Abstract
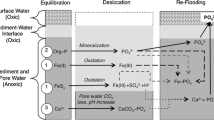
Reservoirs in semi-arid areas are subject to water level fluctuations (WLF) that alter biogeochemical processes in the sediment. We hypothesized that wet–dry cycles may cause internal eutrophication in such systems when they affect densely vegetated shallow areas. To assess the impact of WLF on phosphorus (P) mobilization and benthic P cycling of iron-rich sediments, we tested the effects of (i) sediment drying and rewetting, (ii) the impact of organic matter availability in the form of dried Brazilian Waterweed (Egeria densa), and (iii) alternating redox conditions in the surface water. In principle, drying led to increased P release after rewetting both in plant-free and in plant-amended sediments. Highest P mobilization was recorded in plant amendments under oxygen-free conditions. After re-establishment of aerobic conditions, P concentrations in surface water decreased substantially owing to P retention by sediments. In desiccated and re-inundated sediments, P retention decreased by up to 30 % compared to constantly inundated sediments. We showed that WLF may trigger biochemical interactions conducive to anaerobic P release. Thereby, E. densa showed high P release and even P uptake that was redox-controlled and superimposed sedimentary P cycling. Macrophytes play an important role in the uptake of P from the water but may be also a significant source of P in wet–dry cycles. We estimated a potential for the abrupt release of soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP) by E. densa of 0.09–0.13 g SRP per m2 after each wet–dry cycle. Released SRP may exceed critical P limits for eutrophication, provoking usage restrictions. Our results have implications for management of reservoirs in semi-arid regions affected by WLF.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldous A, McCormick P, Ferguson C, Graham S, Craft C (2005) Hydrologic regime controls soil phosphorus fluxes in restoration and undisturbed wetlands. Restor Ecol 13:341–347. doi:10.1111/j.1526-100X.2005.00043.x
Asaeda T, Trung VK, Manatunge J (2000) Modeling the effects of macrophyte growth and decomposition on the nutrient budget in shallow lakes. Aquat Bot 68:217–237. doi:10.1016/S0304-3770(00)00123-6
Baldwin DS (1996) Effects of exposure to air and subsequent drying on the phosphate sorption characteristics of sediments from a eutrophic reservoir. Limnol Oceanogr 41:1725–1732. doi:10.4319/lo.1996.41.8.1725
Baldwin DS, Mitchell AM (2000) The effects of drying and reflooding on the sediment and soil nutrient dynamics of lowland river–floodplain systems: a synthesis. Regul River 16:457–467. doi:10.1002/1099-1646(200009/10)16:5<457::AID-RRR597>3.0.CO;2-B
Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2014) lme4: Linear mixed-effects models using Eigen and S4. R Package Version 1.1-7. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=lme4
Batzer DP, Sharitz RR (2006) Ecology of freshwater and estuarine wetlands. University of California Press, London. doi:10.2193/2007-148
Bergkamp G, McCartney M, Dugan P, McNeely J, Acreman M (2000) Dams, ecosystem functions and environmental restoration. Prepared for the World Commission on Dams. Thematic review, Environmental Issue II., p 1
Brookes PC, Powlson DS, Jenkinson DS (1982) Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 14:319–329. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(82)90001-3
Casati P, Lara MV, Andreo CS (2000) Induction of a C-4 like mechanism of CO2 fixation in Egeria densa, a submersed aquatic species. Plant Physiol 123:1611–1622
Cheesman AW, Turner BL, Inglett PW, Reddy KR (2010) Phosphorus transformations during decomposition of wetland macrophytes. Sci Total Environ 44:9265–9271. doi:10.1021/es102460h
CHESF 2011. Descrição do Aproveitamento de Luíz Gonzaga. http://www.chesf.gov.br/portal/page/portal/chesf_portal/paginas/sistema_chesf/sistema_chesf_geracao/conteiner_geracao?p_name=8A2EEABD3BE1D002E0430A803301D002. Accessed 23 September 2013
Cooke DG (2005) Restoration and management of lakes and reservoirs, Third Edition. CRC Press. DOI:1566706254
Coops H, Beklioglu M, Crisman TL (2003) The role of water-level fluctuations in shallow lake ecosystems—workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 506–50:23–27. doi:10.1023/B:HYDR.0000008595.14393.77
R Core Team (2013). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL http://www.R-project.org/.
