Abstract
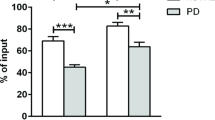
Dopamine (DA) is a crucial transmitter in the neuroimmune network, where it contributes to the nervous system-immune system interplay as well as in the communication among immune cells. DA acts through five different dopaminergic receptors (DR) grouped into two families: the D1-like (D1 and D5) and the D2-like (D2, D3 and D4). By use of 5-color flow cytometric analysis, we examined the expression of DR on human CD4+ naive T lymphocytes (CD3+CD4+CD45RA+CCR7+), central memory (TCM, CD3+CD4+CD45RA-CCR7+) and effector memory T cells (TEM, CD3+CD4+CD45RA-CCR7-). In addition, in cultured CD4+ T cells we investigated the changes in DR expression induced by stimulation with antiCD3/antiCD28 antibodies. Results showed that CD4+ T cells always expressed all the five DR: D1-like DR were identified on average on 11.6–13.1 % and D2-like DR on 3.1–8.1 % of the cells. DR on CD4+ naive T cells, TCM, and TEM had distinct expression patterns: naive T cells expressed more D1-like than D2-like DR, which on the contrary were increased in TCM and TEM cells. In cultured CD4+ T cells stimulation with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 antibodies increased the expression of D1-like DR by 71–84 % and of D2-like DR by 55–97 %. The frequency of DR was higher in apoptotic cells in comparison to viable cells, however stimulation increased all DR on viable cells, without affecting their expression on apoptotic cells. The present results contribute to unravel the complexity of dopaminergic pathways in human CD4+ T lymphocytes, suggesting their involvement in memory functions as well as in apoptotic processes. In view of the role of CD4+ memory T cells in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration during Parkinson’s disease, the relevance of these findings must be assessed in the clinical setting.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amenta F, Bronzetti E, Felici L, Ricci A, Tayebati SK (1999) Dopamine D2-like receptors on human peripheral blood lymphocytes: a radioligand binding assay and immunocytochemical study. J Auton Pharmacol 19:151–159
Bas J, Calopa M, Mestre M, Mollevi DG, Cutillas B, Ambrosio S, Buendia E (2001) Lymphocyte populations in Parkinson’s disease and in rat models of parkinsonism. J Neuroimmunol 113:146–152
Basu S, Dasgupta PS (2000) Dopamine, a neurotransmitter, influences the immune system. J Neuroimmunol 102:113–124
Beaulieu J-M, Gainetdinov RR (2011) The physiology, signalling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 63:182–217
Bergquist J, Silberring J (1998) Identification of catecholamines in the immune system by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 12:683–688
Besser MJ, Ganor Y, Levite M (2005) Dopamine by itself activates either D2, D3 or D1/D5 dopaminergic receptors in normal human T-cells and triggers the selective secretion of either IL-10, TNFalpha or both. J Neuroimmunol 169:161–171
Brito-Melo GE, Nicolato R, de Oliveira AC, Menezes GB, Lélis FJ, Avelar RS, Sá J, Bauer ME, Souza BR, Teixeira AL, Reis HJ (2012) Increase in dopaminergic, but not serotoninergic, receptors in T-cells as a marker for schizophrenia severity. J Psychiatr Res 46:738–742
Calopa M, Bas J, Callen A, Mestre M (2010) Apoptosis of peripheral blood lymphocytes in Parkinson patients. Neurobiol Dis 38:1–7
Capellino S, Cosentino M, Wolff C, Schmidt M, Grifka J, Straub RH (2010) Catecholamine producing cells in the synovial tissue during arthritis: modulation of sympathetic neurotransmitters as new therapeutic target. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1853–1860
Cosentino M, Marino F (2013) Adrenergic and dopaminergic modulation of immunity in multiple sclerosis: teaching old drugs new tricks? J Neuroimmune Pharm 8:163–179
Cosentino M, Marino F, Bombelli R, Ferrari M, Lecchini S, Frigo G (1999) Endogenous catecholamine synthesis, metabolism, storage and uptake in human neutrophils. Life Sci 64:975–981
Cosentino M, Bombelli R, Ferrari M, Marino F, Rasini E, Maestroni GJ, Conti A, Boveri M, Lecchini S, Frigo G (2000) HPLC-ED measurement of endogenous catecholamines in human immune cells and hematopoietic cell lines. Life Sci 68:283–295
