Abstract
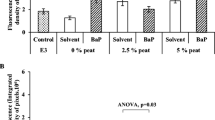
A wide variety of organic contaminants including pesticides, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) have previously been detected in surface waters in the river Ythan catchment, North East Scotland UK. While the concentrations detected were below Water Framework Directive Environmental Quality Standards (WFD-EQSs) environmental exposures to the diverse mixtures of contaminants, known and unknown, may pose chronic and/or sublethal effects to non target organisms. The present study assessed the embryo and algal toxicity potential of freely dissolved organic contaminants from the Ythan catchment using silicone rubber passive sampling devices (SR-PSDs) and miniaturised bioassay techniques. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos and marine phytoplankton species (Diacronema lutheri) were exposed to extracts from SR-PSDs deployed at different locations along the river Ythan and an undeployed procedural blank. Statistically significant developmental and algal toxicities were measured in all tests of extracts from deployed samples compared with the procedural blanks. This indicates environmental exposure to, and the combined toxicity potential of, freely dissolved organic contaminants in the catchment. The present and previous studies in the Ythan catchment, coupling SR-PSDs and bioassay techniques, have both helped to understand the interactions and combined effects of dissolved organic contaminants in the catchment. They have further revealed the need for improvement in the techniques currently used to assess environmental impact.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandow N, Altenburger R, Lübcke-von Varel U, Paschke A, Streck G, Brack W (2009) Partitioning-based dosing: an approach to include bioavailability in the effect-directed analysis of contaminated sediment samples. Environ Sci Technol 43:3891–3896
Barron MG, Carls MG, Heintz R, Rice SD (2004) Evaluation of fish early life-stage toxicity models of chronic embryonic exposures to complex polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon mixtures. Toxicol Sci 78:60–67
Bauer U (2008) Evaluation of silicone-based passive samplers for monitoring organic aquatic pollutants. Griffith University, Brisbane, Australia, Dissertation
Bellas J, Beiras R, Marino-Balsa JC, Fernandez N (2005) Toxicity of organic compounds to marine invertebrate embryos and larvae: a comparison between the sea urchin embryogenesis bioassay and alternative test species. Ecotoxicol 14:337–353
Bendif EM, Probert I, Hervé A, Billard C, Goux D, Lelong C, Cadoret JP, Véron B (2011) integrative taxonomy of the pavlovophyceae (Haptophyta): a reassessment. Protist 162:738–761
Booij K, Smedes F, van Weerlee EM (2002) Spiking of performance reference compounds in low density polyethylene and silicone passive water samplers. Chemosphere 46:1157–1161
Booij K, Vrana B, Huckins JN (2007) Theory, modelling and calibration of passive samplers used in water monitoring. In: Greenwood R, Mills GA, Vrana B (eds) Passive sampling techniques in environmental monitoring, 1st edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 141–169
Braunbeck T, Boettcher M, Hollert H, Kosmehl T, Lammer E, Leist E, Rudolf M, Seitz N (2005) Towards an alternative for the acute fish LC(50) test in chemical assessment: the fish embryo toxicity test goes multi-species-an update. ALTEX 22:87–102
DeLorenzo ME, Scott GI, Ross PE (2001) Toxicity of pesticides to aquatic microorganisms: a review. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:84–98
DIN (2001) German standard methods for the examination of water, waste water and sludge-subanimal testing (group T): Part 6. Toxicity to fish. Determination of the non-acute-poisonous effect of waste water to fish eggs by dilution limits (T 6). DIN 38415–6. German Standardization Organization
EC (2000) Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Off J Eur Commun L 327:1–73
EC (2011). Proposal for a Directive 2011/0429/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as regards priority substances in the field of water policy. Off J Eur Commun 2011;876. [COM final, 2011].
