:1250–1259
Jung I, Lovitt RW (2010b) A comparative study of an intensive malolactic transformation of cider using Lactobacillus brevis and Oenococcus oeni in a membrane bioreactor. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 37:727–740
Jung I, Oh MK, Cho YC, Kong IS (2011) The viability to a wall shear stress and propagation of Bifidobacterium longum in the intensive membrane bioreactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:939–949
Kawai Y, Saito T, Uemura J, Itoh T (1997) Rapid detection method for bacteriocin and distribution of bacteriocin-producing strains in Lactobacillus acidophilus group lactic acid bacteria isolated from human faeces. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:179–182
Kirsop BE, Snell JJS (1984) Maintenance of microorganisms: a manual of laboratory methods. Academic, London
Konings WN, Kok J, Kulipers O, Poolman B (2000) Lactic acid bacteria: the bugs of the new millennium. Curr Opin Microbiol 3:276–282
Liew SL, Ariff AB, Racha AR, Ho YW (2005) Optimization of medium composition for the production of a probiotic microorganism Lactobacillus rhamnosus using response surface methodology. Int J Food Microbiol 102:137–142
Liu SQ (2003) Practical implications of lactate and pyruvate metabolism by Lactic Acid Bacteria in food and beverage fermentations. Int J Food Microbiol 83:115–131
MacKane L, Kandel J (1996) Microbiology essentials and applications. McGraw Hill, New York
Malek I, Beran K, Fencl Z, Mun KV, Ricica J (1969) Continuous cultivation of microorganisms. Academic, London
Mandolstan J, MacQuillen A (1973) Biochemistry of bacterial growth. Blackwell, London
Mataragas M, Drosinos EH, Tsakalidou E, Metaxopoulos J (2004) Influence of nutrients on growth and bacteriocin production by Leuconostoc mesenteroides L124 and Lactobacillus curvatus L442. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 85:191–198
Metsoviti M, Paramithiotis S, Drosinos E, Skandamis P, Panayotou-Galiotou M, Papanikolaou S (2011) Biotechnological valorisation of low-cost sugar-based media for bacteriocin production by Leuconostoc mesenteroides E131. New Biotechnol 28:600–609
Mocquot G, Lefebvre E (1956) A simple procedure to detect nisin in cheese. J Appl Bacteriol 19:322–323
Ostlie HM, Helland MH, Narvhus JA (2003) Growth and metabolism of selected strains of probiotic bacteria in milk. Int J Food Microbiol 87:17–27
Ouwehand A, Salminen S, Isolauri E (2002) Probiotics: an overview of beneficial effects. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 82:279–289
Parente E, Moles M, Ricciardi A (1996) Leucocin F10, a bacteriocin from Leuconostoc carnosum. Int J Food Microbiol 33:231–243
Patton T, Barret J, Brennan J, Moran N (2006) Use of a spectrophotometric bioassay for determination of microbial sensitivity to manuka honey. J Microbiol Method 64:84–95
Sentharan A, Sentharan V, Mattiasson B, Kaul R (1997) Lactic acid fermentation in a recycle batch reactor using immobilized Lactobacillus casei. Biotechnol Bioeng J 55:841–853
Simon L, Fremaux C, Cenatiempo Y, Berjeaud JM (2001) Luminescent method for the detection of antibacterial activities. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:757–763
Todorov SD, Dicks LMT (2004) Influence of growth conditions on the production of a bacteriocin by Lactococcus lactis subp. lactis ST 34BR, a strain isolated from barley beer. J Basic Microbiol J 44:305–316
Todorov SD, Dicks LMT (2005a) Effect on growth medium on bacteriocin production by Lactobacillus plantarum ST194BZ, a strain isolated from boza. Food Tech Biotechnol J 43:165–173
Todorov SD, Dicks LMT (2005b) Characterization of bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria isolated from spoiled black olives. J Basic Microbiol 4:312–322
Todorov SD, Dicks LMT (2006) Screening for bacteriocin -producing lactic acid bacteria from boza, a traditional cereal beverage from Bulgaria. Comparison of bacteriocins. Process Biochem 41:11–19
Todorov SD, Dicks LMT (2007) Bacteriocin production by Lactobacillus pentosus ST712BZ. Braz J Microbiol 38:166–173
Todorov SD, Van Reenen C, Dicks LMT (2004) Optimization of bacteriocin production by Lactobacillus plantarum ST13BR, a strain isolated from barley beer. Gen Appl Microbiol J 50:149–157
Tramer J, Fowler GG (1964) Estimation of nisin in foods. J Sci Food Agric 15:525–528
Turcottea C, Lacroix C, Kheadr E, Grignona L, Flissa I (2004) A rapid turbidometric microplate bioassay for accurate quantification of lactic acid bacteria bacteriocins. J Microbiol Methods 90:283–293
Vesterlund S, Paltta J, Lauková A, Karp M et al (2004) Rapid screening method for the detection of antimicrobial substances. J Microbiol Method 57:23–31
Wee Y-J, Kim J-N, Ryu H-W (2006) Biotechnological production of lactic acid and its recent applications. Food Technol Biotechnol 44:136–172
Willis PA (1977) Anaerobic bacteriology: clinical and laboratory practices. Butterworth, London
Zhang Y, Henson MA (2001) Bifurcation analysis of continuous biochemical reactor models. Biotechnol Prog J 17:647–660
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zacharof, MP., Lovitt, R.W. Partially chemically defined liquid medium development for intensive propagation of industrial fermentation lactobacilli strains . Ann Microbiol 63, 1235–1245 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0581-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0581-x