Abstract
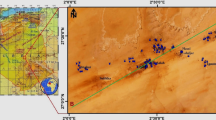
An attempt has been made to delineate the hydrochemistry for a small island based on the major ions and heavy metal concentrations. In this investigation, six sampling campaigns were conducted to measure the concentrations of major ions (Ca, Mg, Na, K, HCO3, Cl, and SO4) and heavy metals (Zn, Cr, Pb, Mn, As, and Cu) in groundwater samples collected from seven sampling stations (boreholes) located on Kapas Island, Terengganu, Malaysia. The distribution of major ions is illustrated by a piper plot where Ca–HCO3 is the dominant type. In addition, the concentrations of heavy metals demonstrate that Mn shows as being the highest concentrated heavy metal in the groundwater sampled in the sampling campaigns; the average Mn content in groundwater sampled was 54.05 μg/L. However, a comparison of the heavy metal (Mn, Cr, Zn, As, Pb, and Cu) concentrations in groundwater samples with the Drinking Water Quality Standard prescribed by World Health Organization reveals that none of these heavy metals exceeded the recommended threshold limits. The principal component analyses (PCA) extracted four components that control the groundwater chemistry. Components 1 and 2 from the PCA analyses extracted approximately 52.11 % of the total variance, which represent the heavy metals (As and Mn) and physical parameters (pH, redox potential, electrical conductivity, temperature, and total dissolved solids). Based on the output of the PHREEQC hydrogeochemical software, several species of heavy metals exist, in which the dominant species found are Mn2+, PbCO3, Cu(OH)2, and Zn+.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah MP (1981) Laporan penyiasatan kajibumi. Ibu Pejabat Penyiasatan Kajibumi, Malaysia
Ahmed AM, Sulaiman WN (2001) Evaluation of groundwater and soil pollution in a landfill area using electrical resistivity imaging survey. Environ Manag 28(5):655–663
Ali CA, Mohamed KR and Abdullah I (2001) Pemetaan Awalan Air Panas Kawasan Lojing, Gua Musang, Kelantan in Komoo I., Tjia H. D. and Leman , M. S. Eds, Warisan Geologi Malaysia: Selangor Malaysia, LESTARI
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation, Washington
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (2005) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution, 2nd edn. Balkema, Rotterdam
Aris AZ, Abdullah MH, Ahmed A, Woong KK (2007) Controlling factors of groundwater hydrochemistry in a small island's aquifer. Int J Environ Sci Technol 4(4):441–450
Baumann T, Fruhstorfer P, Klein T, Niessner R (2006) Colloid and heavy metal transport at landfill sites in direct contact with groundwater. Water Res 40(14):2776–2786
Bissen M, Frimmel FH (2003) Arsenic—a review. Part I: occurrence, toxicity, speciation, mobility. Acta Hydrochim et Hydrobiol 31(1):9–18
Chowdhury M, Meharg A, Deacon C, Hossain M, Norton G (2012) Hydrogeochemistry and arsenic contamination of groundwater in the Haor Basins of Bangladesh. Water Qual Expo Health 4(2):67–78
Christodoulidou M, Charalambous C, Aletrari M, Nicolaidou Kanari P, Petronda A, Ward NI (2012) Arsenic concentrations in groundwaters of Cyprus. J Hydrol 468–469:94–100
Critto A, Carlon C, Marcomini A (2003) Characterization of contaminated soil and groundwater surrounding an illegal landfill (S. Giuliano, Venice, Italy) by principal component analysis and kriging. Environ Pollut 122(2):235–244
Frost F, Franke D, Pierson K, Woodruff L, Raasina B, Davis R, Davies J (1993) A seasonal study of arsenic in groundwater, Snohomish County, Washington, USA. Environ Geochem Heal 15(4):209–214
Haloi N, Sarma H (2012) Heavy metal contaminations in the groundwater of Brahmaputra flood plain: an assessment of water quality in Barpeta District, Assam (India). Environ Monit Assess 184(10):6229–6237
Hem JD (1963) Chemical equilibria affecting the behaviour of manganese in natural water. Hydrol Sci J 8:30–37
Hem JD (1985) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. Water supply paper 2254. Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey, Washington
Hem JD (1989) Study and Interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water, 3rd edn. United States Geological Survey, Washington
Herdan J, Feeney R, Kounaves SP, Flannery AF, Storment CW, Kovacs GTA, Darling RB (1998) Field evaluation of an electrochemical probe for in situ screening of heavy metals in groundwater. Environ Sci Technol 32(1):131–136
Hitchon B (2006) Lead and zinc in formation waters, Alberta Basin, Canada: their relation to the pine point ore fluid. Appl Geochem 21(1):109–133
Isa NM, Aris AZ, Sulaiman WNA (2012) Extent and severity of groundwater contamination based on hydrochemistry mechanism of sandy tropical coastal aquifer. Sci Total Environ 438:414–425
Jain CK, Ali I (2000) Arsenic: occurrence, toxicity and speciation techniques. Water Res 34(17):4304–4312
Kargar M, Khorasani N, Karami M, Rafiee G, Naseh R (2012) Statistical source identification of major and trace elements in groundwater downward the tailings dam of Miduk Copper Complex, Kerman, Iran. Environ Monit Assess 184(10):6173–6185