Emelogu ES, Pollard P, Robinson CD, Smedes F, Webster L, Oliver IW, McKenzie C, Seiler T, Hollert H, Moffat CF (2013a) Investigating the significance of dissolved organic contaminants in aquatic environments: coupling passive sampling with in vitro bioassays. Chemosphere 90:210–219
Emelogu ES, Pollard P, Robinson CD, Webster L, McKenzie C, Napier F, Steven L, Moffat CF (2013b) Identification of selected organic contaminants in streams associated with agricultural activities and comparison between autosampling and silicone rubber passive sampling. Sci Total Environ 445:261–272
Emelogu ES, Pollard P, Dymond P, Robinson CD, Webster L, McKenzie C, Dobson J, Bresnan E, Moffat CF (2013c) Occurrence and potential combined toxicity of dissolved organic contaminants in the Forth estuary and Firth of Forth, Scotland assessed using passive samplers and an algal toxicity test. Sci Total Environ 461–462:230–239
EC (2010) Directive 2010/63/EU of the European parliament and of the council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. Off J EU L 276:33–79, 2010
Farwell A, Nero V, Croft M, Bal P, Dixon DG (2006) Modified Japanese medaka embryo-larval bioassay for rapid determination of developmental abnormalities. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 51:600–607
Green J (1975) The fine-structure and taxonomy of the haptophycean flagellate Pavlova lutheri (Droop) comb. nov. (=Monochrysis lutheri Droop). J Mar Biol Assoc U K 55:785–793
Greenwood R, Mills G, Vrana B (2007) Passive sampling techniques in environmental monitoring. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Greenwood R, Mills GA, Vrana B (2009) Review: Potential applications of passive sampling for monitoring non-polar industrial pollutants in the aqueous environment in support of REACH. J Chromatogr A 1216:631–639
Guillard RRL, Ryther JH (1962) Studies of marine planktonic diatoms: I. Cyclotella nana hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (cleve) gran. Can J Microbiol 8:229–239
Hallare A, Nagel K, Köhler H, Triebskorn R (2006) Comparative embryotoxicity and proteotoxicity of three carrier solvents to zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63:378–388
Heger S, Bluhm K, Agler MT, Maletz S, Schäffer A, Seiler T, Angenent LT, Hollert H (2012) Biotests for hazard assessment of biofuel fermentation. Energy Environ Sci 5:9778–9788
Hollert H, Keiter S, König N, Rudolf M, Ulrich M, Braunbeck T (2003) A new sediment contact assay to assess particle-bound pollutants using zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. J Soil Sediment 3:197–207
Huckins JN (2006) Monitors of organic chemicals in the environment : semipermeable membrane devices. Springer, New York, NY
Huckins JN, Tubergen MW, Manuweera GK (1990) Semi permeable membrane devices containing model lipid: a new approach to monitoring the bioavailability of lipophilic contaminants and estimating their bioconcentration potential. Chemosphere 20:533–552
Huckins JN, Petty JD, Lebo JA, Almeida FV, Booij K, Alvarez DA, Cranor WL, Clark RC, Mogensen BB (2002) Development of the permeability/performance reference compound approach for in situ calibration of semipermeable membrane devices. Environ Sci Technol 36:85–91
Hutchinson TH, Shillabeer N, Winter MJ, Pickford DB (2006) Acute and chronic effects of carrier solvents in aquatic organisms: a critical review. Aquat Toxicol 76:69–92
ISO (1989) Water quality––fresh water algal growth inhibition test with Scenedesmus subspicatus and Selenastrum capricornutum. International Organization of Standardization (ISO 8692:1989)
ISO (1995) Water quality––marine algal growth inhibition test with Skeletonema costatum and Phaeodactylum tricornutum. ISO International Organization of Standardization (ISO 10253:1995)
ISO (2007) Water quality – determination of the acute toxicity of waste water to zebrafish eggs. (Danio rerio). ISO International Organization of Standardization (ISO 15088:2007)
ISO (2012) Water quality—fresh water algal growth inhibition test with unicellular green algae. ISO International Organization of Standardization (ISO 8692:2012)
Kramer NI, Busser FJM, Oosterwijk MTT, Schirmer K, Escher BI, Hermens JLM (2010) Development of a partition-controlled dosing system for cell assays. Chem Res Toxicol 23:1806–1814
Lammer E, Carr GJ, Wendler K, Rawlings JM, Belanger SE, Braunbeck T (2009) Is the fish embryo toxicity test (FET) with the zebrafish (Danio rerio) a potential alternative for the fish acute toxicity test? Comput Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 149:196–209
Lee LEJ, Clemons JH, Bechtel DG, Caldwell SJ, Han KB, Pasitschniak-Arts M, Mosser DD, Bols NC (1993) Development and characterization of a rainbowtrout liver cell line expressing cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenaseactivity. Cell Biol Toxicol 9:279–294
