Abstract
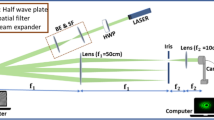
Present work describes the principle and realization of diffraction Lloyd’s mirror interferometer. In this new system light diffracted from an aperture is divided into two wavefronts which are again superimposed on each other with the help of a Lloyd’s mirror. This setup generates two beam interference fringes analogous to that the well known Lloyd’s mirror interferometer. It has been shown that these interference fringes can be produced with vertical as well as horizontal polarized incident light. Experimental test results on phase objects using this system are also presented. Further, applications of this interferometer are discussed in various emerging fields.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malacara-Hernández, D., Servín, M., Malacara, Z.: Interferogram Analysis for Optical Testing. Marcel Dekker, New York (2005)
Hariharan, P.: Optical interferometry. Academic Press, San Diego (2003)
A.A. Hamza, M.A. Mabrouk, W.A. Ramadan, A.M. Emara, “Refractive index and thickness determination of thin-films using Lloyd’s interferometer” Opt. Commun. 225, 341–348 (2003)
R. Kumar, D.P. Chhachhia, A.K. Aggarwal, “Retrieval of infinite-fringe mode information from beam folding interferometer for direct phase visualization” J. Opt. A: Pure Appl. Opt. 8, 747–751 (2006)
R. Kumar, A.K. Aggarwal, “Interferometric moiré pattern encoded security holograms with concealed phase pattern” Opt. Commun. 279, 120–123 (2007)
J. Boor, N. Geyer, U. Gösele, V. Schmidt, “Three-beam interference lithography: upgrading Lloyd’s interferometer for single exposure hexagonal patterning” Opt. Lett. 34, 1783–1785 (2009)
R. Kumar, S.K. Kaura, D.P. Chhachhia, A.K. Aggarwal, “Direct visualization of Young’s boundary diffraction wave” Opt. Commun. 276, 54–57 (2007)
M. Born, E. Wolf: Principles of Optics. Pergamon, Oxford (1993)
P.H. Langenbeck, “Lloyd Interferometer Applied to Flatness Testing” Appl. Opt. 6, 1707–1714 (1967)
R.N. Wolfe, F.C. Eisen, “Irradiance distribution in a Lloyd mirror interference pattern” J. Opt. Soc. Am. 38, 706–711 (1948)
R. Kumar, D.P. Chhachhia, A.K. Aggarwal, “Folding mirror schlieren diffraction interferometer” Appl. Opt. 45, 6708–6711 (2006)
R. Kumar, S.K. Kaura, A.K. Sharma, D.P. Chhachhia and A.K. Aggarwal, “Knife-edge diffraction pattern as an interference phenomenon: an experimental reality” Opt. Laser Tech. 39, 256–261 (2007)
G.S. Settles: Schlieren and Shadowgraph Techniques: Visualizing Phenomena in Transparent Media. Springer, Berlin (2001)
R. Kumar, “Structure of boundary diffraction wave revisited” Appl. Phys. B -Lasers Opt. 90, 379–382 (2008)
R. G. Kouyoumjian, P. H. Pathak, “A uniform geometrical theory of diffraction for an edge in a perfectly conducting surface” Proc. IEEE 62, 1448–1461 (1974)
A. Rubinowicz, “Thomas Young and the theory of diffraction” Nature 180, 160–162
T.W. Ebbesen, H.J. Lezec, H.F. Ghaemi, T. Thio, P.A. Wolff, “Extraordinary optical transmission through subwavelength hole arrays” Nature 391, 667–669 (1998)
C. Genet, T.W. Ebbesen, “Light in tiny holes” Nature 445, 39–46 (2007)
J. Weiner, “The physics of light transmission through subwavelength apertures and aperture arrays” Rep. Prog. Phys. 72, 064401 (2009)
T. Young, “The Bakerian lecture: On the theory of light and colors” Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London 20, 12–48 (1802)
S.V. Kukhlevsky, “Enhanced transmission of light through subwavelength nanoapertures by far-field multiplebeam interference” Phys. Rev. A 78, 023826 (2008)
R. Kumar, “Extraordinary optical transmission by interference of diffracted wavelets” Opt. Appl. 40, In Press (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12596-013-0135-z.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R. Diffraction Lloyd mirror interferometer. J Opt 39, 90–101 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-010-0025-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-010-0025-6