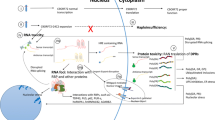
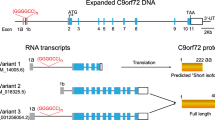
Abstract
Motor neuron disorders, and particularly amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), are fatal diseases that are due to the loss of motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord, with progressive paralysis and premature death. It has been recently shown that the most frequent genetic cause of ALS, frontotemporal dementia (FTD), and other neurological diseases is the expansion of a hexanucleotide repeat (GGGGCC) in the non-coding region of the C9ORF72 gene. The pathogenic mechanisms that produce cell death in the presence of this expansion are still unclear. One of the most likely hypotheses seems to be the gain-of-function that is achieved through the production of toxic RNA (able to sequester RNA-binding protein) and/or toxic proteins. In recent works, different authors have reported that antisense oligonucleotides complementary to the C9ORF72 RNA transcript sequence were able to significantly reduce RNA foci generated by the expanded RNA, in affected cells. Here, we summarize the recent findings that support the idea that the buildup of “toxic” RNA containing the GGGGCC repeat contributes to the death of motor neurons in ALS and also suggest that the use of antisense oligonucleotides targeting this transcript is a promising strategy for treating ALS/frontotemporal lobe dementia (FTLD) patients with the C9ORF72 repeat expansion. These data are particularly important, given the state of the art antisense technology, and they allow researchers to believe that a clinical application of these discoveries will be possible soon.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeJesus-Hernandez M, Mackenzie IR, Boeve BF, Boxer AL, Baker M, Rutherford NJ, Nicholson AM, Finch NA, Flynn H, Adamson J, Kouri N, Wojtas A, Sengdy P, Hsiung GY, Karydas A, Seeley WW, Josephs KA, Coppola G, Geschwind DH, Wszolek ZK, Feldman H, Knopman DS, Petersen RC, Miller BL, Dickson DW, Boylan KB, Graff-Radford NR, Rademakers R (2011) Expanded GGGGCC hexanucleotide repeat in noncoding region of C9ORF72 causes chromosome 9p-linked FTLD and ALS. Neuron 72:245–256
Renton AE, Majounie E, Waite A, Simón-Sánchez J, Rollinson S, Gibbs JR, Schymick JC, Laaksovirta H, van Swieten JC, Myllykangas L, Kalimo H, Paetau A, Abramzon Y, Remes AM, Kaganovich A, Scholz SW, Duckworth J, Ding J, Harmer DW, Hernandez DG, Johnson JO, Ryten KMK, Trabzuni D, Guerreiro RJ, Orrell RW, Neal J, Murray A, Pearson J, Jansen IE, Sondervan D, Seelaar H, Blake D, Young K, Halliwell N, Callister JB, Toulson G, Richardson A, Gerhard A, Snowden J, Mann D, Neary D, Nalls MA, Peuralinna T, Jansson L, Isoviita VM, Kaivorinne AL, Hölttä-Vuori M, Ikonen E, Sulkava R, Benatar M, Wuu J, Chiò A, Restagno G (2011) A hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72 is the cause of chromosome 9p21-linked ALS-FTLD. Neuron 72:257–268
Gijselinck I, Van Langenhove T, van der Zee J, Sleegers K, Philtjens S, Kleinberger G, Janssens J, Bettens K, Van Cauwenberghe C, Pereson S, Engelborghs S, Sieben A, De Jonghe P, Vandenberghe R, Santens P, De Bleecker J, Maes G, Bäumer V, Dillen L, Joris G, Cuijt I, Corsmit E, Elinck E, Van Dongen J, Vermeulen S, Van den Broeck M, Vaerenberg C, Mattheijssens M, Peeters K, Robberecht W, Cras P, Martin JJ, De Deyn PP, Cruts M, Van Broeckhoven C (2012) A C9orf72 promoter repeat expansion in a Flanders-Belgian cohort with disorders of the frontotemporal lobar degeneration-amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spectrum: a gene identification study. Lancet Neurol 11:54–65
