Abstract
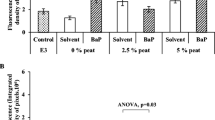
In aquatic environments, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) mostly occur as complex mixtures, for which risk assessment remains problematic. To better understand the effects of PAH mixture toxicity on fish early life stages, this study compared the developmental toxicity of three PAH complex mixtures. These mixtures were extracted from a PAH-contaminated sediment (Seine estuary, France) and two oils (Arabian Light and Erika). For each fraction, artificial sediment was spiked at three different environmental concentrations roughly equivalent to 0.5, 4, and 10 μg total PAH g−1 dw. Japanese medaka embryos were incubated on these PAH-spiked sediments throughout their development, right up until hatching. Several endpoints were recorded at different developmental stages, including acute endpoints, morphological abnormalities, larvae locomotion, and genotoxicity (comet and micronucleus assays). The three PAH fractions delayed hatching, induced developmental abnormalities, disrupted larvae swimming activity, and damaged DNA at environmental concentrations. Differences in toxicity levels, likely related to differences in PAH proportions, were highlighted between fractions. The Arabian Light and Erika petrogenic fractions, containing a high proportion of alkylated PAHs and low molecular weight PAHs, were more toxic to Japanese medaka early life stages than the pyrolytic fraction. This was not supported by the toxic equivalency approach, which appeared unsuitable for assessing the toxicity of the three PAH fractions to fish early life stages. This study highlights the potential risks posed by environmental mixtures of alkylated and low molecular weight PAHs to early stages of fish development.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PAH:
-
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
- BSD:
-
Blue sac disease
- dpf:
-
Days post fertilization
- MELAc:
-
Medaka Embryo-Larval Assay with sediment contact exposure
- dw:
-
Dry weight
- ERS:
-
Egg rearing solution
- ELS:
-
Early life stages
- MEM:
-
Minimum Essential Medium
- MN:
-
Micronucleus
- PY:
-
Pyrolytic
- HO:
-
Heavy oil
- LO:
-
Light oil
- TEF:
-
Toxic equivalent factor
- TEQ:
-
Toxic equivalency
References
Barron MG (2002) Environmental contaminants altering behaviour. In: Dell'Omo G (ed) Behavioural ecotoxicology. Wiley, Chichester
Barron MG, Carls MG, Short JW, Rice SD (2003) Photoenhanced toxicity of aqueous phase and chemically dispersed weathered Alaska North Slope crude oil to pacific herring eggs and larvae. Environ Toxicol Chem 22(3):650–660
Barron MG, Carls MG, Heintz R, Rice SD (2004a) Evaluation of fish early life-stage toxicity models of chronic embryonic exposures to complex polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon mixtures. Toxicol Sci 78(1):60–67
Barron MG, Heintz R, Rice SD (2004b) Relative potency of PAHs and heterocycles as aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists in fish. Mar Environ Res 58(2–5):95–100
Baršienė J, Dedonytė V, Rybakovas A, Andreikėnaitė L, Andersen OK (2006) Investigation of micronuclei and other nuclear abnormalities in peripheral blood and kidney of marine fish treated with crude oil. Aquat Toxicol 78(Supplement (0)):S99–S104
Belanger SE, Rawlings JM, Carr GJ (2013) Use of fish embryo toxicity for the prediction of acute fish toxicity to chemicals. Environ Toxicol Chem 32(8):1768–1783
Billiard SM, Meyer JN, Wassenberg DM, Hodson PV, Di Giulio RT (2008) Nonadditive effects of PAHs on early vertebrate development: mechanisms and implications for risk assessment. Toxicol Sci 105(1):5–23
Cachot J, Geffard O, Augagneur S, Lacroix S, Le Menach K, Peluhet L, Couteau J, Denier X, Devier MH, Pottier D, Budzinski H (2006) Evidence of genotoxicity related to high PAH content of sediments in the upper part of the Seine estuary (Normandy, France). Aquat Toxicol 79(3):257–267
Cachot J, Law M, Pottier D, Peluhet L, Norris M, Budzinski H, Winn R (2007) Characterization of toxic effects of sediment-associated organic pollutants using the λ transgenic medaka. Environ Sci Technol 41(22):7830–7836
Carls MG, Thedinga JF (2010) Exposure of pink salmon embryos to dissolved polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons delays development, prolonging vulnerability to mechanical damage. Mar Environ Res 69(5):318–325
Carls MG, Rice SD, Hose JE (1999) Sensitivity of fish embryos to weathered crude oil: Part I. Low-level exposure during incubation causes malformations, genetic damage, and mortality in larval pacific herring (Clupea pallasi). Environ Toxicol Chem 18(3):481–493