Crawley MJ (2007) The R book. John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.
De Groot C-J, Van Wijck C (1993) The impact of desiccation of a freshwater marsh (Garcines Nord, Camargue, France) on sediment-water-vegetation interactions. Hydrobiologia 252:83–94. doi:10.1007/BF00000130
De Vicente I, Andersen FØ, Hansen HCB, Cruz-Pizarro L, Jensen HS (2010) Water level fluctuations may decrease phosphate adsorption capacity of the sediment in oligotrophic high mountain lakes. Hydrobiologia 651:253–264. doi:10.1007/s10750-010-0304-x
De Winton MD, Champion PD, Clayton JS, Wells RDS (2009) Spread and status of seven submerged pest plants in New Zealand lakes. N Z J Mar Fresh 43:547–561. doi:10.1080/00288330909510021
Dieter D, Herzog H, Hupfer M (2015) Effects of drying on phosphorus uptake of re-flooded lake sediments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:17065–17081. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4904-x
Gilbert JD, Guerrero F, de Vicente I (2014) Sediment desiccation as a driver of phosphate availability in the water column of Mediterranean wetlands. Sci Total Environ 466–467:965–975. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.07.123
Gordon H, Haygarth PM, Bardgett RD (2008) Drying and rewetting effects on soil microbial community composition and nutrient leaching. Soil Biol Biochem 40:302–311. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.08.008
Granéli W, Solander D (1988) Influence of aquatic macrophytes on phosphorus cycling in lakes. Hydrobiologia 170:245–266. doi:10.1007/BF00024908
Gunkel G, Sobral M (2013) Re-oligotrophication as a challenge for tropical reservoir management with reference to Itaparica Reservoir, São Francisco, Brazil. Water Sci Technol 67:708–714. doi:10.2166/wst.2012.583
Gunkel G, Lima D, Selge F, Sobral M, Calado S (2015) Aquatic ecosystem services of reservoirs in semiarid areas: sustainability and reservoir management. WIT Trans Ecol Environ 197:187–200
Hilt S, Gross EM, Hupfer M, Morscheid H, Mählmann J, Melzer A, Poltz J, Sandrock S, Scharf E-M, Schneider S, van de Weyer K (2006) Restoration of submerged vegetation in shallow eutrophic lakes—a guideline and state of the art in Germany. Limnologica - Ecology and Management of Inland Waters 36:155–171. doi:10.1016/j.limno.2006.06.001
Hupfer M, Gächter R, Giovanoli R (1995) Transformation of phosphorus species in settling seston and during early sediment diagenesis. Aquat Sci 57:305–324. doi:10.1007/BF00878395
Hupfer M, Gloess S, Grossart H-P (2007) Polyphosphate-accumulating microorganisms in aquatic sediments. Aquat Microb Ecol 47:299–311. doi:10.3354/ame047299
Jensen HS, Kristensen P, Jeppesen E, Skytthe A (1992) Iron:phosphorus ratio in surface sediment as an indicator phosphate release from aerobic sediments in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 235(236):731–743. doi:10.1007/BF00026261
Kerr JG, Burford M, Olley J, Udy J (2010) The effects of drying on phosphorus sorption and speciation in subtropical river sediments. Mar Freshwater Res 61:928–935. doi:10.1071/MF09124
Kleeberg A (2013) Impact of aquatic macrophyte decomposition on sedimentary nutrient and metal mobilization in the initial stages of ecosystem development. Aquat Bot 105:41–49. doi:10.1016/j.aquabot.2012.12.003
Kolding J, van Zwieten PAM (2012) Relative lake level fluctuations and their influence on productivity and resilience in tropical lakes and reservoirs. Fish Res 115–116:99–109. doi:10.1016/j.fishres.2011.11.008
Krolová M, Čížková H, Hejzlar J, Poláková S (2013) Response of littoral macrophytes to water level fluctuations in a storage reservoir. Knowl Manag Aquat Ecosys 408:1–21. doi:10.1051/kmae/2013042