Nuytemans K, Bademci G, Kohli MM, Beecham GW, Wang L, Young JI, Nahab F, Martin ER, Gilbert JR, Benatar M, Haines JL, Scott WK, Züchner S, Pericak-Vance MA, Vance JM (2013) C9ORF72 intermediate repeat copies are a significant risk factor for Parkinson disease. Ann Hum Genet. doi:10.1111/ahg.12033
Harms MB, Cady J, Zaidman C, Cooper P, Bali T, Allred P, Cruchaga C, Baughn M, Libby RT, Pestronk A, Goate A, Ravits J, Baloh RH (2013) Lack of C9ORF72 coding mutations supports a gain of function for repeat expansions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol Aging 34:2234.e13–2234.e19
Cacace R, Van Cauwenberghe C, Bettens K, Gijselinck I, van der Zee J, Engelborghs S, Vandenbulcke M, Van Dongen J, Bäumer V, Dillen L, Mattheijssens M, Peeters K, Cruts M, Vandenberghe R, De Deyn PP, Van Broeckhoven C, Sleegers K (2013) C9orf72 G4C2 repeat expansions in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 34:1712.e1–1712.e7
Hensman Moss DJ, Poulter M, Beck J, Hehir J, Polke JM, Campbell T, Adamson G, Mudanohwo E, McColgan P, Haworth A, Wild EJ, Sweeney MG, Houlden H, Mead S, Tabrizi SJ (2014) C9orf72 expansions are the most common genetic cause of Huntington disease phenocopies. Neurology 82(4):292–299
Chen-Plotkin AS, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2010) TAR DNA-binding protein 43 in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol 6:211–220
Ravits J, Appel S, Baloh RH, Barohn R, Brooks BR, Elman L, Floeter MK, Henderson C, Lomen-Hoerth C, Macklis JD, McCluskey L, Mitsumoto H, Przedborski S, Rothstein J, Trojanowski JQ, van den Berg LH, Ringel S (2013) Deciphering amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: what phenotype, neuropathology and genetics are telling us about pathogenesis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener 14(Suppl 1):5–18
Ferrari R, Kapogiannis D, Huey ED, Momeni P (2011) FTLD and ALS: a tale of two diseases. Curr Alzheimer Res 8(3):273–294
Ling SC, Polymenidou M, Cleveland DW (2013) Converging mechanisms in ALS and FTLD: disrupted RNA and protein homeostasis. Neuron 79(3):416–438. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.07.033
Johnson JO, Mandrioli J, Benatar M, Abramzon Y, Van Deerlin VM, Trojanowski JQ, Gibbs JR, Brunetti M, Gronka S, Wuu J, Ding J, McCluskey L, Martinez-Lage M, Falcone D, Hernandez DG, Arepalli S, Chong S, Schymick JC, Rothstein J, Landi F, Wang YD, Calvo A, Mora G, Sabatelli M, Monsurrò MR, Battistini S, Salvi F, Spataro R, Sola P, Borghero G, Galassi G, Scholz SW, Taylor JP, Restagno G, Chiò A, Traynor BJ, ITALSGEN Consortium (2010) Exome sequencing reveals VCP mutations as a cause of familial ALS. Neuron 68:857–864
Al-Chalabi A, Jones A, Troakes C, King A, Al-Sarraj S, van den Berg LH (2012) The genetics and neuropathology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 124:339–352
Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Micsenyi MC, Chou TT, Bruce J, Schuck T, Grossman M, Clark CM, McCluskey LF, Miller BL, Masliah E, Mackenzie IR, Feldman H, Feiden W, Kretzschmar HA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314:130–133
Morris HR, Waite AJ, Williams NM, Neal JW, Blake DJ (2012) Recent advances in the genetics of the ALS-FTLD complex. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 12(3):243–250
Nlend Nlend R, Meyer K, Schümperli D (2010) Repair of pre-mRNA splicing: prospects for a therapy for spinal muscular atrophy. RNA Biol 7(4):430–440
Porensky PN, Burghes AH (2013) Antisense oligonucleotides for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy. Hum Gene Ther 24(5):489–498
Winer L, Srinivasan D, Chun S, Lacomis D, Jaffa M, Fagan A, Holtzman DM, Wancewicz E, Bennett CF, Bowser R, Cudkowicz M, Miller TM (2013) SOD1 in cerebral spinal fluid as a pharmacodynamic marker for antisense oligonucleotide therapy. JAMA Neurol 70:201–207
Smith RA, Miller TM, Yamanaka K, Monia BP, Condon TP, Hung G, Lobsiger CS, Ward CM, McAlonis-Downes M, Wei H, Wancewicz EV, Bennett CF, Cleveland DW (2006) Antisense oligonucleotide therapy for neurodegenerative disease. J Clin Invest 116:2290–2296
Miller TM, Pestronk A, David W, Rothstein J, Simpson E, Appel SH, Andres PL, Mahoney K, Allred P, Alexander K, Ostrow LW, Schoenfeld D, Macklin EA, Norris DA, Manousakis G, Crisp M, Smith R, Bennett CF, Bishop KM, Cudkowicz ME (2013) An antisense oligonucleotide against SOD1 delivered intrathecally for patients with SOD1 familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a phase 1, randomised, first-in-man study. Lancet Neurol 12(5):435–442. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70061-9. Epub 2013 Mar 29
Donnelly CJ, Zhang PW, Pham JT, Heusler AR, Mistry NA, Vidensky S, Daley EL, Poth EM, Hoover B, Fines DM, Maragakis N, Tienari PJ, Petrucelli L, Traynor BJ, Wang J, Rigo F, Bennett CF, Blackshaw S, Sattler R, Rothstein JD (2013) RNA Toxicity from the ALS/FTLD C9ORF72 expansion is mitigated by antisense intervention. Neuron 80(2):415–428
Lagier-Tourenne C, Baughn M, Rigo F, Sun S, Liu P, Li HR, Jiang J, Watt AT, Chun S, Katz M, Qiu J, Sun Y, Ling SC, Zhu Q, Polymenidou M, Drenner K, Artates JW, McAlonis-Downes M, Markmiller S, Hutt KR, Pizzo DP, Cady J, Harms MB, Baloh RH, Vandenberg SR, Yeo GW, Fu XD, Bennett CF, Cleveland DW, Ravits J (2013) Targeted degradation of sense and antisense C9orf72 RNA foci as therapy for ALS and frontotemporal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(47):E4530–E4539
Sareen D, O’Rourke JG, Meera P, Muhammad AK, Grant S, Simpkinson M, Bell S, Carmona S, Ornelas L, Sahabian A, Gendron T, Petrucelli L, Baughn M, Ravits J, Harms MB, Rigo F, Bennett CF, Otis TS, Svendsen CN, Baloh RH (2013) Targeting RNA foci in iPSC-derived motor neurons from ALS patients with a C9ORF72 repeat expansion. Sci Transl Med 5(208):208ra–149
Majounie E, Renton AE, Mok K, Dopper EG, Waite A, Rollinson S, Chiò A, Restagno G, Nicolaou N, Simon-Sanchez J, van Swieten JC, Abramzon Y, Johnson JO, Sendtner M, Pamphlett R, Orrell RW, Mead S, Sidle KC, Houlden H, Rohrer JD, Morrison KE, Pall H, Talbot K, Ansorge O, Hernandez DG, Arepalli S, Sabatelli M, Mora G, Corbo M, Giannini F, Calvo A, Englund E, Borghero G, Floris GL, Remes AM, Laaksovirta H, McCluskey L, Trojanowski JQ, Van Deerlin VM, Schellenberg GD, Nalls MA, Drory VE, Lu CS, Yeh TH, Ishiura H, Chromosome 9-ALS/FTLD Consortium, French research network on FTLD/FTLD/ALS, ITALSGEN Consortium (2012) Frequency of the C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeat expansion in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Neurol 11(4):323–330