Çavaş T, Ergene-Gözükara S (2005) Induction of micronuclei and nuclear abnormalities in Oreochromis niloticus following exposure to petroleum refinery and chromium processing plant effluents. Aquat Toxicol 74(3):264–271
Colavecchia MV, Backus S, Hodson PV, Parrott JL (2004) Toxicity of oil sands to early life stages of fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas). Environ Toxicol Chem 23(7):1709–1718
Couillard CM (2002) A microscale test to measure petroleum oil toxicity to mummichog embryos. Environ Toxicol 17(3):195–202. doi:10.1002/tox.10049
de Esch C, Slieker R, Wolterbeek A, Woutersen R, de Groot D (2012) Zebrafish as potential model for developmental neurotoxicity testing: a mini review. Neurotoxicol Teratol 34(6):545–553
Dobbins LL, Brain RA, Brooks BW (2008) Comparison of the sensitivities of common in vitro and in vivo assays of estrogenic activity: application of chemical toxicity distributions. Environ Toxicol Chem 27(12):2608–2616
EC (2006) Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, and Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACh). vol L 396. Official Journal of the European Union at www.reach-compliance.eu/english/legislation/docs/launchers/launch-2006-1907-EC-06.html
Embry MR, Belanger SE, Braunbeck TA, Galay-Burgos M, Halder M, Hinton DE, Léonard MA, Lillicrap A, Norberg-King T, Whale G (2010) The fish embryo toxicity test as an animal alternative method in hazard and risk assessment and scientific research. Aquat Toxicol 97(2):79–87
Emran F, Rihel J, Dowling JE (2008) A behavioral assay to measure responsiveness of zebrafish to changes in light intensities. J Vis Exp 20:e923. doi:10.3791/923
Faksness L-G, Brandvik PJ, Sydnes LK (2008) Composition of the water accommodated fractions as a function of exposure times and temperatures. Mar Pollut Bull 56(10):1746–1754
Fallahtafti S, Rantanen T, Brown RS, Snieckus V, Hodson PV (2012) Toxicity of hydroxylated alkyl-phenanthrenes to the early life stages of Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Aquat Toxicol 106–107:56–64
Gesto M, Tintos A, Soengas JL, Míguez JM (2009) β-Naphthoflavone and benzo[a]pyrene alter dopaminergic, noradrenergic, and serotonergic systems in brain and pituitary of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72(1):191–198
Hayashi M, Ueda T, Uyeno K, Wada K, Kinae N, Saotome K, Tanaka N, Takai A, Sasaki YF, Asano N, Sofuni T, Ojima Y (1998) Development of genotoxicity assay systems that use aquatic organisms. Mutat Res Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen 399(2):125–133
Hollert H, Keiter S, König N, Rudolf M, Ulrich M, Braunbeck T (2003) A new sediment contact assay to assess particle-bound pollutants using zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. J Soils Sediments 3(3):197–207. doi:10.1065/jss2003.09.085
Incardona JP, Carls MG, Teraoka H, Sloan CA, Collier TK, Scholz NL (2005) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-independent toxicity of weathered crude oil during fish development. Environ Health Perspect 113(12):1755–1762
Incardona JP, Day HL, Collier TK, Scholz NL (2006) Developmental toxicity of 4-ring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in zebrafish is differentially dependent on AH receptor isoforms and hepatic cytochrome P4501A metabolism. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 217(3):308–321
INERIS (2003) Hydrocarbures Aromatiques Polycycliques (HAPs) Evaluation de la relation dose-réponse pour des effets cancérigènes: Approche substance par substance et approche par mélange - Evaluation de la relation dose-réponse pour des effets non cancérigènes: valeurs toxiques de référence. Institut national de l'environnement industriel et des risques, Verneuil-en-Halatte
Irons TD, Kelly PE, Hunter DL, MacPhail RC, Padilla S (2013) Acute administration of dopaminergic drugs has differential effects on locomotion in larval zebrafish. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 103(4):792–813
Kim Y, Cooper KR (1999) Toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in the embryos and newly hatched larvae of the Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Chemosphere 39(3):527–538
Kiparissis Y, Akhtar P, Hodson PV, Brown RS (2003) Partition-controlled delivery of toxicants: a novel in vivo approach for embryo toxicity testing. Environ Sci Technol 37(10):2262–2266. doi:10.1021/es026154r
Le Bihanic F, Perrichon P, Le Menach K, Budzinski H, Cousin X, Cachot J (2014) Development of a reference artificial sediment for chemical testing adapted to the MELA sediment contact assay. Environ Sci Pollut Res this issue.
