Abstract
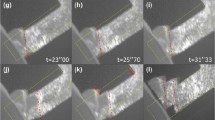
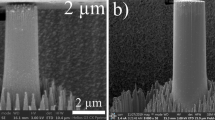
In this article, our most recent progress on applying a unique quantitative transmission electron microscope deformation technique on micronanoscaled metal pillars will be reviewed. We found that single-crystal pillars fabricated through focused ion beam always contain high density of defects. However, if the sample size is small enough, then both face-centered-cubic metals and body-centered-cubic metal pillars can experience “mechanical annealing,” i.e., a phenomena referring to the reduction of dislocation density in the deforming volume, when dislocation generation is outweighed by dislocation annihilation through the free surface. We also found that when the sample size was reduced below 1 μm or so, stress saturation and deformation mechanism transition occurred in a hexagonal-close-packed Ti alloy. Unlike crystalline materials, metallic glasses do not allow the presence and movement of dislocations or deformation twinning. However, we demonstrated the metallic glasses also follow the well-established tenet for crystalline materials: i.e., smaller is stronger and can reach its theoretical elastic limit under appropriate testing conditions. In addition, for the tested size regime, we found that high-energy electron beam has no obvious effect on the mechanical properties of materials with metallic bond. However, for materials with covalent bond and ionic bond, significant electron beam effects have been confirmed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.D. Uchic, D.M. Dimiduk, J.N. Florando, and W.D. Nix, Science 305, 986 (2004).
M.D. Uchic, P.A. Shade, and D.M. Dimiduk, Annual Review of Materials Research, vol. 39 (Palo Alto, CA: Annual Reviews, 2009), pp. 361–386.
S.H. Oh, M. Legros, D. Kiener, and G. Dehm, Nat. Mater. 8, 95 (2009).
Z.W. Shan, R.K. Mishra, S.A.S. Asif, O.L. Warren, and A.M. Minor, Nat. Mater. 7, 115 (2008).
J.R. Greer, W.C. Oliver, and W.D. Nix, Acta Mater. 53, 1821 (2005).
W.D. Nix, J.R. Greer, G. Feng, and E.T. Lilleodden, Thin Solid Films 515, 3152 (2007).
L. Huang, Q.J. Li, Z.W. Shan, J. Li, J. Sun, and E. Ma, Nat. Commun. 2, 579 (2011).
C. Chisholm, H. Bei, M.B. Lowry, J. Oh, S.A.A. Asif, O.L. Warren, Z.W. Shan, E.P. George, and A.M. Minor, Acta Mater. 60, 2258 (2012).
Q. Yu, Z.W. Shan, J. Li, X.X. Huang, L. Xiao, J. Sun, and E. Ma, Nature 463, 335 (2010).
L. Tian, Y.Q. Cheng, Z.W. Shan, J. Li, C.C. Wang, X.D. Han, J. Sun, and E. Ma, Nat. Commun. 3, 609 (2012).
Z.W. Shan, J. Li, Y.Q. Cheng, A.M. Minor, S.A.S. Asif, O.L. Warren, and E. Ma, Phys. Rev. B 77, 155419 (2008).
K. Zheng, C.C. Wang, Y.Q. Cheng, Y.H. Yue, X.D. Han, Z. Zhang, Z.W. Shan, S.X. Mao, M.M. Ye, Y.D. Yin, and E. Ma, Nat. Commun. 1, 144 (2010).
O. Kraft, P.A. Gruber, R. Moenig, and D. Weygand, Annual Review of Materials Research, vol. 40, ed. D.R.R.M.Z.F. Clarke (Palo Alto, CA: Annual Reviews, 2010), pp. 293–317.
D.S. Gianola and C. Eberl, JOM 61, 24 (2009).
S.S. Brenner, J. Appl. Phys. 27, 1484 (1956).
S.S. Brenner, J. Appl. Phys. 28, 1023 (1957).
S.S. Brenner, Science 128, 568 (1958).
A.M. Minor, S.A.S. Asif, Z.W. Shan, E.A. Stach, E. Cyrankowski, T.J. Wyrobek, and O.L. Warren, Nat. Mater. 5, 697 (2006).
J. Weertman and J.R. Weertman, Elementary Dislocation Theory (New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 1992), pp. 11, 213.
Z.J. Wang, Q.J. Li, Z.W. Shan, J. Li, J. Sun, and E. Ma, Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 122405 (2012).
D. Kiener and A.M. Minor, Acta Mater. 59, 1328 (2011).
C.R. Weinberger and W. Cai, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 14304 (2008).
J.R. Greer, C.R. Weinberger, and W. Cai, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 493, 21 (2008).
J.Y. Kim and J.R. Greer, Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 10916 (2008).
S. Brinckmann, J.Y. Kim, and J.R. Greer, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 155502 (2008).
J.R. Greer, C.R. Weinberger, and W. Cai, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 493, 21 (2008).
M.A. Meyers, O. Vohringer, and V.A. Lubarda, Acta Mater. 49, 4025 (2001).
J.A. Knapp and D.M. Follstaedt, J. Mater. Res. 19, 218 (2004).
M.D. Uchic, P.A. Shade, and D.M. Dimiduk, JOM 61 (3), 36 (2009).
O. Kraft, Nat. Mater. 9, 295 (2010).
Y.Q. Cheng and E. Ma, Acta Mater. 59, 1800 (2011).
C.C. Wang, J. Ding, Y.Q. Cheng, J.C. Wan, L. Tian, J. Sun, Z.W. Shan, J. Li, and E. Ma, Acta Mater. 60, 5370 (2012).
D.C. Jang and J.R. Greer, Nat. Mater. 9, 215 (2010).
Z.J. Wang, Z.W. Shan, J. Li, J. Sun, and E. Ma, Acta Mater. 60, 1368 (2012).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Grants from NSFC (50925104 and 11132006) and 973 Programs of China (2010CB631003). We also appreciate the support from the 111 Project of China (B06025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, Z. In Situ TEM Investigation of the Mechanical Behavior of Micronanoscaled Metal Pillars. JOM 64, 1229–1234 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-012-0436-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-012-0436-8