Katsuro A, Yasuhiko K, Yoshinori S, Takashi T, Hayao S (2004) Heavy metal distribution in river waters and sediments around a firefly village, Shikoku Japan: application of multivariate analysis. Anal Sci 20:79–85
Kim MJ, Nriagu J, Haack S (2000) Carbonate ions and arsenic dissolution by groundwater. Environ Sci Technol 34(15):3094–3100
Ledin A, Pettersson C, Allard B, Aastrup M (1989) Background concentration ranges of heavy metals in Swedish groundwaters from crystalline rocks: a review. Water Air Soil Pollut 47:419–426
Lee M, Paik IS, Kim I, Kang H, Lee S (2007) Remediation of heavy metal contaminated groundwater originated from abandoned mine using lime and calcium carbonate. J Hazard Mater 144:208–214
Leung CM, Jiao JJ (2006) Heavy metal and trace element distributions in groundwater in natural slopes and highly urbanized spaces in Mid-Levels area, Hong Kong. Water Res 40(4):753–767
Mishra VK, Tripathi BD (2008) Concurrent removal and accumulation of heavy metals by the three aquatic macrophytes. Bioresour Technol 99:7091–7097
Mokhtar M, Aris AZ, Abdullah MH, Yusoff MK, Abdullah MP, Idris AR, Raja Uzir RI (2009) A pristine environment and water quality in perspective—Maliau Basin. Borneo's Mysterious World Water Environ J 23(3):219–228
Mosier DL, Page NJ (1988) Descriptive and grade-tonnage models of volcanogenic manganese deposits in oceanic environments—a modification. US Geol Surv Bull 1811:28
Mulligan CN, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (2001) Remediation technologies for metal-contaminated soils and groundater: an evolution. Eng Geol 60:193–207
Norrström A, Knutsson G (2012) Stable lead isotopes as tracers of groundwater pollution in the water supply for a small village. Environ Earth Sci 67(4):1085–1095
Nouri J, Mahvi AH, Babaei AA, Jahed GR, Ahmadpour E (2006) Investigation of heavy metals in groundwater. Pak J Biol Sci 9(3):377–384
Parga JR, Cocke DL, Valenzuela JL, Gomes JA, Kesmez M, Irwin G, Moreno H, Weir M (2005) Arsenic removal via electrocoagulation from heavy metal contaminated groundwater in La Comarca Lagunera M´exico. J Hazard Mater B124:247–254
Peng JF, Song YH, Yuan P, Cui XY, Qiu GL (2009) The remediation of heavy metals contaminated sediment. J Hazard Mater 161:633–640
Radojevic M, Bashkin VN (2006) Practical environmental analysis. RSC Publishing, Cambridge
Rattan RK, Datta SP, Chhonkar PK, Suribabu K, Singh AK (2005) Long-term impact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metal content in soils, crops and groundwater—a case study. Agric Ecosyst Environ 109(3–4):310–322
Samuding K, Abustan I, Rahman MTA, Isa MH (2009) Distribution of heavy metals profile in groundwater system at solid waste disposal site. Eur J Sci Res 37(1):58–66
Sang Y, Li F, Gu Q, Liang C, Chen J (2008) Heavy metal-contaminated groundwater treatment by a novel nanofiber membrane. Desalination 223:349–360
Shokrzadeh M, Saravi SSS (2009) The study of heavy metals (zinc, lead, cadmium, and chromium) in water sampled from Gorgan coast (Iran), Spring 2008. Toxicol Environ Chem 91(3):405–407
Shuib MK (2003) Transpression in the strata of Pulau Kapas, Terengganu. Geol Soc Malaysia Bull 46:299–306
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (1996) Aquatic chemistry: chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters, 3rd edn. Willey, New York
Subyani AM, Ahmadi MEA (2010) Multivariate statistical analysis of groundwater quality in Wadi Ranyah, Saudi Arabia. JAKU Earth Sci 21(2):29–46
WHO (World Health Organization) (2011) Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality. 1:4rd edition
Yi Y, Wang Z, Zhang K, Yu G, And Duan X (2008) Sediment pollution and its effect on fish through food chain in the Yangtze River. Int J Sediment Res 23:338–347
Zandsalimi S, Karimi N, Kohandel A (2011) Arsenic in soil, vegetation and water of a contaminated region. Int J Environ Sci Technol 8(2):331–338
Zheng N, Wang Q, Liang Z, Zheng D (2008) Characterization of heavy metal concentrations in the sediments of three freshwater rivers in Huludao City, Northeast China. Environ Pollut 154:135–142
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Ministry of Higher Education, Vot No. 07/11/09/696FR. The provision of allowance Graduate Research Funding (GRF) by Universiti Putra Malaysia and MOHE Budget Mini Scholarship is gratefully acknowledged, as is the valuable help from the Faculty of Environmental Studies and Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, in preparing boreholes for this research and also for the lab analyses. Special thanks to the Minerals and Geoscience Department Malaysia, Terengganu, for providing helpful information about the geology of the study area.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Isa, N.M., Aris, A.Z., Lim, W.Y. et al. Evaluation of heavy metal contamination in groundwater samples from Kapas Island, Terengganu, Malaysia. Arab J Geosci 7, 1087–1100 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0818-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0818-9