Le Bihanic F, Morin B, Cousin X, Le Menach K, Budzinski H, Cachot J (in revision) Developmental toxicity of PAH mixtures in fish early life stages. Part I: adverse effects in Rainbow T. Environ Sci Pollut Res this issue
Legendre P, Legendre L (1998) Numerical Ecology. Elsevier Science BV, Amsterdam
Morin B, Filatreau J, Vicquelin L, Barjhoux I, Guinel S, Leray-Forget J, Cachot J (2011) Detection of DNA damage in yolk-sac larvae of the Japanese Medaka, Oryzias latipes, by the comet assay. Anal Bioanal Chem 399(6):2235–2242. doi:10.1007/s00216-010-4602-y
Nisbet ICT, LaGoy PK (1992) Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 16(3):290–300
OECD (1992) Guidelines for the testing of chemicals fish early life stage toxicity test, Test No. 210. Section 2: Effects on biotic systems. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
Orrego R, Guchardi J, Beyger L, Krause R, Holdway D (2011) Comparative embryotoxicity of pulp mill extracts in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), American flagfish (Jordanella floridae) and Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Aquat Toxicol 104(3–4):299–307
Rhodes S, Farwell A, Mark Hewitt L, MacKinnon M, George Dixon D (2005) The effects of dimethylated and alkylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on the embryonic development of the Japanese medaka. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 60(3):247–258
Rocha PS, Luvizotto GL, Kosmehl T, Böttcher M, Storch V, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2009) Sediment genotoxicity in the Tietê River (São Paulo, Brazil): in vitro comet assay versus in situ micronucleus assay studies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72(7):1842–1848
Safe S (1993) Development of bioassays and approaches for the risk assessment of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlodibenzo-p-dioxin and related compounds. Environ Health Perspect Suppl 101(3):317–325
Strähle U, Scholz S, Geisler R, Greiner P, Hollert H, Rastegar S, Schumacher A, Selderslaghs I, Weiss C, Witters H, Braunbeck T (2012) Zebrafish embryos as an alternative to animal experiments—a commentary on the definition of the onset of protected life stages in animal welfare regulations. Reprod Toxicol 33(2):128–132
Sundberg H, Ishaq R, Akerman G, Tjarnlund U, Zebuhr Y, Linderoth M, Broman D, Balk L (2005) A bio-effect directed fractionation study for toxicological and chemical characterization of organic compounds in bottom sediment. Toxicol Sci 84(1):63–72. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfi067
Turcotte D, Akhtar P, Bowerman M, Kiparissis Y, Brown S, Hodson PV (2011) Measuring the toxicity of alkyl-phenanthrenes to early life stages of medaka (Oryzias latipes) using partition-controlled delivery. Environ Toxicol Chem 30(2):487–495
Turner A, Rawling MC (2001) The influence of salting out on the sorption of neutral organic compounds in estuaries. Water Res 35(18):4379–4389
Van den Berg M, Birnbaum LS, Denison M, De Vito M, Farland W, Feeley M, Fiedler H, Hakansson H, Hanberg A, Haws L, Rose M, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tohyama C, Tritscher A, Tuomisto J, Tysklind M, Walker N, Peterson RE (2006) The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol Sci 93(2):223–241
Vicquelin L, Jl L-F, Peluhet L, Le Menach K, Deflandre B, Anschutz P, Etcheber H, Morin B, Budzinski H, Cachot J (2011) A new spiked sediment assay using embryos of the Japanese medaka specifically designed for a reliable toxicity assessment of hydrophobic chemicals. Aquat Toxicol 105(3–4):235–245
Vignet C, Bégout ML, Péan S, Lyphout L, Leguay D, Cousin X (2013) Systematic screening of behavioral responses in two zebrafish strains. Zebrafish 10(3):365–375
Wassenberg DM, Di Giulio RT (2004) Synergistic embryotoxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists with cytochrome P4501A inhibitors in Fundulus heteroclitus. Environ Health Perspect 112:1658–1664
Wassenberg DM, Nerlinger AL, Battle LP, Giulio RTD (2005) Effects of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon heterocycles, carbazole and dibenzothiophene, on in vivo and in vitro cyp1a activity and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-derived embryonic deformities. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:2526–2532
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the French National Agency for Research’s “Contaminant, Ecosystème et santé” program, as part of the ConPhyPoP (2009–002) research project. It was also included in the LABEX COTE cluster of excellence for continental and coastal ecosystems. Following the project, Florane Le Bihanic received PhD fellowship from “Ministère de l’Enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche”. The authors wish to thank CEDRE for providing oils, as well as Laure Landi for laboratory management.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Henner Hollert
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le Bihanic, F., Clérandeau, C., Le Menach, K. et al. Developmental toxicity of PAH mixtures in fish early life stages. Part II: adverse effects in Japanese medaka. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 13732–13743 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2676-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2676-3