Cosentino M, Marino F, Bombelli R, Ferrari M, Rasini E, Lecchini S, Frigo G (2002a) Stimulation with phytohaemagglutinin induces the synthesis of catecholamines in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells:role of protein kinase C and contribution of intracellular calcium. J Neuroimmunol 125:125–133
Cosentino M, Zaffaroni M, Marino F, Bombelli R, Ferrari M, Rasini E, Lecchini S, Ghezzi A, Frigo G (2002b) Catecholamine production and tyrosine hydroxylase expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from multiple sclerosis patients: effect of cell stimulation and possible relevance for activation-induced apoptosis. J Neuroimmunol 133:233–240
Cosentino M, Rasini E, Colombo C, Marino F, Blandini F, Ferrari M, Samuele A, Lecchini S, Nappi G, Frigo G (2004) Dopaminergic modulation of oxidative stress and apoptosis in human peripheral blood lymphocytes: evidence for a D1-like receptor-dependent protective effect. Free Radic Biol Med 36:1233–1240
Cosentino M, Zaffaroni M, Ferrari M, Marino F, Bombelli R, Rasini E, Frigo G, Ghezzi A, Comi G, Lecchini S (2005) Interferon-gamma and interferon-beta affect endogenous catecholamines in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: implications for multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 162:112–121
Cosentino M, Fietta AM, Ferrari M, Rasini E, Bombelli R, Carcano E, Saporiti F, Meloni F, Marino F, Lecchini S (2007) Human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells selectively express tyrosine hydroxylase and contain endogenous catecholamines subserving an autocrine/paracrine inhibitory functional loop. Blood 109:632–642
Cosentino M, Zaffaroni M, Trojano M, Giorelli M, Pica C, Rasini E, Bombelli R, Ferrari M, Ghezzi A, Comi G, Livrea P, Lecchini S, Marino F (2012) Dopaminergic modulation of CD4+CD25(high) regulatory T lymphocytes in multiple sclerosis patients during interferon-β therapy. Neuroimmunomodulation 19:283–292
Dauer W, Przedborski S (2003) Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 39:889–909
Fiszer U, Piotrowska K, Korlak J, Czlonkowska A (1994) The immunological status in Parkinson’s disease. Med Lab Sci 48:196–200
González H, Contreras F, Prado C, Elgueta D, Franz D, Bernales S, Pacheco R (2013) Dopamine receptor D3 expressed on CD4+ T cells favors neurodegeneration of dopaminergic neurons during Parkinson’s disease. J Immunol 190:5048–5056
Harari A, Vallelian F, Pantaleo G (2004) Phenotypic heterogeneity of antigen-specific CD4 T cells under different conditions of antigen persistence and antigen load. Eur J Immunol 34:3525–3533
Kustrimovic N, Rasini E, Legnaro M, Riboldazzi G, Bono G, Ghezzi C, Siani F, Blandini F, Marino F, Cosentino M (2013) Changes in CD4+ T lymphocyte subsets and expression of dopaminergic receptors in peripheral blood of patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroimmune Pharm 8(Suppl):S29
Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F (2000) Dynamics of T lymphocyte responses: intermediates, effectors, and memory cells. Science 290:92–97
Laurie C, Reynolds A, Coskun O, Bowman E, Gendelman HE, Mosley RL (2007) CD4+ T cells from Copolymer-1 immunized mice protect dopaminergic neurons in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroimmunol 183:60–68
Lecoeur H, Ledru E, Prévost MC, Gougeon ML (1997) Strategies for phenotyping apoptotic peripheral human lymphocytes comparing ISNT, annexin-V and 7-AAD cytofluorometric staining methods. J Immunol Methods 209:111–123
Levite M (2012) Dopamine in the immune system: dopamine receptors in immune cells, potent effects, endogenous production and involvement in immune and neuropsychiatric diseases. In: Levite M (ed) Nerve-driven-immunity – neurotransmitters and neuropeptides in the immune system. Springer, Wien, pp 1–45
Levite M, Chowers Y, Ganor Y, Besser M, Hershkovits R, Cahalon L (2001) Dopamine interacts directly with its D3 and D2 receptors on normal human T cells, and activates β-integrin function. Eur J Immunol 31:3504–3512
Marino F, Cosentino M, Bombelli R, Ferrari M, Lecchini S, Frigo G (1999) Endogenous catecholamine synthesis, metabolism storage, and uptake in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Exp Hematol 27:489–495
McKenna F, McLaughlin PJ, Lewis BJ, Sibbring GC, Cummerson JA, Bowen-Jones D, Moots RJ (2002) Dopamine receptor expression on human T- and B-lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils and NK cells: a flow cytometric study. J Neuroimmune 132:34–40
