Abstract
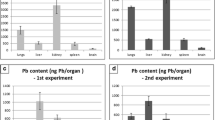
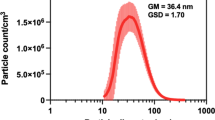
Cadmium nanoparticles can represent a risk in both industrial and environmental settings, but there is little knowledge on the impacts of their inhalation, especially concerning longer-term exposures. In this study, mice were exposed to cadmium oxide (CdO) nanoparticles in whole body inhalation chambers for 4 to 72 h in acute and 1 to 13 weeks (24 h/day, 7 days/week) in chronic exposure to investigate the dynamics of nanoparticle uptake and effects. In the acute experiment, mice were exposed to 2.95 × 106 particles/cm3 (31.7 μg CdO/m3). The same concentration and a lower one (1.18 × 106 particles/cm3, 12.7 μg CdO/m3) were used for the chronic exposure. Transmission electron microscopy documented distribution of nanoparticles into all studied organs. Major portion of nanoparticles was retained in the lung, but longer exposure led to a greater relative redistribution into secondary organs, namely the kidney, and also the liver and spleen. Accumulation of Cd in the lung and liver occurred already after 24 h and in the brain, kidney, and spleen after 72 h of exposure, and a further increase of Cd levels was observed throughout the chronic exposure. There were significant differences in both Cd accumulation and effects between the two exposure doses. Lung weight in the higher exposure group increased up to 2-fold compared to the control. Histological analyses showed dose-dependent alterations in lung and liver morphology and damage to their tissue. Modulation of oxidative stress parameters including glutathione levels and increased lipid peroxidation occurred mainly after the greater chronic exposure. The results emphasize risk of longer-term inhalation of cadmium nanoparticles, since adverse effects occurring after shorter exposures gradually progressed with a longer exposure duration.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akerman ME, Chan WCW, Laakkonen P, Bhatia SN, Ruoslahti E (2002) Nanocrystal targeting in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:12617–12621
Alessandrini F, Ziesenis A, Takenaka S, Karg E, Heyder J, Ring J, Behrendt H (2003) Effects of inhaled CdO particles on the sphingolipid synthesis of rat lungs. Inhal Toxicol 15:343–356
Bastos AS, Loureiro APDM, de Oliveira TF, Corbi SCT, Caminaga RMS, Júnior CR, Orrico SRP (2012) Quantitation of malondialdehyde in gingival crevicular fluid by a high-performance liquid chromatography-based method. Anal Biochem 423:141–146
Bernard A, Buchet JP, Roels H, Masson P, Lauwerys R (1979) Renal excretion of proteins and enzymes in workers exposed to cadmium. Eur J Clin Investig 9:11–22
Bláhová L, Kohoutek J, Lebedová J, Bláha L, Večeřa Z, Buchtová M, Míšek I, Hilscherová K (2014) Simultaneous determination of reduced and oxidized glutathione in tissues by a novel liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method: application in an inhalation study of Cd nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem 406:5867–5876
Blum JL, Rosenblum LK, Grunig G, Beasley MB, Xiong JQ, Zelinkoff JT (2014) Short-term inhalation of cadmium oxide nanoparticles alters pulmonary dynamics associated with lung injury, inflammation, and repair in a mouse model. Inhal Toxicol 26:48–58
Blum JL, Xiong JQ, Hoffman C, Zelikoff JT (2012) Cadmium associated with inhaled cadmium oxide nanoparticles impacts fetal and neonatal development and growth. Toxicol Sci 126:478–486
Buckley BJ, Bassett DJ (1987) Glutathione redox status of control and cadmium oxide-exposed rat lungs during oxidant stress. J Toxicol Environ Health 22:287–299
Campos-Ramos A, Aragón-Piña A, Galindo-Estrada I, Querol X, Alastuey A (2009) Characterization of atmospheric aerosols by SEM in a rural area in the western part of México and its relation with different pollution sources. Atmos Environ 43:6159–6167