Laskov C, Herzog C, Lewandowski J, Hupfer M (2007) Miniaturized photometrical methods for the rapid analysis of phosphate, ammonium, ferrous iron, and sulfate in pore water of freshwater sediments. Limnol Oceanogr-Meth 5:63–71. doi:10.4319/lom.2007.5.63
Marion L, Paillisson J-M (2003) A mass balance assessment of the contribution of floating-leaved macrophytes in nutrient stocks in an eutrophic macrophyte dominated lake. Aquat Bot 75:249–260. doi:10.1016/S0304-3770(02)00177-8
Mitchell A, Baldwin DS (1998) Effects of desiccation/oxidation on the potential for bacterially mediated P release from sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 43:481–487. doi:10.4319/lo.1998.43.3.0481
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(00)88444-5
Nilsson C (2009) Reservoirs. In: Likens GE (ed) Encyclopedia of inland waters. Elsevier, Academic Press, Oxford, pp 625–633
Precht E, Huettel M (2004) Rapid wave-driven advective pore water exchange in a permeable coastal sediment. J Sea Res 51:93–107. doi:10.1016/j.seares.2003.07.003
Psenner R, Pucsko R, Sager M (1984) Die Fraktionierung organischer und anorganischer Phosphorverbindungen von Sedimenten – Versuch einer Definition ökologisch wichtiger Fraktionen. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, Supplement 70:111–155
Qiu S, McComb A (1994) Effects of oxygen concentration on phosphorus release from reflooded air-dried wetland sediments. Mar Freshwater Res 45:1319–1328. doi:10.1071/MF9941319
Qiu S, McComb A (1995) Planktonic and microbial contributions to phosphorus release from fresh and air-dried sediments. Mar Freshwater Res 46:1039–1045. doi:10.1071/MF9951039
Qiu S, McComb A (2002) Interrelations between iron extractability and phosphate sorption in reflooded air-dried sediments. Hydrobiologia 472:39–44
Rangel LM, Silva LHS, Rosa P, Roland F, Huszar VLM (2012) Phytoplankton biomass is mainly controlled by hydrology and phosphorus concentrations in tropical hydroelectric reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 693:13–28. doi:10.1007/s10750-012-1083-3
Ribaudo C, Bertrin V, Dutartre A (2014) Dissolved gas and nutrient dynamics within an Egeria densa Planch. bed. Acta Bot Gallica 161:233–241. doi:10.1080/12538078.2014.932703
Schönbrunner IM, Preiner S, Hein T (2012) Impact of drying and reflooding of sediment on phosphorus dynamics of river-floodplain systems. Sci Total Environ 432:329–337. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.06.025
Selge F, Matta E, Hinkelmann R, Gunkel G (2015) Nutrient load concept- reservoir vs. bay impacts: a case study from a semi-arid watershed. Conference paper at 17th IWA International Conference on Diffuse Pollution and Eutrophication, Berlin, Germany
Shilla D, Asaeda T, Fujino T, Sanderson B (2006) Decomposition of dominant submerged macrophytes: implications for nutrient release in Myall Lake, NSW, Australia. Wet Ecol Manag 14:427–433. doi:10.1007/s11273-006-6294-9
Smith VH (2003) Eutrophication of freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems: a global problem. Environ Sci Pollut Res 10:126–139. doi:10.1065/espr2002.12.142
Smith AS, Jacinthe P-A (2013) A mesocosm study of the effects of wet–dry cycles on nutrient release from constructed wetlands in agricultural landscapes. Environ Sci 16:106–115. doi:10.1039/C3EM00465A
Søndergaard M, Jensen JP, Jeppesen E (2003) Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 506:135–145. doi:10.1023/B:HYDR.0000008611.12704.dd
Tang X, Wu M, Li Q, Lin L, Zhao W (2014) Impacts of water level regulation on sediment physic-chemical properties and phosphorus adsorption–desorption behaviors. Ecol Eng 70:450–458. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.06.022