Brouwer JR, Willemsen R, Oostra BA (2009) Microsatellite repeat instability and neurological disease. Bioessays 31:71–83
Pearson CE, Nichol Edamura K, Cleary JD (2005) Repeat instability: mechanisms of dynamic mutations. Nat Rev Genet 6:729–742
Todd PK, Paulson HL (2010) RNA-mediated neurodegeneration in repeat expansion disorders. Ann Neurol 67:291–300
Wojciechowska M, Krzyzosiak WJ (2011) Cellular toxicity of expanded RNA repeats: focus on RNA foci. Hum Mol Genet 20(19):3811–3821
Mori K, Weng SM, Arzberger T, May S, Rentzsch K, Kremmer E, Schmid B, Kretzschmar HA, Cruts M, Van Broeckhoven C, Haass C, Edbauer D (2013) The C9orf72 GGGGCC repeat is translated into aggregating dipeptide-repeat proteins in FTLD/ALS. Science 339:1335–1338
Ash PE, Bieniek KF, Gendron TF, Caulfield T, Lin WL, Dejesus-Hernandez M, van Blitterswijk MM, Jansen-West K, Paul JW III, Rademakers R, Boylan KB, Dickson DW, Petrucelli L (2013) Unconventional translation of C9ORF72 GGGGCC expansion generates insoluble polypeptides specific to c9FTD/ALS. Neuron 77:639–646
Ciura S, Lattante S, Le Ber I, Latouche M, Tostivint H, Brice A, Kabashi E (2013) Loss of function of C9orf72 causes motor deficits in a zebrafish model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol. doi:10.1002/ana.23946
Xi Z, Zinman L, Moreno D, Schymick J, Liang Y, Sato C, Zheng Y, Ghani M, Dib S, Keith J, Robertson J, Rogaeva E (2013) Hypermethylation of the CpG island near the G4C2 repeat in ALS with a C9orf72 expansion. Am J Hum Genet 92:981–989
Fratta P, Poulter M, Lashley T, Rohrer JD, Polke JM, Beck J, Ryan N, Hensman D, Mizielinska S, Waite AJ, Lai MC, Gendron TF, Petrucelli L, Fisher EM, Revesz T, Warren JD, Collinge J, Isaacs AM, Mead S (2013) Homozygosity for the C9orf72 GGGGCC repeat expansion in frontotemporal dementia. Acta Neuropathol 126:401–409
Harms M, Benitez BA, Cairns N, Cooper B, Cooper P, Mayo K, Carrell D, Faber K, Williamson J, Bird T, Diaz-Arrastia R, Foroud TM, Boeve BF, Graff-Radford NR, Mayeux R, Chakraverty S, Goate AM, Cruchaga C, NIA-LOAD/NCRAD Family Study Consortium (2013) C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeat expansions in clinical Alzheimer disease. JAMA Neurol 70:736–741
Zu T, Liu Y, Bañez-Coronel M, Reid T, Pletnikova O, Lewis J, Miller TM, Harms MB, Falchook AE, Subramony SH, Ostrow LW, Rothstein JD, Troncoso JC, Ranum LP (2013) RAN proteins and RNA foci from antisense transcripts in C9ORF72 ALS and frontotemporal dementia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA Nov 18. [Epub ahead of print]
Kim HJ, Kim NC, Wang YD, Scarborough EA, Moore J, Diaz Z, MacLea KS, Freibaum B, Li S, Molliex A, Kanagaraj AP, Carter R, Boylan KB, Wojtas AM, Rademakers R, Pinkus JL, Greenberg SA, Trojanowski JQ, Traynor BJ, Smith BN, Topp S, Gkazi AS, Miller J, Shaw CE, Kottlors M, Kirschner J, Pestronk A, Li YR, Ford AF, Gitler AD, Benatar M, King OD, Kimonis VE, Ross ED, Weihl CC, Shorter J, Taylor JP (2013) Mutations in prion-like domains in hnRNPA2B1 and hnRNPA1 cause multisystem proteinopathy and ALS. Nature 495:467–e473