Choi HS, Ashitate Y, Lee JH, Kim SH, Matsui A, Insin N, Bawendi MG, Semmler-Behnke M, Frangioni JV, Tsuda A (2010) Rapid translocation of nanoparticles from the lung airspaces to the body. Nat Biotechnol 28:1300–1303
Dong C (2015) Protective effect of proanthocyanidins in cadmium induced neurotoxicity in mice. Drug. Research 65(10):555–560
Elder A, Gelein R, Silva V, Feikert T, Opanashuk L, Carter J, Potter R, Maynard A, Ito Y, Finkelstein J, Oberdörster G (2006) Translocation of inhaled ultrafine manganese oxide particles to the central nervous system. Environ Health Perspect 114:1172–1178
Elinder C, Edling C, Lindberg E, Kagedal B, Vesterberg O (1985) Assessment of renal function in workers previously exposed to cadmium. Br J Ind Med 42:754–760
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione-S-transferases, the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Hopkins LE, Patchin ES, Chiu P-L, Brandenberger C, Smiley-Jewell S, Pinkerton KE (2014) Nose-to-brain transport of aerosolized quantum dots following acute exposure. Nanotoxicology 18:1199–1216
Jain S, Rachamalla M, Kulkarni A, Kaur J, Tikoo K (2013) Pulmonary fibrotic response to inhalation of ZnO nanoparticles and toluene co-exposure through directed flow nose only exposure chamber. Inhal Toxicol 25:703–713
Kirschvink N, Martin N, Fievez L, Smith N, Marlin D, Gustin P (2006) Airway inflammation in cadmium-exposed rats is associated with pulmonary oxidative stress and emphysema. Free Radic Res 40:241–250
Krug HF (2014) Nanosafety research—are we on the right track? Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 53:12304–12319
Liang G, Pu Y, Yin L, Liu R, Ye B, Su Y, Li Y (2009) Influence of different sizes of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on hepatic and renal functions in rats with correlation to oxidative stress. J Toxicol Environ Health A 72:740–745
Liu J, Qu W, Kadiiska MB (2009) Role of oxidative stress in cadmium toxicity and carcinogenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238:209–214
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Ma-Hock L, Brill S, Wohlleben W, Farias PMA, Chaves CR, Tenório DPLA, Fontes A, Santos BS, Landsiedel R, Strauss V, Treumann S, van Ravenzwaay B (2012) Short term inhalation toxicity of a liquid aerosol of CdS/Cd(OH)2 core shell quantum dots in male Wistar rats. Toxicol Lett 208:115–124
Mason H, Davison A, Wright A, Guthrie C, Fayers P, Venables K, Smith N, Chettle D, Franklin D, Scott M, Holden H, Gompertz D, Newmantaylor A (1988) Relations between liver cadmium, cumulative exposure, and renal function in cadmium alloy workers. Br J Ind Med 45:793–802
Mitsumori K, Shibutani M, Sato S, Onodera H, Nakagawa J, Hayashi Y, Ando M (1998) Relationship between the development of hepato-renal toxicity and cadmium accumulation in rats given minimum to large amounts of cadmium chloride in the long-term: preliminary study. Arch Toxicol 72:545–552
Oravisjärvi K, Timonen KL, Wiikinkoski T, Ruuskanen AR, Heinänen K, Ruuskanen J (2003) Source contributions to PM2.5 particles in the urban air of a town situated close to a steel works. Atmos Environ 37:1013–1022
Oszlánczi G, Papp A, Szabó A, Nagymajtényi L, Sápi A, Kónya Z, Paulik E, Vezér T (2011) Nervous system effects in rats on subacute exposure by lead-containing nanoparticles via the airways. Inhal Toxicol 23:173–181
Papp A, Oszlánczi G, Horváth E, Paulik E, Kozma G, Sápi A, Kónya Z, Szabó A (2012) Consequences of subacute intratracheal exposure of rats to cadmium oxide nanoparticles: electrophysiological and toxicological effects. Toxicol Ind Health 28:933–941
Papp T, Schiffmann D, Weiss D, Castranova V, Vallyathan V, Rahman Q (2008) Human health implications of nanomaterial exposure. Nanotoxicology 2:9–27
Roels H, Lauwerys R, Buchet J, Bernard A, Vos A, Oversteyns M (1989) Health significance of cadmium induced renal dysfunction: a five year follow up. Br J Ind Med 46:755–764
