Abstract
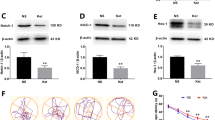
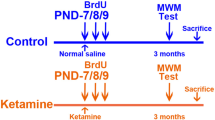
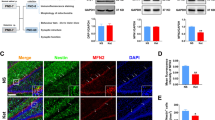
Ketamine has been reported to cause neonatal neurotoxicity via a neuronal apoptosis mechanism; however, no in vivo research has reported whether ketamine could affect postnatal neurogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG). A growing number of experiments suggest that postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis is the foundation of maintaining normal hippocampus function into adulthood. Therefore, this study investigated the effect of ketamine on hippocampal neurogenesis. Male Sprague–Dawley rats were divided into two groups: the control group (equal volume of normal saline), and the ketamine-anesthesia group (40 mg/kg ketamine in four injections at 1 h intervals). The S-phase marker 5-bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) was administered after ketamine exposure to postnatal day 7 (PND-7) rats, and the neurogenesis in the hippocampal DG was assessed using single- or double-immunofluorescence staining. The expression of GFAP in the hippocampal DG was measured by western blot analysis. Spatial reference memory was tested by Morris water maze at 2 months after PND-7 rats exposed to ketamine treatment. The present results showed that neonatal ketamine exposure significantly inhibited neural stem cell (NSC) proliferation, decreased astrocytic differentiation, and markedly enhanced neuronal differentiation. The disruptive effect of ketamine on the proliferation and differentiation of NSCs lasted at least 1 week and disappeared by 2 weeks after ketamine exposure. Moreover, the migration of newborn neurons in the granule cell layer and the growth of astrocytes in the hippocampal DG were inhibited by ketamine on PND-37 and PND-44. Finally, ketamine caused a deficit in hippocampal-dependent spatial reference memory tasks at 2 months old. Our results suggested that ketamine may interfere with hippocampal neurogenesis and long-term neurocognitive function in PND-7 rats. These findings may provide a new perspective to explain the adult neurocognitive dysfunction induced by neonatal ketamine exposure.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrous DN, Koehl M, Le Moal M (2005) Adult neurogenesis: from precursors to network and physiology. Physiol Rev 85:523–569
Altman J, Bayer SA (1990) Migration and distribution of two populations of hippocampal granule cell precursors during the perinatal and postnatal periods. J Comp Neurol 301:365–381
Arvidsson A, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2001) N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated increase of neurogenesis in adult rat dentate gyrus following stroke. Eur J Neurosci 14:10–18
Asadi P, Ghafouri HB, Yasinzadeh M, Kasnavieh SM, Modirian E (2013) Ketamine and atropine for pediatric sedation: a prospective double-blind randomized controlled trial. Pediatr Emerg Care 29:136–139
Ashwell KWS, Paxinos G (2008) Atlas of the developing rat nervous system. Elsevier, San Diego
Barreto GE, Sun X, Xu L, Giffard RG (2011) Astrocyte proliferation following stroke in the mouse depends on distance from the infarct. PLoS ONE 6:e27881
Bartley J, Soltau T, Wimborne H, Kim S, Martin-Studdard A et al (2005) BrdU-positive cells in the neonatal mouse hippocampus following hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. BMC Neurosci 6:15
Belnoue L, Grosjean N, Ladeveze E, Abrous DN, Koehl M (2013) Prenatal stress inhibits hippocampal neurogenesis but spares olfactory bulb neurogenesis. PLoS ONE 8:e72972
Byrnes ML, Reynolds JN, Brien JF (2001) Effect of prenatal ethanol exposure during the brain growth spurt of the guinea pig. Neurotoxicol Teratol 23:355–364
