Abstract
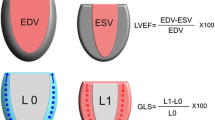
In a group of septic patients, we assess the short-term prognostic value of LV systolic performance, evaluated through conventional left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and left ventricular global longitudinal strain (LV GLS). One hundred forty-seven patients with sepsis were recruited; LVEF by planimetry and peak GLS by 2D speckle tracking could be assessed within 24 h. The study population was stratified according to SOFA tertiles assessed at the time of the echocardiogram (G1: SOFA score <5; G2: SOFA score 5–7; G3: SOFA score >7). Day-7 follow-up data were used as reference. Patients in G2 and G3 show a significant hemodynamic derangement, paralleling the more pronounced organ damage by definition; nevertheless, LVEF and GLS are comparable among the three groups (both p > 0.1). All-cause mortality at day-7 follow-up is slightly lower in G1 (9%) versus G2 and G3 (14 and 26%, respectively, p = NS). Analyses through ROC curves focusing on day-7 mortality show that the SOFA score fairly correlates with events (AUC 0.635, p = 0.037), while low LVEF (AUC 0.35, p = 0.022) and less negative GLS (AUC 0.73, p = 0.001) do so. In multivariate analyses, mortality by day-7 follow-up is more likely per higher GLS (i.e., indicative of worst systolic dysfunction, HR 1.22/%, p = 0.005) and per increasing SOFA score (HR 1.22/unit, p = 0.010), whereas LVEF, adjusted for age and SOFA score, does not enter the prognostic model. In the very short term in patients with severe sepsis, LV systolic function assessment by means of GLS predicts the short-term prognosis, independent of SOFA.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR (2001) Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med 29:1303–1310
Martin GS (2012) Sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock: changes in incidence, pathogens and outcomes. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 10:701–706
Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M (2003) The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med 348:1546–1554
Kumar A, Roberts D, Wood KE, Light B, Parrillo JE, Sharma S, Suppes R, Feinstein D, Zanotti S, Taiberg L, Gurka D, Kumar A, Cheang M (2006) Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit Care Med 34:1589–1596
Funk D, Sebat F, Kumar A (2009) A systems approach to the early recognition and rapid administration of best practice therapy in sepsis and septic shock. Curr Opin Crit Care 15:301–307
Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, De MA, Bruining H, Reinhart CK, Suter PM, Thijs LG (1996) The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. on behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med 22:707–710
Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE (1985) APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med 13:818–829
Livingston BM, MacKirdy FN, Howie JC, Jones R, Norrie JD (2000) Assessment of the performance of five intensive care scoring models within a large Scottish database. Crit Care Med 28:1820–1827
Jones AE, Trzeciak S, Kline JA (2009) The Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score for predicting outcome in patients with severe sepsis and evidence of hypoperfusion at the time of emergency department presentation. Crit Care Med 37:1649–1654
Parker MM, Shelhamer JH, Bacharach SL, Green MV, Natanson C, Frederick TM, Damske BA, Parrillo JE (1984) Profound but reversible myocardial depression in patients with septic shock. Ann Intern Med 100:483–490
Bouhemad B, Nicolas-Robin A, Arbelot C, Arthaud M, Feger F, Rouby JJ (2009) Acute left ventricular dilatation and shock-induced myocardial dysfunction. Crit Care Med 37:441–447
Vieillard-Baron A, Caille V, Charron C, Belliard G, Page B, Jardin F (2008) Actual incidence of global left ventricular hypokinesia in adult septic shock. Crit Care Med 36:1701–1706
Pulido JN, Afessa B, Masaki M, Yuasa T, Gillespie S, Herasevich V, Brown DR, Oh JK (2012) Clinical spectrum, frequency, and significance of myocardial dysfunction in severe sepsis and septic shock. Mayo Clin Proc 87:620–628
Russo C, Jin Z, Homma S, Rundek T, Elkind MS, Sacco RL, Di Tullio MR (2013) Relationship of multidirectional myocardial strain with radial thickening and ejection fraction and impact of left ventricular hypertrophy: a study in a community-based cohort. Echocardiography 30:794–802
Burns AT, La GA, D’hooge J, MacIsaac AI, Prior DL (2010) Left ventricular strain and strain rate: characterization of the effect of load in human subjects. Eur J Echocardiogr 11:283–289
