Abstract
Purpose
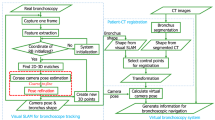
Flexible fiber-optic bronchoscopy is a widespread medical procedure for the diagnosis and treatment of lung diseases. Navigation systems are needed to track the flexible endoscope within the bronchial tree. Electromagnetic (EM) tracking is currently the only technology used clinically for this purpose. The registration between EM tracking and patient anatomy may become inaccurate due to breathing motion, so the addition of image-based tracking has been proposed as a hybrid EM-image-based system.
Methods
When EM tracking is used as an initialization for image registration, small changes in the initialization may lead to different local minima and noise is amplified by hybrid tracking. The tracking output is modeled as continuous and uses splines for interpolation, thus smoothness is greatly improved. The bronchoscope pose relative to computed tomography data is interpolated using Catmull–Rom splines for position and spherical linear interpolation (SLERP) for orientation.
Results
The hybrid method was evaluated using ground truth poses manually selected by experts, where mean inter-expert agreement was determined as 1.26 mm. Using four dynamic phantom data sets, the accuracy was 4.91 mm, which is equivalent to previous methods. Compared to state-of-art methods, inter-frame smoothness was improved from 2.77–3.72 to 1.24 mm.
Conclusions
Hybrid image and electromagnetic endoscope guidance provides a more realistic and physically plausible solution with significantly less jitter. This quantitative result is confirmed by visual comparison of real and virtual video, where the virtual video output is much more consistent and robust, with fewer occasions of tracking loss or unexpected movement compared with previous methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atasoy S, Noonan DP, Benhimane S, Navab N, Yang, GZ (2008) A global approach for automatic fibroscopic video mosaicing in minimally invasive diagnosis. In: Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (MICCAI), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5241. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 850–857
Azuma R, Bishop G (1994) Improving static and dynamic registration in an optical see-through hmd. In: Proceedings of the 21st annual conference on computer graphics and interactive techniques. ACM, pp 197–204
Baillot Y, Eliason JJ, Schmidt GS, Swan JEI, Brown D, Julier S, Livingston MA, Rosenblum L (2003) Evaluation of the ShapeTape tracker for wearable, mobile interaction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE, virtual reality, pp 285–286
Balter JM, Wright JN, Newell LJ, Friemel B, Dimmer S, Cheng Y, Wong J, Vertatschitsch E, Mate TP (2005) Accuracy of a wireless localization system for radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol *Biol*Phys 61(3):933–937. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.11.009. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360301604028391
Besl P, McKay H (1992) A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 14(2):239–256
Bricault I, Ferretti G, Cinquin P (1998) Registration of real and CT-derived virtual bronchoscopic images to assist transbronchial biopsy. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 17(5):703–714
Catmull E, Rom R (1974) A class of interpolating splines. Comput Aided Geom Des 317–326
Deguchi D, Ishitani K, Kitasaka T, Mori K, Suenaga Y, Takabatake H, Mori M, Natori H (2007) A method for bronchoscope tracking using position sensor without fiducial markers. In: Proceedings of SPIE medical imaging, vol 6511. SPIE, p 65110N
Deguchi D, Mori K, Feuerstein M, Kitasaka T, Maurer CR, Suenaga Y, Takabatake H, Mori M, Natori H (2009) Selective image similarity measure for bronchoscope tracking based on image registration. Med Image Anal 13(4):621–633
Deligianni F, Chung A, Yang GZ (2004) Patient-specific bronchoscope simulation with pq-space-based 2D/3D registration. Comput Aided Surg 9(5):215–226
Feuerstein M, Sugiura T, Deguchi D, Reichl T, Kitasaka T, Mori K (2010) Marker-free registration for electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy under respiratory motion. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on medical imaging and augmented reality (MIAR), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6326. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 237–246
Fitzpatrick JM, West JB (1998) Predicting error in rigid-body point-based registration. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 14(5):694–702
Gergel I, dos Santos TR, Tetzlaff R, Maier-Hein L, Meinzer HP, Wegner I (2010) Particle filtering for respiratory motion compensation during navigated bronchoscopy. In: Wong KH, Miga MI (eds) Proceedings of SPIE medical imaging 2010: visualization, image-guided procedures, and modeling, vol 7625. SPIE, p 76250W
Gergel I, Tetzlaff R, Meinzer HP, Wegner I (2011) Evaluation of electromagnetically tracked transbronchial needle aspiration in a ventilated porcine lung. In: Proceedings of SPIE medical imaging 2011: visualization, image-guided procedures, and modeling, pp 79640P–79640P-6
Hanley J, Debois MM, Mah D, Mageras GS, Raben A, Rosenzweig K, Mychalczak B, Schwartz LH, Gloeggler PJ, Lutz W, Ling CC, Leibel SA, Fuks Z, Kutcher GJ (1999) Deep inspiration breath-hold technique for lung tumors: the potential value of target immobilization and reduced lung density in dose escalation. Int J Radiat Oncol*Biol*Phys 45(3):603–611