Nakano K, Higashi T, Hashimoto K, Takagi R, Tanaka Y, Matsushita S (2008) Antagonizing dopamine D1-like receptor inhibits Th17 cell differentiation: preventive and therapeutic effects on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 373:286–291
Nakano K, Higashi T, Takagi R, Hashimoto K, Tanaka Y, Matsushita S (2009) Dopamine released by dendritic cells polarizes Th2 differentiation. Int Immunol 21:645–654
Nakano K, Yamaoka K, Hanami K, Saito K, Sasaguri Y, Yanagihara N, Tanaka S, Katsuki I, Matsushita S, Tanaka Y (2011) Dopamine induces IL-6-dependent IL-17 production via D1-like receptor on CD4 naive T cells and D1-like receptor antagonist SCH-23390 inhibits cartilage destruction in a human rheumatoid arthritis/SCID mouse chimera model. J Immunol 186:3745–3752
Reynolds AD, Kadiu I, Garg SK, Glanzer JG, Nordgren T, Ciborowski P, Banerjee R, Gendelman HE (2008) Nitrated alpha-synuclein and microglial neuroregulatory activities. J Neuroimmune Pharm 3:59–74
Ricci A, Bronzetti E, Mignini F, Tayebati SK, Zaccheo D, Amenta F (1999) Dopamine D1-like receptor subtypes in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Neuroimmunol 96:234–240
Sallusto F, Lenig D, Förster R, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A (1999) Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions. Nature 401:708–712
Sallusto F, Geginat J, Lanzavecchia A (2004) Central memory and effector memory T cell subsets: function, generation, and maintenance. Annu Rev Immunol 22:745–763
Sanchez-Guajardo V, Barnum CJ, Tansey MG, Romero-Ramos M (2013) Neuroimmunological processes in Parkinson’s disease and their relation to α-synuclein: microglia as the referee between neuronal processes and peripheral immunity. ASN Neuro 5:113–139
Sarkar C, Das S, Chakroborty D, Chowdhury UR, Basu B, Dasgupta PS, Basu S (2006) Cutting Edge: Stimulation of dopamine D4 receptors induce T cell quiescence by up-regulating Kruppel-like factor-2 expression through inhibition of ERK1/ERK2 phosphorylation. J Immunol 177:7525–7529
Sarkar C, Basu B, Chakroborty D, Dasgupta PS, Basu S (2010) The immunoregulatory role of dopamine: an update. Brain Behav Immun 24:525–528
Saunders JA, Estes KA, Kosloski LM, Allen HE, Dempsey KM, Torres-Russotto DR, Meza JL, Santamaria PM, Bertoni JM, Murman DL, Ali HH, Standaert DG, Mosley RL, Gendelman HE (2012) CD4+ regulatory and effector/memory T cell subsets profile motor dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroimmune Pharm 7:927–38
Schetz JA (2009) Dopamine receptors, introduction. IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY. http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/FamilyIntroductionForward?familyId=20. Accessed on 31 Jan 2014
Stone DK, Reynolds AD, Mosley RL, Gendelman HE (2009) Innate and adaptive immunity for the pathobiology of Parkinson’s disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 11:2151–66
Vile JM, Strange PG (1995) High-affinity binding sites for neuroleptic drugs in human peripheral blood lymphocytes and their relation to dopamine receptors. A long-standing controversy. Biochem Pharmacol 49:747–753
Zaffaroni M, Marino F, Bombelli R, Rasini E, Monti M, Ferrari M, Ghezzi A, Comi G, Lecchini S, Cosentino M (2008) Therapy with interferon-beta modulates endogenous catecholamines in lymphocytes of patients with multiple sclerosis. Exp Neurol 214:315–321
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from Fondazione CARIPLO to Marco Cosentino (Project 2011-0504: Dopaminergic modulation of CD4+ T lymphocytes: relevance for neurodegeneration and neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease - The dopaminergic neuro-immune connection). Natasa Kustrimovic has a postdoc fellow appointment supported by the grant.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kustrimovic, N., Rasini, E., Legnaro, M. et al. Expression of Dopaminergic Receptors on Human CD4+ T Lymphocytes: Flow Cytometric Analysis of Naive and Memory Subsets and Relevance for the Neuroimmunology of Neurodegenerative Disease. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 9, 302–312 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-014-9541-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-014-9541-5