Calini D, Corrado L, Del Bo R, Gagliardi S, Pensato V, Verde F, Corti S, Mazzini L, Milani P, Castellotti B, Bertolin C, Sorarù G, Cereda C, Comi GP, D’Alfonso S, Gellera C, Ticozzi N, Landers JE, Ratti A, Silani V, The SLAGEN Consortium (2013) Analysis of hnRNPA1, A2/B1, and A3 genes in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiology of Aging 2695.e11e2695.e12
Kwak S, Nishimoto Y, Yamashita T (2008) Newly identified ADAR-mediated A-to-I editing positions as a tool for ALS research. RNA Biol 5(4):193–197
Nishimoto Y, Yamashita T, Hideyama T, Tsuji S, Suzuki N, Kwak S (2008) Determination of editors at the novel A-to-I editing positions. Neurosci Res 61:201–206
Hideyama T, Yamashita T, Aizawa H, Tsuji S, Kakita A, Takahashi H, Kwak S (2012) Profound downregulation of the RNA editing enzyme ADAR2 in ALS spinal motor neurons. Neurobiol Dis 45(3):1121–1128
Kuner R, Groom AJ, Bresink I, Kornau HC, Stefovska V, Müller G, Hartmann B, Tschauner K, Waibel S, Ludolph AC, Ikonomidou C, Seeburg PH, Turski L (2005) Late-onset motoneuron disease caused by a functionally modified AMPA receptor subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:5826–5831
Kawahara Y, Ito K, Sun H, Aizawa H, Kanazawa I, Kwak S (2004) Glutamate receptors: RNA editing and death of motor neurons. Nature 427:801
Almeida S, Gascon E, Tran H, Chou HJ, Gendron TF, Degroot S, Tapper AR, Sellier C, Charlet-Berguerand N, Karydas A, Seeley WW, Boxer AL, Petrucelli L, Miller BL, Gao FB (2013) Modeling key pathological features of frontotemporal dementia with C9ORF72 repeat expansion in iPSC-derived human neurons. Acta Neuropathol 126(3):385–399
Echeverria GV, Cooper TA (2012) RNA-binding proteins in microsatellite expansion disorders: mediators of RNA toxicity. Brain Res 1462:100–111
Dias N, Stein CA (2002) Antisense oligonucleotides: basic concepts and mechanisms. Mol Cancer Ther 1:347–355
Bennett CF, Swayze EE (2010) RNA targeting therapeutics: molecular mechanisms of antisense oligonucleotides as a therapeutic platform. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 50:259–293
Kole R, Krainer AR, Altman S (2012) RNA therapeutics: beyond RNA interference and antisense oligonucleotides. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11(2):125–140
Aoki Y, Yokota T, Wood MJ (2013) Development of multiexon skipping antisense oligonucleotide therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Biomed Res Int 2013:402369
Lu QL, Mann CJ, Lou F, Bou-Gharios G, Morris GE, Xue SA, Fletcher S, Partridge TA, Wilton SD (2003) Functional amounts of dystrophin produced by skipping the mutated exon in the mdx dystrophic mouse. Nat Med 9:1009–1014
Lu QL, Rabinowitz A, Chen YC, Yokota T, Yin H, Alter J, Jadoon A, Bou-Gharios G, Partridge T (2005) Systemic delivery of antisense oligoribonucleotide restores dystrophin expression in body-wide skeletal muscles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:198–203
Heemskerk H, de Winter C, van Kuik P, Heuvelmans N, Sabatelli P, Rimessi P, Braghetta P, van Ommen GJ, de Kimpe S, Ferlini A (2010) Preclinical PK and PD studies on 2′-O-methyl-phosphorothioate RNA antisense oligonucleotides in the mdx mouse model. Mol Ther 18:1210–1217