Häussinger K, Ballin A, Becker HD, Bölcskei P, Dierkesmann R, Dittrich I, Frank W, Freitag L, Gottschall R, Guschall WR, Hartmann W, Hauck R, Herth F, Kirsten D, Kohlhäufl M, Kreuzer A, Loddenkemper R, Macha N, Markus A, Stanzel F, Steffen H, Wagner M (2004) Recommendations for quality standards in bronchoscopy. Pneumologie 58(5):344–356
Hautmann H, Schneider A, Pinkau T, Peltz F, Feussner H (2005) Electromagnetic catheter navigation during bronchoscopy: validation of a novel method by conventional fluoroscopy. Chest 128(1):382–387
Hekimian-Williams C, Grant B, Liu X, Zhang Z, Kumar P (2010) Accurate localization of RFID tags using phase difference. In: IEEE international conference on RFID, 2010, pp 89–96
Höller K, Penne J, Schneider A, Jahn J, Boronat JG, Wittenberg T, Feussner H, Hornegger J (2009) Endoscopic orientation correction. In: Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (MICCAI), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5761. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 459–466
Housden R, Treece G, Gee A, Prager R, Street T (2007) Hybrid systems for reconstruction of freehand 3D ultrasound data. CUED/F-INFENG/TR 574, University of Cambridge, Department of Engineering
Hummel J, Figl M, Bax M, Shahidi R, Bergmann H, Birkfellner W (2009) Evaluation of dynamic electromagnetic tracking deviation. In: Miga MI, Wong KH (eds) Proceedings of SPIE medical imaging 2009: visualization, image-guided procedures, and modeling, vol 7261. SPIE, p 72612U
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61(2):69–90
Klein T, Traub J, Hautmann H, Ahmadian A, Navab N (2007) Fiducial-free registration procedure for navigated bronchoscopy. In: Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (MICCAI), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4791. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 475
Koizumi N, Sumiyama K, Suzuki N, Hattori A, Tajiri H, Uchiyama A (2002) Development of three-dimensional endoscopic ultrasound system with optical tracking. In: Dohi T, Kikinis R (eds) Proceedings of internaional conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (MICCAI), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2488. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 60–65
Kupelian P, Willoughby T, Mahadevan A, Djemil T, Weinstein G, Jani S, Enke C, Solberg T, Flores N, Liu D, Beyer D, Levine L (2007) Multi-institutional clinical experience with the Calypso system in localization and continuous, real-time monitoring of the prostate gland during external radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol*Biol*Phys 67(4):1088–1098. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.10.026
Li Y, Aissaoui R, Lacoste M, Dansereau J (2004) Development and evaluation of a new body-seat interface shape measurement system. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 51(11):2040–2050
Luo X, Feuerstein M, Sugiura T, Kitasaka T, Imaizumi K, Hasegawa Y, Mori K (2010) Towards hybrid bronchoscope tracking under respiratory motion: evaluation on a dynamic motion phantom. In: Wong KH, Miga MI (eds) Proceedings of SPIE medical imaging 2010: visualization, image-guided procedures, and modeling, vol 7625. SPIE, p 76251B
Luo X, Reichl T, Feuerstein M, Kitasaka T, Mori K (2010) Modified hybrid bronchoscope tracking based on sequential Monte Carlo sampler: dynamic phantom validation. In: Asian conference on computer vision, Queenstown, New Zealand, pp 409–421
Markelj P, Tomazevic D, Likar B, Pernus F (2010) A review of 3D/2D registration methods for image-guided interventions. Med Image Anal 16(3):642–661
Mirota D, Taylor RH, Ishii M, Hager GD (2009) Direct endoscopic video registration for sinus surgery. In: Miga MI, Wong KH (eds) Proceedings of SPIE medical imaging 2009: visualization, image-guided procedures, and modeling, vol 7261. SPIE, p 72612K
Mori K, Deguchi D, Akiyama K, Kitasaka T, Maurer CR, Suenaga Y, Takabatake H, Mori M, Natori H (2005) Hybrid bronchoscope tracking using a magnetic tracking sensor and image registration. In: Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (MICCAI), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3750. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 543–550
Mori K, Hasegawa J, Toriwaki J, Anno H, Katada K (1995) Automated extraction and visualization of bronchus from 3D CT images of lung. In: Proceedings of the first international conference on computer vision, virtual reality and robotics in medicine, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 905. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 542–548
Mountney P, Stoyanov D, Yang GZ (2010) Three-dimensional tissue deformation recovery and tracking. IEEE Signal Process Mag 27(4):14–24
Nakamoto M, Ukimura O, Gill I, Mahadevan A, Miki T, Hashizume M, Sato Y (2008) Realtime organ tracking for endoscopic augmented reality visualization using miniature wireless magnetic tracker. In: Dohi T, Sakuma I, Liao H (eds) Proceedings of the international workshop on medical imaging and augmented reality (MIAR), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5128. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 359–366. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-79982-5_39. http://www.springerlink.com/content/j6846v117v1xw683/
Okatani T, Deguchi K (1997) Shape reconstruction from an endoscope image by shape from shading technique for a point light source at the projection center. Comput Vis Image Underst 66(2):131