Sadauskas E, Jacobsen NR, Danscher G, Stoltenberg M, Vogel U, Larsen A, Kreyling W, Wallin H (2009) Biodistribution of gold nanoparticles in mouse lung following intratracheal instillation. Chem. Cent J 3
Sajid M, Ilyas M, Basheer C, Tariq M, Daud M, Baig N, Shehzad F (2015) Impact of nanoparticles on human and environment: review of toxicity factors, exposures, control strategies, and future prospects. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:4122–4143
Sharifi S, Behzadi S, Laurent S, Forrest ML, Stroeve P, Mahmoudi M (2012) Toxicity of nanomaterials. Chem Soc Rev 41:2323–2343
Shvedova AA, Kisin E, Murray AR, Johnson VJ, Gorelik O, Arepalli S, Hubbs AF, Mercer RR, Keohavong P, Sussman N, Jin J, Yin J, Stone S, Chen BT, Deye G, Maynard A, Castranova V, Baron PA, Kagan VE (2008) Inhalation vs. aspiration of single-walled carbon nanotubes in C57BL/6 mice: inflammation, fibrosis, oxidative stress, and mutagenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol Physiol 295:L552–L565
Singhal RK, Anderson ME, Meister A (1987) Glutathione, a first line of defense against cadmium toxicity. FASEB J 1:220–223
Srinivas A, Rao PJ, Selvam G, Goparaju A, Murthy PB, Reddy PN (2012) Oxidative stress and inflammatory responses of rat following acute inhalation exposure to iron oxide nanoparticles. Hum Exp Toxicol 31:1113–1131
Srinivas A, Rao PJ, Selvam G, Murthy PB, Reddy PN (2011) Acute inhalation toxicity of cerium oxide nanoparticles in rats. Toxicol Lett 205:105–115
Srivastava AK, Pandey S, Sood KN, Halder SK, Kishore R (2008) Novel growth morphologies of nano- and micro-structured cadmium oxide. Mater Lett 62:727–730
Sung JH, Ji JH, Park JD, Yoon JU, Kim DS, Jeon KS, Song MY, Jeong J, Han BS, Han JH, Chung YH, Chang HK, Lee JH, Cho MH, Kelman BJ, IJ Y (2009) Subchronic inhalation toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Toxicol Sci 108:452–461
Takenaka S, Karg E, Kreyling WG, Lentner B, Schulz H, Ziesenis A, Schramel P, Heyder J (2004) Fate and toxic effects of inhaled ultrafine cadmium oxide particles in the rat lung. Inhal Toxicol 16(Suppl 1):83–92
Večeřa Z, Mikuška P, Moravec P, Smolík J (2011) Unique exposure system for the whole body inhalation experiments with small animals. TANGER Ltd NANOCON 2011:652–654
Wang J, Chen C, Liu Y, Jiao F, Li W, Lao F, Li Y, Li B, Ge C, Zhou G, Gao Y, Zhao Y, Chai Z (2008) Potential neurological lesion after nasal instillation of TiO(2) nanoparticles in the anatase and rutile crystal phases. Toxicol Lett 183:72–80
Yuan G, Dai S, Yin Z, Lu H, Jia R, Xu J, Song X, Shu Y, Zhao X (2014) Toxicological assessment of combined lead and cadmium: acute and sub-chronic toxicity study in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 65:260–268
Zhao Y, Chen L, Gao S, Toselli P, Stone P, Li W (2010) The critical role of the cellular thiol homeostasis in cadmium perturbation of the lung extracellular matrix. Toxicology 267:60–69
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Pavel Moravec from Institute of Chemical Process Fundamentals, CAS, v.v.i., Prague, Czech Republic for helping with the generation of the CdONPs and SMPS measurement with nanoDMA. The work was supported by the Czech Science Foundation grant No. P503/11/2315 and P503/12/G147 and by project LO1214 funded by the National Sustainability Programme of the Czech Republic. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The experiments were performed in accordance with the ethical approval of the Institute of Animal Physiology and Genetics (no. 081/2010).
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 150 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lebedová, J., Bláhová, L., Večeřa, Z. et al. Impact of acute and chronic inhalation exposure to CdO nanoparticles on mice. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 24047–24060 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7600-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7600-6