Douglas AG, Wood MJ (2013) Splicing therapy for neuromuscular disease. Mol Cell Neurosci 56:169–185
Evers MM, Tran HD, Zalachoras I, Pepers BA, Meijer OC, den Dunnen JT, van Ommen GJ, Aartsma-Rus A, van Roon-Mom WM (2013) Ataxin-3 protein modification as a treatment strategy for spinocerebellar ataxia type 3: removal of the CAG containing exon. Neurobiol Dis 58:49–56
Gao Z, Cooper TA (2013) Antisense oligonucleotides: rising stars in eliminating RNA toxicity in myotonic dystrophy. Hum Gene Ther 24(5):499–507
Mulders SA, van den Broek WJ, Wheeler TM, Croes HJ, van Kuik-Romeijn P, de Kimpe SJ, Furling D, Platenburg GJ, Gourdon G, Thornton CA, Wieringa B, Wansink DG (2009) Triplet-repeat oligonucleotide-mediated reversal of RNA toxicity in myotonic dystrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(33):13915–13920
González-Barriga A, Mulders SA, van de Giessen J, Hooijer JD, Bijl S, van Kessel ID, van Beers J, van Deutekom JC, Fransen JA, Wieringa B, Wansink DG (2013) Design and analysis of effects of triplet repeat oligonucleotides in cell models for myotonic dystrophy. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2:e81
Ostergaard ME, Southwell AL, Kordasiewicz H, Watt AT, Skotte NH, Doty CN, Vaid K, Villanueva EB, Swayze EE, Frank Bennett C, Hayden MR, Seth PP (2013) Rational design of antisense oligonucleotides targeting single nucleotide polymorphisms for potent and allele selective suppression of mutant Huntingtin in the CNS. Nucleic Acids Res 41(21):9634–9650
Anthony K, Feng L, Arechavala-Gomeza V, Guglieri M, Straub V, Bushby K, Cirak S, Morgan J, Muntoni F (2012) Exon skipping quantification by quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction in Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients treated with the antisense oligomer eteplirsen. Hum Gene Ther Methods 23(5):336–345
Goemans NM, Tulinius M, van den Akker JT, Burm BE, Ekhart PF, Heuvelmans N, Holling T, Janson AA, Platenburg GJ, Sipkens JA, Sitsen JM, Aartsma-Rus A, van Ommen GJ, Buyse G, Darin N, Verschuuren JJ, Campion GV, de Kimpe SJ, van Deutekom JC (2011) Systemic administration of PRO051 in Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy. N Engl J Med 364(16):1513–1522
Tanganyika-de Winter CL, Heemskerk H, Karnaoukh TG, van Putten M, de Kimpe SJ, van Deutekom J, Aartsma-Rus A (2012) Long-term exon skipping studies with 2’-O-methyl phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotides in dystrophic mouse models. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 1:e44
Suzuki N, Maroof AM, Merkle FT, Koszka K, Intoh A, Armstrong I, Moccia R, Davis-Dusenbery BN, Eggan K (2013) The mouse C9ORF72 ortholog is enriched in neurons known to degenerate in ALS and FTLD. Nat Neurosci 16(12):1725–1727
Rigo F, Hua Y, Krainer AR, Bennett CF (2012) Antisense-based therapy for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy. J Cell Biol 199(1):21–25
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riboldi, G., Zanetta, C., Ranieri, M. et al. Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy for the Treatment of C9ORF72 ALS/FTD Diseases. Mol Neurobiol 50, 721–732 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8724-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8724-7