Townsend SA (1999) The seasonal pattern of dissolved oxygen, and hypolimnetic deoxygenation, in two tropical Australian reservoirs. Lakes Reserv Res Manage 4:41–53. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1770.1999.00077.x
Uhlmann D, Paul L, Hupfer M, Fischer R (2011) Lakes and reservoirs. In: Wilderer P (ed) Treatise on water sciences, vol 2., pp 157–213
Wagener T, Sivapalan M, Troch PA, McGlynn BL, Harman CJ, Gupta HV, Kumar P, Rao PSC, Basu NB, Wilson JS (2010) The future of hydrology: an evolving science for a changing world. Water Resour Res 46:W05301. doi:10.1029/2009WR008906
Wantzen KM, Rothhaupt K-O, Mörtl M, Cantonati M, Tóth LG, Fischer P (2008) Ecological effects of water-level fluctuations in lakes: an urgent issue. Hydrobiologia 613:1–4. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9192-6
Watts CJ (2000a) Seasonal phosphorus release from exposed, re-inundated littoral sediments of two Australian reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 431:27–39. doi:10.1023/A:1004098120517
Watts CJ (2000b) The effect of organic matter on sedimentary phosphorus release in an Australian reservoir. Hydrobiologia 431:13–25. doi:10.1023/A:1004046103679
Wells RDS, Clayton JS (1991) Submerged vegetation and spread of Egeria densa Planchon in Lake Rotorua, central North Island, New Zealand. N Z J Mar Fresh 25:63–70. doi:10.1080/00288330.1991.9516454
Wilson J, Baldwin D (2008) Exploring the “Birch effect” in reservoir sediments: influence of inundation history on aerobic nutrient release. Chem Ecol 24:379–386. doi:10.1080/02757540802497582
Zak D, Gelbrecht J (2007) The mobilisation of phosphorus, organic carbon and ammonium in the initial stage of fen rewetting (a case study from NE Germany). Biogeochemistry 85:141–151. doi:10.1007/s10533-007-9122-2
Zak D, Gelbrecht J, Zerbe S, Shatwell T, Barth M, Cabezas A, Steffenhagen P (2014) How helophytes influence the phosphorus cycle in degraded inundated peat soils—implications for fen restoration. Ecol Eng, Wetland Restoration– Challenges and Opportunities 66:82–90. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.10.003
Zohary T, Ostrovsky I (2011) Ecological impacts of excessive water level fluctuations in stratified freshwater lakes. Inland Waters 1:47–59. doi:10.5268/iw-1.1.406
Zuur AF, Ieno EN, Walker NJ, Saveliev AA, Smith GM (2009) Mixed effects models and extensions in ecology with R. Springer, New York. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-87458-6
Zwirnmann E, Krüger A, Gelbrecht J (1999) Analytik im Zentralen Chemielabor. Jahresbericht des IGB (Leibniz-Institut für Gewässerökologie und Binnenfischerei) 9:3–24
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank S. Calado for her support during several sampling campaigns in Brazil. We are grateful to F. Selge, D. Lima, and M. Rodriguez for their help with field work. Our colleagues H.-J. Exner, C. Herzog, A. Lüder, S. Jordan, and M. Uber helped with technical support. We also thank H. Nottebrock, G. Gunkel, and two anonymous reviewers for critical comments and for improving the manuscript. This study was funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) within the project “INNOVATE” (01LL0904C).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Thomas Hein
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keitel, J., Zak, D. & Hupfer, M. Water level fluctuations in a tropical reservoir: the impact of sediment drying, aquatic macrophyte dieback, and oxygen availability on phosphorus mobilization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 6883–6894 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5915-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5915-3