Palmieri V, Innocenti F, Guzzo A, Guerrini E, Vignaroli D, Pini R (2015) Left ventricular systolic longitudinal function as predictor of outcome in patients with sepsis. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 8:e003865
Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Goldstein SA, Kuznetsova T, Lancellotti P, Muraru D, Picard MH, Rietzschel ER, Rudski L, Spencer KT, Tsang W, Voigt JU (2015) Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 16:233–270
Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Pellikka PA, Picard MH, Roman MJ, Seward J, Shanewise JS, Solomon SD, Spencer KT, Sutton MS, Stewart WJ (2005) Recommendations for chamber quantification: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography’s guidelines and standards committee and the chamber quantification writing group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 18:1440–1463
Voigt JU, Pedrizzetti G, Lysyansky P, Marwick TH, Houle H, Baumann R, Pedri S, Ito Y, Abe Y, Metz S, Song JH, Hamilton J, Sengupta PP, Kolias TJ, D’hooge J, Aurigemma GP, Thomas JD, Badano LP (2015) Definitions for a common standard for 2D speckle tracking echocardiography: consensus document of the EACVI/ASE/Industry Task Force to standardize deformation imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 28:183–193
Hochstadt A, Meroz Y, Landesberg G (2011) Myocardial dysfunction in severe sepsis and septic shock: more questions than answers? J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 25:526–535
Jardin F, Fourme T, Page B, Loubieres Y, Vieillard-Baron A, Beauchet A, Bourdarias JP (1999) Persistent preload defect in severe sepsis despite fluid loading: a longitudinal echocardiographic study in patients with septic shock. Chest 116:1354–1359
Hestenes SM, Halvorsen PS, Skulstad H, Remme EW, Espinoza A, Hyler S, Bugge JF, Fosse E, Nielsen EW, Edvardsen T (2014) Advantages of strain echocardiography in assessment of myocardial function in severe sepsis: an experimental study. Crit Care Med 42:e432–e440
De GL, Engvall J, Oscarsson A (2015) Strain echocardiography in septic shock—a comparison with systolic and diastolic function parameters, cardiac biomarkers and outcome. Crit Care 19:122
Basu S, Frank LH, Fenton KE, Sable CA, Levy RJ, Berger JT (2012) Two-dimensional speckle tracking imaging detects impaired myocardial performance in children with septic shock, not recognized by conventional echocardiography. Pediatr Crit Care Med 13:259–264
Dalla K, Hallman C, Bech-Hanssen O, Haney M, Ricksten SE (2015) Strain echocardiography identifies impaired longitudinal systolic function in patients with septic shock and preserved ejection fraction. Cardiovasc Ultrasound 13:30
Orde SR, Pulido JN, Masaki M, Gillespie S, Spoon JN, Kane GC, Oh JK (2014) Outcome prediction in sepsis: speckle tracking echocardiography based assessment of myocardial function. Crit Care 18:R149
Ferreira FL, Bota DP, Bross A, Melot C, Vincent JL (2001) Serial evaluation of the SOFA score to predict outcome in critically ill patients. JAMA 286:1754–1758
Innocenti F, Bianchi S, Guerrini E, Vicidomini S, Conti A, Zanobetti M, Pini R (2014) Prognostic scores for early stratification of septic patients admitted to an emergency department-high dependency unit. Eur J Emerg Med 21:254–259
Yu S, Leung S, Heo M, Soto GJ, Shah RT, Gunda S, Gong MN (2014) Comparison of risk prediction scoring systems for ward patients: a retrospective nested case–control study. Crit Care 18:R132
Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J, Muzzin A, Knoblich B, Peterson E, Tomlanovich M (2001) Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med 345:1368–1377
Dellinger RP (2015) The surviving sepsis campaign: where have we been and where are we going? Cleve Clin J Med 82:237–244
Shahul S, Gulati G, Hacker MR, Mahmood F, Canelli R, Nizamuddin J, Mahmood B, Mueller A, Simon BA, Novack V, Talmor D (2015) Detection of myocardial dysfunction in septic shock: a speckle-tracking echocardiography study. Anesth Analg 121:1547–1554
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of human and animal rights
The study protocol was approved by the Toscana–Area vasta–Centro inter-institutional ethics committee (Registration Number OSS.13.031).
Informed consent
All patients signed an informed consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Innocenti, F., Palmieri, V., Guzzo, A. et al. SOFA score and left ventricular systolic function as predictors of short-term outcome in patients with sepsis. Intern Emerg Med 13, 51–58 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-016-1579-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-016-1579-3