Abstract
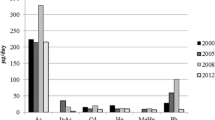
The main purpose of this study was to establish the temporal trend in the daily dietary intake of arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg), and lead (Pb) by the population of Catalonia, Spain. Concentrations of these elements were determined in samples of a number of food items widely consumed in that country. The dietary intake of As, Cd, Hg, and Pb was then estimated for various age–gender groups of population: children, adolescents, adults, and seniors. In the present study, the dietary intakes of As, inorganic As, Cd, Hg, methylmercury, and Pb were 328.37, 16.22, 19.47, 11.39, 10.25, and 101.47 μg/day, respectively, while in a previous (2006) survey, the dietary intakes of As, inorganic As, Cd, Hg, methylmercury, and Pb were 261.01, 33.17, 9.80, 12.61, 11.35, and 45.13 μg/day, respectively. The estimated intakes of Cd, Hg, and Pb are still notably lower than the respective PTWIs, while that of inorganic As is also lower than its BMDL01. In summary, the results of this study indicate that, currently, the dietary intakes of As, Cd, Hg, and Pb should not mean additional health risks for the consumers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferré-Huguet, Martí-Cid R, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2008) Risk assessment of metals from consuming vegetables, fruits and rice grown on soils irrigated with waters of the Ebro River in Catalonia, Spain. Biol Trace Elem Res 123:1–14
Ferré-Huguet N, Nadal M, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2009) Monitoring metals in blood and hair of the population living near a hazardous waste incinerator: temporal trend. Biol Trace Elem Res 128:191–199
Nadal M, Ferré-Huguet N, Martí-Cid R, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2008) Exposure to metals through the consumption of fish and seafood by the population living near the Ebro river in Catalonia, Spain: health risks. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 14:780–795
Bocio A, Nadal M, Domingo JL (2005) Human exposure to metals through the diet in Tarragona, Spain: temporal trend. Biol Trace Elem Res 104:193–201
Martí-Cid R, Llobet JM, Castell V, Domingo JL (2008) Dietary intake of arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead by the population of Catalonia, Spain. Biol Trace Elem Res 125:120–132
Martí-Cid R, Perelló G, Domingo JL (2009) Dietary exposure to metals by individuals living near a hazardous waste incinerator in Catalonia, Spain: temporal trend. Biol Trace Elem Res 131:245–254
Domingo JL (1994) Metal-induced developmental toxicity in mammals: a review. J Toxicol Environ Health 42:123–141
Sharma RK, Agrawal M (2005) Biological effects of heavy metals: an overview. J Environ Biol 6:301–313
Llobet JM, Falcó G, Casas C, Teixidó A, Domingo JL (2003) Concentrations of arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead in common foods and estimated daily intake by children, adolescents, adults, and seniors of Catalonia, Spain. J Agric Food Chem 51:838–842
Bocio A, Llobet JM, Domingo JL, Corbella J, Teixidó A, Casas C (2003) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in foodstuffs: human exposure through the diet. J Agric Food Chem 51:3191–3195
Bocio A, Llobet JM, Domingo JL (2004) Human exposure to polychlorinated diphenyl ethers through the diet in Catalonia, Spain. J Agric Food Chem 52:1769–1772
Domingo JL, Falcó G, Llobet JM, Casas C, Teixidó A, Müller L (2003) Polychlorinated naphthalenes in foods: estimated dietary intake by the population of Catalonia, Spain. Environ Sci Technol 37:2332–2335
Falcó G, Domingo JL, Llobet JM, Teixidó A, Casas C, Müller L (2003) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in foods: human exposure through the diet in Catalonia, Spain. J Food Prot 66:2325–2331
Falcó G, Bocio A, Llobet JM, Domingo JL, Casas C, Teixidó A (2004) Dietary intake of hexachlorobenzene in Catalonia, Spain. Sci Total Environ 322:63–70
Llobet JM, Bocio A, Domingo JL, Teixidó A, Casas C, Müller L (2003) Levels of polychlorinated biphenyls in foods from Catalonia, Spain: estimated dietary intake. J Food Prot 66:479–484
Llobet JM, Domingo JL, Bocio A, Casas C, Teixidó A, Müller L (2003) Human exposure to dioxins through the diet in Catalonia, Spain: carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risk. Chemosphere 50:1193–1200