Dong C, Rovnaghi CR, Anand KJ (2012) Ketamine alters the neurogenesis of rat cortical neural stem progenit or cells. Crit Care Med 40:2407–2416
Dupret D, Fabre A, Dobrossy MD, Panatier A, Rodriguez JJ et al (2007) Spatial learning depends on both the addition and removal of new hippocampal neurons. PLoS Biol 5:e214
Dupret D, Revest JM, Koehl M, Ichas F, De Giorgi F et al (2008) Spatial relational memory requires hippocampal adult neurogenesis. PLoS ONE 3:e1959
Erasso DM, Camporesi EM, Mangar D, Saporta S (2013) Effects of isoflurane or propofol on postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in young and aged rats. Brain Res 1530:1–12
Esposito MS, Piatti VC, Laplagne DA, Morgenstern NA, Ferrari CC et al (2005) Neuronal differentiation in the adult hippocampus recapitulates embryonic development. J Neurosci 25:10074–10086
Fang F, Xue Z, Cang J (2012) Sevoflurane exposure in 7-day-old rats affects neurogenesis, neurodegeneration and neurocognitive function. Neurosci Bull 28:499–508
Guerra GG, Robertson CM, Alton GY, Joffe AR, Cave DA et al (2011) Neurodevelopmental outcome following exposure to sedative and analgesic drugs for complex cardiac surgery in infancy. Paediatr Anaesth 21:932–941
Guidi S, Ciani E, Severi S, Contestabile A, Bartesaghi R (2005) Postnatal neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the guinea pig. Hippocampus 15:285–301
Ikonomidou C, Bosch F, Miksa M, Bittigau P, Vockler J et al (1999) Blockade of NMDA receptors and apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Science 283:70–74
Joo JY, Kim BW, Lee JS, Park JY, Kim S et al (2007) Activation of NMDA receptors increases proliferation and differentiation of hippocampal neural progenitor cells. J Cell Sci 120:1358–1370
Kee N, Teixeira CM, Wang AH, Frankland PW (2007) Preferential incorporation of adult-generated granule cells into spatial memory networks in the dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci 10:355–362
Keith JR, Wu Y, Epp JR, Sutherland RJ (2007) Fluoxetine and the dentate gyrus: memory, recovery of function, and electrophysiology. Behav Pharmacol 18:521–531
Kempermann G, Gage FH (2002) Genetic influence on phenotypic differentiation in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 134:1–12
Kempermann G, Gast D, Kronenberg G, Yamaguchi M, Gage FH (2003) Early determination and long-term persistence of adult-generated new neurons in the hippocampus of mice. Development 130:391–399
Kitayama T, Yoneyama M, Tamaki K, Yoneda Y (2004) Regulation of neuronal differentiation by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors expressed in neural progenitor cells isolated from adult mouse hippocampus. J Neurosci Res 76:599–612
Liu F, Paule MG, Ali S, Wang C (2011) Ketamine-induced neurotoxicity and changes in gene expression in the developing rat brain. Curr Neuropharmacol 9:256–261
Lledo PM, Alonso M, Grubb MS (2006) Adult neurogenesis and functional plasticity in neuronal circuits. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:179–193
Luk KC, Kennedy TE, Sadikot AF (2003) Glutamate promotes proliferation of striatal neuronal progenitors by an NMDA receptor-mediated mechanism. J Neurosci 23:2239–2250
Luskin MB (1993) Restricted proliferation and migration of postnatally generated neurons derived from the forebrain subventricular zone. Neuron 11:173–189
Manning EE, Ransome MI, Burrows EL, Hannan AJ (2012) Increased adult hippocampal neurogenesis and abnormal migration of adult-born granule neurons is associated with hippocampal-specific cognitive deficits in phospholipase C-beta1 knockout mice. Hippocampus 22:309–319
Mongiat LA, Schinder AF (2011) Adult neurogenesis and the plasticity of the dentate gyrus network. Eur J Neurosci 33:1055–1061
Nacher J, McEwen BS (2006) The role of N-methyl-D-asparate receptors in neurogenesis. Hippocampus 16:267–270