Lohmann R, Booij K, Smedes F, Vrana B (2012) Use of passive sampling devices for monitoring and compliance checking of POP concentrations in water. Environ Sci Pollut R 19:1885–1895
Mayer P, Holmstrup M (2008) Passive dosing of soil invertebrates with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: limited chemical activity explains toxicity cutoff. Environ Sci Technol 42:7516–7521
Mayer P, Tolls JT, Hermens JLM, Mackay D (2003) Equilibrium sampling devices. Environ Sci Technol 37:184A–191A
Monteyne E, Roose P, Janssen CR (2013) Application of a silicone rubber passive sampling technique for monitoring PAHs and PCBs at three Belgian coastal harbours. Chemosphere 91:390–398
Nagel R (2002) DarT: The embryo test with the zebrafish Danio rerio—a general model in ecotoxicology and toxicology. ALTEX 19:38–48
OECD, (1992a) OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals. Section 2: Effects on biotic systems test no. 203: acute toxicity for fish. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris, France
OECD, (1992b) OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals. Section 2: Effects on biotic systems test no. 210: fish early-life stage toxicity test. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris, France
Reichenberg F, Mayer P (2006) Two complementary sides of bioavailability: accessibility and chemical activity of organic contaminants in sediments and soils. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:1239–1245
Rusina TP, Smedes F, Koblizkova M, Klanova J (2009) Calibration of silicone rubber passive samplers: experimental and modeled relations between sampling rate and compound properties. Environ Sci Technol 44:362–367
Sawasdee B, Köhler H (2009) Embryo toxicity of pesticides and heavy metals to the ramshorn snail, Marisa cornuarietis (Prosobranchia). Chemosphere 75:1539–1547
Schirmer K, Dixon D, Greenberg B, Bols N (1998) Ability of 16 priority PAHs to be directly cytotoxic to a cell line from the rainbow trout gill. Toxicology 127:129–141
Seiler TB, Rastall A, Leist E, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2006) Membrane dialysis extraction (MDE): a novel approach for extracting toxicologically relevant hydrophobic organic compounds from soils and sediments for assessment in biotests. J Soil Sediment 6:20–29
SEPA (2010) RBMP Water body information sheet for water body 23231 in North East Scotland. SEPA; 2010. [http://apps.sepa.org.uk/rbmp/pdf/23231.pdf. (Accessed 1004/2013).
SEPA (2011) Diffuse pollution monitored catchments (DPMC's) Ythan sites: Phase 2 characterisation report nitrates and pesticides impacts and pressures in the Ythan Catchment
Smedes F (2007) Monitoring of chlorinated biphenyls and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by passive sampling in concert with deployed mussels. In: Greenwood R, Mills G, Vrana B (eds) Passive sampling techniques in environmental monitoring. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 407–447
Smith KEC, Dom N, Blust R, Mayer P (2010) Controlling and maintaining exposure of hydrophobic organic compounds in aquatic toxicity tests by passive dosing. Aquat Toxicol 98:15–24
Strähle U, Scholz S, Geisler R, Greiner P, Hollert H, Rastegar S, Schumacher A, Selderslaghs I, Weiss C, Witters H (2012) Zebrafish embryos as an alternative to animal experiments—a commentary on the definition of the onset of protected life stages in animal welfare regulations. Reprod Toxicol 33:128–132
Tanneberger K, Rico-Rico A, Kramer NI, Busser FJM, Hermens JLM, Schirmer K (2010) Effects of solvents and dosing procedure on chemical toxicity in cell-based in vitro assays. Environ Sci Technol 44:4775–4781
Trimble A, Lydy M (2006) Effects of triazine herbicides on organophosphate insecticide toxicity in Hyalella azteca. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 51:29–34
Van der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:57–149
Vinturella AE, Burgess RM, Coull BA, Thompson KM, Shine JP (2004) Use of passive samplers tomimic uptake of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by benthic polychaetes. Environ Sci Technol 38:1154–1160
Vrana B, Allan IJ, Greenwood R, Mills GA, Dominiak E, Svensson K, Knutsson J, Morrison G (2005) Passive sampling techniques for monitoring pollutants in water. Trends Anal Chem 24:845–868
Acknowledgments
Funding to ESE from the Institute for Innovation, Design and Sustainability Research (IDEAS), Robert Gordon University, Aberdeen, UK is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Markus Hecker
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emelogu, E.S., Seiler, TB., Pollard, P. et al. Evaluations of combined zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo and marine phytoplankton (Diacronema lutheri) toxicity of dissolved organic contaminants in the Ythan catchment, Scotland, UK. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 5537–5546 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2488-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2488-x