Serra-Majem L, Ribas L, Salvador G, Castells C, Serra J, Jover L, Treserras R, Farran A, Román B, Raidó B, Taberner JL, Salleras L, Ngo J (2003) Avaluació de l’estat nutricional de la població catalana 2002–2003. Evolució dels hàbits alimentaris i del consum d’aliments i nutrients a Catalunya (1992–2003). Direcció General de Salut Pública. Departament de Sanitat i Seguretat Social. Generalitat de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain (in Catalan)
FAO/WHO (1993) Evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants, technical report series 837. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
EFSA (2009) Scientific Opinion on Arsenic in Food (Question No EFSA-Q-2008-425). Adopted on October 2009
Jalón M, Urieta I, Macho M, Azpiri M (1997) Metales Pesados y Arsénico. In Vigilancia de la Contaminación Química de los Alimentos en la Comunidad Autónoma del País Vasco 1990–1995, Servicio Central de Publicaciones del Gobierno Vasco: Vitoria, Spain, pp 29–43 (in Spanish)
Tsuda T, Inoue T, Kojima M, Aoki S (1995) Market basket and duplicate portion estimation of dietary intakes of cadmium, mercury, arsenic, copper, manganese, and zinc by Japanese adults. J Assoc Off Anal Chem Int 78:1363–1368
Llobet JM, Granero S, Schuhmacher M, Corbella J, Domingo JL (1998) Biological monitoring of environmental pollution and human exposure to metals in Tarragona. Spain. IV. Estimation of the dietary intake. Trace Elem Electrol 15:136–141
Rubio C, Hardisson A, Reguera JI, Revert C, Lafuente MA, González-Iglesias T (2006) Cadmium dietary intake in the Canary Islands, Spain. Environ Res 100:123–129
Ysart G, Miller P, Croasdale M, Crews H, Robb P, Baxter M, de L'Argy C, Harrison N (2000) 1997 UK total diet study-dietary exposures to aluminum, arsenic, cadmium, chromium, copper, lead, mercury, nickel, selenium, tin and zinc. Food Addit Contam 17:775–786
Urieta I, Jalón M, Equileror I (1996) Food surveillance in the Basque Country (Spain). II. Estimation of the dietary intake of organochlorine pesticides, heavy metals, arsenic, aflatoxin M1, iron and zinc through the Total Diet Study, 1990/91. Food Addit Contam 13:29–52
Leblanc JC, Malmauret L, Guerin T, Bordet F, Boursier B, Verger P (2000) Estimation of the dietary intake of pesticide residues, lead, cadmium, arsenic and radionuclides in France. Food Addit Contam 17:925–932
Larsen EH, Andersen NL, Moller A, Petersen A, Mortensen GK, Petersen J (2002) Monitoring the content and intake of trace elements from food in Denmark. Food Addit Contam 19:33–46
Wilhelm M, Wittsiepe J, Schrey P, Budde U, Idel H (2002) Dietary intake of cadmium by children and adults from Germany using duplicate portion sampling. Sci Total Environ 285:11–19
Zheng N, Wang Q, Zhang X, Zheng D, Zhang Z, Zhang S (2007) Population health risk due to dietary intake of heavy metals in the industrial area of Huludao city, China. Sci Total Environ 387:96–104
EFSA (2004) Opinion of the Scientific Panel on contaminants in the food chain [CONTAM] related to mercury and methylmercury in food (Question No EFSA-Q-2003-030). Adopted on February 2004
Kwon YM, Lee HS, Yoo DC, Kim CH, Kim GS, Kim JA, Lee YN, Kim YS, Kang KM, No KM, Paek OJ, Seo JH, Choi H, Park SK, Choi DM, Kim DS, Choi DW (2009) Dietary exposure and risk assessment of mercury from the Korean total diet study. J Toxicol Environ Health A 72:1484–1492
Schuhmacher M, Bosque MA, Domingo JL, Corbella J (1991) Dietary intake of lead and cadmium from foods in Tarragona Province, Spain. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 46:320–328
Perelló G, Martí-Cid R, Llobet JM, Domingo JL (2008) Effects of various cooking processes on the concentrations of arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead in foods. J Agric Food Chem 56:11262–11269
Acknowledgment
Financial support for this study was provided by the Catalan Food Safety Agency, Department of Health, Generalitat de Catalunya, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martorell, I., Perelló, G., Martí-Cid, R. et al. Human Exposure to Arsenic, Cadmium, Mercury, and Lead from Foods in Catalonia, Spain: Temporal Trend. Biol Trace Elem Res 142, 309–322 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8787-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8787-x