Nacher J, Rosell DR, Alonso-Llosa G, McEwen BS (2001) NMDA receptor antagonist treatment induces a long-lasting increase in the number of proliferating cells, PSA-NCAM-immunoreactive granule neurons and radial glia in the adult rat dentate gyrus. Eur J Neurosci 13:512–520
Nie H, Peng Z, Lao N, Dong H, Xiong L (2013) Effects of sevoflurane on self-renewal capacity and differentiation of cultured neural stem cells. Neurochem Res 38:1758–1767
Paule MG, Li M, Allen RR, Liu F, Zou X et al (2011) Ketamine anesthesia during the first week of life can cause long-lasting cognitive deficits in rhesus monkeys. Neurotoxicol Teratol 33:220–230
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, vol 2. Academic Press, Sydney
Pfenninger EG, Durieux ME, Himmelseher S (2002) Cognitive impairment after small-dose ketamine isomers in comparison to equianalgesic racemic ketamine in human volunteers. Anesthesiology 96:357–366
Porzionato A, Macchi V, Zaramella P, Sarasin G, Grisafi D et al (2013) Effects of postnatal hyperoxia exposure on the rat dentate gyrus and subventricular zone. Brain Struct Funct 220(1):229–247
Sibbe M, Forster E, Basak O, Taylor V, Frotscher M (2009) Reelin and Notch1 cooperate in the development of the dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 29:8578–8585
Stone SS, Teixeira CM, Zaslavsky K, Wheeler AL, Martinez-Canabal A et al (2011) Functional convergence of developmentally and adult-generated granule cells in dentate gyrus circuits supporting hippocampus-dependent memory. Hippocampus 21:1348–1362
Stratmann G, May LD, Sall JW, Alvi RS, Bell JS et al (2009a) Effect of hypercarbia and isoflurane on brain cell death and neurocognitive dysfunction in 7-day-old rats. Anesthesiology 110:849–861
Stratmann G, Sall JW, May LD, Bell JS, Magnusson KR et al (2009b) Isoflurane differentially affects neurogenesis and long-term neurocognitive function in 60-day-old and 7-day-old rats. Anesthesiology 110:834–848
Vadodaria KC, Jessberger S (2014) Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus: then and now. Front Neurosci 8:55
van Praag H, Schinder AF, Christie BR, Toni N, Palmer TD et al (2002) Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature 415:1030–1034
Wilder RT, Flick RP, Sprung J, Katusic SK, Barbaresi WJ, Mickelson C, Gleich SJ, Schroeder DR, Weaver AL, Warner DO (2009) Early exposure to anesthesia and learning disabilities in a population-based birth cohort. Anesthesiology 110:796–804
Young D, Lawlor PA, Leone P, Dragunow M, During MJ (1999) Environmental enrichment inhibits spontaneous apoptosis, prevents seizures and is neuroprotective. Nat Med 5:448–453
Yu-Qing Wu, Liang Tuo, Huang He et al (2014) Ketamine inhibits proliferation of neural stem cell from neonatal rat hippocampus in vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem 34:1792–1801
Zhang K, Zhao T, Huang X, Wu LY, Wu K et al (2014) Notch1 mediates postnatal neurogenesis in hippocampus enhanced by intermittent hypoxia. Neurobiol Dis 64:66–78
Zou X, Patterson TA, Divine RL, Sadovova N, Zhang X et al (2009a) Prolonged exposure to ketamine increases neurodegeneration in the developing monkey brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 27:727–731
Zou X, Patterson TA, Sadovova N, Twaddle NC, Doerge DR et al (2009b) Potential neurotoxicity of ketamine in the developing rat brain. Toxicol Sci 108:149–158
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81171013), the Key Subject of Colleges and Universities Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (10KJA320052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Liu, CM., Sun, J. et al. Ketamine Affects the Neurogenesis of the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus in 7-Day-Old Rats. Neurotox Res 30, 185–198 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9615-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9615-7