Summary
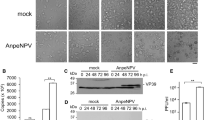
Recently investigators showed that polydnavirus DNA from the parasitic wasp Glyptapanteles indiensis could transform gypsy moth L. dispar cell lines in vitro (McKelvey et al., 1996). Here we show GiPDV DNA is capable of transforming in vitro to varying degrees lepidopteran (IPLB-TN-R2, IPLB-SF-21, IAL-PID2, IPLB-HvT1) and coleopteran (IPLB-DU182E) insect cell lines derived from various somatic tissue types. An insect cell line derived from dipteran Aedes albopictus (C7/10) could not be transformed with G. indiensis polydnavirus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht, U.; Wyler, T.; Pfister-Wilhelm, R.; Gruber, A.; Stettler, P.; Heiniger, P.; Kurt, E.; Schumperli, D.; Lanzrein, B. Polydnavirus of the parasitic wasp Chelonus inanitus (Braconidae): characterization, genome organization and time point of replication. J. Gen. Virol. 75:3353–3363; 1994.
Ashburner, M. Medfly transformed-official! Science 270:1941–1942; 1995.
Ausubel, F. M.; Brent, R.; Kingston, R. E.; Moore, D. D.; Seidman, J. G.; Smith, J. H.; Struhl, K. Current protocols in molecular biology. Vol. 1, Chapter 2. New York: John Wiley and Sons; 1994.
Fleming, J. A. G.; Summers, M. D. Polydnavirus DNA is integrated in the DNA of its parasitoid wasp host. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:9770–9774; 1991.
Giraud, C.; Devauchelle, G.; Bergoin, M. The densovirus of Junonia coenia (JcDNV) as an insect expression vector. Virology 186:207–218; 1992.
Gruber, A.; Stettler, P.; Heiniger, P.; Schumperli, D.; Lanzrein, B. Polydnavirus DNA of the braconid wasp Chelonis inanitus is integrated in the wasp’s genome and excised only in later pupal and adult stages of the female. J. Gen. Virol. 77:2873–2879; 1996.
Handler, A. M.; O’Brochta, D. A. Prospects for gene transformation in insects. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 36:159–183; 1991.
King, L. A.; Possee, R. D. The baculovirus expression system. London, United Kingdom: Chapman & Hall; 1992.
Lavine, M. D.; Beckage, N. E. Polydnaviruses: potent mediators of host insect immune dysfunction. Parasitol. Today 11:368–378; 1995.
Lynn, D. E.; Dougherty, E. M.; McClintock, J. T.; Loeb, M. Development of cell lines from various tissues of lepidoptera. In: Kuroda, Y.; Kurstak, E.; Maramorosch, K., ed. Invertebrate and fish tissue culture. Tokyo: Japan Scientific Societies Press; 1988:239–242.
Lynn, D. E.; Hung, A. C. F. Development of continuous cell lines from the egg parasitoids Trichogramma confusum and T. exiguum. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 18:99–104; 1991.
Lynn, D. E.; Oberlander, H. The establishment of cell lines from imaginal wing discs of Spodoptera frugiperda and Plodia interpunctella. J. Insect Physiol. 29:591–596; 1983.
Lynn, D. E.; Stoppleworth, A. Established cell lines from the beetle, Diabrotica undecimpunctata (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). In Vitro 20:365–368; 1984.
McKelvey, T. A.; Lynn, D. E.; Gundersen-Rindal, D.; Guzo, D.; Stoltz, D. A.; Guthrie, K. P.; Taylor, P. B.; Dougherty, E. M. Transformation of gypsy moth (Lymantria dispar) cell lines by infection with Glyptapanteles indiensis polydnavirus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 225:764–770; 1996.
Sarver, N.; Stollar, V. Sindbis virus-induced cytopathic effect in clones of Aedes albopictus. Virology 80:390–400; 1977.
Southern, E. M. Gel electrophoresis of restriction fragments. J. Mol. Biol. 98:503–517; 1975.
Stoltz, D. B. The polydnavirus life cycle. In: Beckage, N. E.; Thompson, S. N.; Federici, B. A., ed. Parasites and pathogens of insects. Vol. 1. San Diego: Academic Press; 1993:167–187.
Stoltz, D. B.; Guzo, D.; Cook, D. Studies on polydnavirus transmission. Virology 155:120–131; 1986.
Rochford, R.; Dougherty, E. M.; Lynn, D. E. Establishment of a cell line from embryos of the cabbage looper, Trichoplusia ni (Hubner). In Vitro 20:823–825; 1984.
Vaughn, J. L.; Goodwin, R. H.; Tompkins, G. J.; McCawley, P. The establishment of two cell lines from the insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). In Vitro 13:213–217; 1977.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gundersen-Rindal, D., Lynn, D.E. & Dougherty, E.M. Transformation of lepidopteran and coleopteran insect cell lines by Glyptapanteles indiensis polydnavirus DNA. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 35, 111–114 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-999-0010-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-999-0010-z