Pagoulatos N, Rohling RN, Edwards WS, Kim Y (2000) New spatial localizer based on fiber optics with applications in 3D ultrasound imaging. In: Mun SK (ed) Proceedings of SPIE medical imaging 2000: image display and visualization, vol 3976. SPIE, pp 595–602
Rashid H, Burger P (1992) Differential algorithm for the determination of shape from shading using a point light source. Image Vis Comput 10(2):119–127
Reichl T, Gergel I, Menzel M, Hautmann H, Wegner I, Meinzer HP, Navab N (2012) Real-time motion compensation for EM bronchoscope tracking with smooth output—ex-vivo validation. In: Proceedings of SPIE medical imaging 2012: image-guided procedures, robotic interventions, and modeling, vol 8316. SPIE, p 83163A
Reichl T, Luo X, Menzel M, Hautmann H, Mori K, Navab N (2011) Deformable registration of bronchoscopic video sequences to CT volumes with guaranteed smooth output. In: Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (MICCAI), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6891. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 17–24
Schwarz Y, Greif J, Becker HD, Ernst A, Mehta A (2006) Real-time electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy to peripheral lung lesions using overlaid CT images: the first human study. Chest 129(4):988–994
Shimada J, Itoh K, Yamaguchi S, Nishikawa A, Miyazaki F (2005) Magnetic navigation system for thoracoscopic surgery of the pig lung partial resection with transbronchial marking. In: Proceedings of international congress on computer assisted radiology and surgery (CARS), vol 1281. Elsevier, pp 752–755. doi:10.1016/j.ics.2005.03.164. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S053151310500422X
Shoemake K (1985) Animating rotation with quaternion curves. In: Proceedings of conference on computer graphics and interactive techniques (SIGGRAPH). ACM, New York, pp 245–254
Sluimer I, Schilham A, Prokop M, van Ginneken B (2006) Computer analysis of computed tomography scans of the lung: a survey. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 25(4):385–405
Solomon SB, White P, Wiener CM, Orens JB, Wang KP (2000) Three-dimensional CT-guided bronchoscopy with a real-time electromagnetic position sensor: a comparison of two image registration methods. Chest 118(6):1783–1787
Soper T, Haynor D, Glenny R, Seibel E (2010) In vivo validation of a hybrid tracking system for navigation of an ultrathin bronchoscope within peripheral airways. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57(3):736–745
Suter MJ, Reinhardt JM, Sonka M, Higgins WE, Hoffman EA, McLennan G (2004) Three-dimensional true color topographical analysis of the pulmonary airways. In: Amini AA, Manduca A (eds) Proceedings of SPIE medical imaging 2004: physiology, function, and structure from medical images, vol 5369. SPIE, pp 189–198
Tachihara M, Ishida T, Kanazawa K, Sugawara A, Watanabe K, Uekita K, Moriya H, Yamazaki K, Asano F, Munakata M (2007) A virtual bronchoscopic navigation system under X-ray fluoroscopy for transbronchial diagnosis of small peripheral pulmonary lesions. Lung Cancer 57(3):322–327
Tschirren J, Hoffman EA, McLennan G, Sonka M (2005) Intrathoracic airway trees: segmentation and airway morphology analysis from low-dose CT scans. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 24(12): 1529–1539
Wegner I, Tetzlaff R, Biederer J, Wolf I, Meinzer H (2008) An evaluation environment for respiratory motion compensation in navigated bronchoscopy. In: Proceedings of SPIE medical imaging, vol 6918. SPIE, p 691811
Wengert C, Reeff M, Cattin P, Szekely G (2006) Fully automatic endoscope calibration for intraoperative use. In: Proceedings of Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin (BVM), Informatik aktuell. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 419–423
Wille A, Broll M, Winter S (2011) Phase difference based RFID navigation for medical applications. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on RFID (RFID), pp 98–105
Willoughby TR, Kupelian PA, Pouliot J, Shinohara K, Aubin M, Roach M, Skrumeda LL, Balter JM, Litzenberg DW, Hadley SW, Wei JT, Sandler HM (2006) Target localization and real-time tracking using the calypso 4d localization system in patients with localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol*Biol*Phys 65(2):528–534. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.01.050
Yamamoto S, Ueno K, Imamura F, Matsuoka H, Nagatomo I, Omiya Y, Yoshimura M, Kusunoki Y (2004) Usefulness of ultrathin bronchoscopy in diagnosis of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 46(1): 43–48
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft under grants NA 620/2-1 and 446 JAP 113/348/0-1, the European Union FP7 under grant 256984, the JSPS Grant for Scientific Research, and the TUM Graduate School of Information Science in Health (GSISH). The authors would like to thank Marco Feuerstein for help with Fig. 6.
Ethical standards All human and animal studies have been approved by the appropriate ethics committee and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. All persons gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reichl, T., Luo, X., Menzel, M. et al. Hybrid electromagnetic and image-based tracking of endoscopes with guaranteed smooth output. Int J CARS 8, 955–965 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0835-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0835-5