Abstract
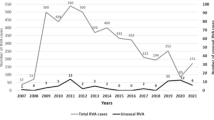
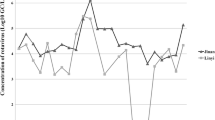
Rotavirus C (RVC) is detected in both sporadic cases and outbreaks of gastroenteritis worldwide. However, the epidemic dynamics of RVC in populations remain poorly understood because the detection rate is low. In this study, raw sewage samples were collected from a wastewater treatment plant in Yokohama, Japan, over 5 years, in 12-month period from September to August, to identify the RVC strains in these samples and compare them with the RVC strains circulating in the population. RVC strains were detected in 15 of the 118 raw sewage samples collected between 2007 and 2012. The highest number of positive samples detected per period (seven) was in 2008–2009. A fragment (225 nucleotides) of the VP7 gene of RVC from 14 sewage samples was sequenced. The nucleotide sequences of 11 strains were completely consistent with those of clinical strains identified in Yokohama. A phylogenetic analysis showed that 13 strains from the sewage samples clustered with several Yokohama outbreak strains and were closely related to the clinical strains (except sewage-derived strain Y11-SW0805-C). Our study demonstrates a correlation between clinical and sewage strains of RVC based on a genetic analysis, and shows that monitoring environmental samples is an effective way to study the strains circulating in a population, including in asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic patients, even when these infections are not detected in clinical samples. This is the first report of the surveillance of RVC in sewage samples in Yokohama, Japan, for molecular epidemiological analysis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apostol, L. N., Imagawa, T., Suzuki, A., Masago, Y., Lupisan, S., Olveda, R., et al. (2012). Genetic diversity and molecular characterization of enteroviruses from sewage-polluted urban and rural rivers in the Philippines. Virus Genes, 45(2), 207–217.
Barril, P. A., Giordano, M. O., Isa, M. B., Masachessi, G., Ferreyra, L. J., Castello, A. A., et al. (2010). Correlation between rotavirus A genotypes detected in hospitalized children and sewage samples in 2006, Córdoba, Argentina. Journal of Medical Virology, 82(7), 1277–1281.
Bridger, J. C., Pedley, S., & McCrae, M. A. (1986). Group C rotaviruses in humans. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 23(4), 760–763.
Bucardo, F., Lindgren, P. E., Svensson, L., & Nordgren, J. (2011). Low prevalence of rotavirus and high prevalence of norovirus in hospital and community wastewater after introduction of rotavirus vaccine in Nicaragua. PLoS One, 6(10), e25962.
Castello, A. A., Argüelles, M. H., Rota, R. P., Humphrey, C. D., Olthoff, A., Gentsch, J. R., et al. (2009). Detection and characterization of group C rotavirus in Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1997–2003. Journal of Medical Virology, 81(6), 1109–1116.
Divizia, M., Gabrieli, R., Macaluso, A., Bagnato, B., Palombi, L., Buonomo, E., et al. (2005). Nucleotide correlation between HAV isolates from human patients and environmental samples. Journal of Medical Virology, 75(1), 8–12.
Estes, M. K., & Kapikian, A. Z. (2007). Rotaviruses. In D. M. Knipe, P. M. Howley, D. E. Griffin, M. A. Martin, R. A. Lamb, B. Roizman, & S. E. Straus (Eds.), Fields virology (5th ed., pp. 1917–1974). Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins.
Fumian, T. M., Leite, J. P., Rose, T. L., Prado, T., & Miagostovich, M. P. (2011). One year environmental surveillance of rotavirus specie A (RVA) genotypes in circulation after the introduction of the Rotarix® vaccine in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Water Research, 45(17), 5755–5763.
Haramoto, E., Katayama, H., Phanuwan, C., & Ohgaki, S. (2008). Quantitative detection of sapoviruses in wastewater and river water in Japan. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 46(3), 408–413.
Hoehne, M., & Schreier, E. (2006). Detection of Norovirus genogroup I and II by multiplex real-time RT- PCR using a 3′-minor groove binder-DNA probe. BMC Infectious Diseases, 6, 69.
Jothikumar, N., Lowther, J. A., Henshilwood, K., Lees, D. N., Hill, V. R., & Vinjé, J. (2005). Rapid and sensitive detection of noroviruses by using taqman-based one-step reverse transcription-pcr assays and application to naturally contaminated. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71(4), 1870–1875.
Katayama, H., Shimasaki, A., & Ohgaki, S. (2002). Development of a virus concentration method and its application to detection of enterovirus and norwalk virus from coastal seawater. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68(3), 1033–1039.
Kumazaki, M., & Usuku, S. (2014). Epidemiological and genetic analysis of human group C rotaviruses isolated from outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis in Yokohama, Japan, between 2006 and 2012. Archives of Virology, 159(4), 761–771.
Kuzuya, M., Fujii, R., Hamano, M., Nishijima, M., & Ogura, H. (2007). Detection and molecular characterization of human group C rotaviruses in Okayama Prefecture, Japan, between 1986 and 2005. Journal of Medical Virology, 79(8), 1219–1228.
La Rosa, G., Pourshaban, M., Iaconelli, M., Vennarucci, V. S., & Muscillo, M. (2010). Molecular detection of hepatitis E virus in sewage samples. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76(17), 5870–5873.
Lodder, W. J., Rutjes, S. A., Takumi, K., & de Roda Husman, A. M. (2013). Aichi virus in sewage and surface water, the Netherlands. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 19(8), 1222–1230.
Martella, V., Bányai, K., Lorusso, E., Decaro, N., Bellacicco, A., Desario, C., et al. (2007). Genetic heterogeneity in the VP7 of group C rotaviruses. Virology, 367(2), 358–366.
Matthijnssens, J., Otto, P. H., Ciarlet, M., Desselberger, U., Van Ranst, M., & Johne, R. (2012). VP6-sequence-based cutoff values as a criterion for rotavirus species demarcation. Archives of Virology, 157(6), 1177–1182.
Meleg, E., Bányai, K., Martella, V., Jiang, B., Kocsis, B., Kisfali, P., et al. (2008). Detection and quantification of group C rotaviruses in communal sewage. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74(11), 3394–3399.
Muscillo, M., Fratini, M., Graffeo, R., Sanguinetti, M., Martella, V., Green, K. Y., et al. (2013). GIV noroviruses in wastewaters and in stool specimens from hospitalized patients. Food and Environmental Virology, 5(4), 194–202.
Parashar, U. D., Hummelman, E. G., Bresee, J. S., Miller, M. A., & Glass, R. I. (2003). Global illness and deaths caused by rotavirus disease in children. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 9(5), 565–572.
Rodger, S. M., Bishop, R. F., & Holmes, I. H. (1982). Detection of a rotavirus-like agent associated with diarrhea in an infant. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 16(4), 724–726.
Saif, L. J., Bohl, E. H., Theil, K. W., Cross, R. F., & House, J. A. (1980). Rotavirus-like, calicivirus-like, and 23-nm virus-like particles associated with diarrhea in young pigs. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 12(1), 105–111.
Thompson, J. D., Higgins, D. G., & Gibson, T. J. (1994). CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Research, 22(22), 4673–4680.
Acknowledgments
We thank Satoshi Ueki for his continued technical assistance. This work was supported by all the staff at the Environmental Planning Bureau and the Public Health Center, Yokohama, Japan, who collected specimens and provided data.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumazaki, M., Usuku, S. Nucleotide Correlations Between Rotavirus C Isolates in Clinical Samples from Outbreaks and in Sewage Samples. Food Environ Virol 7, 269–275 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-014-9175-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-014-9175-z