Abstract
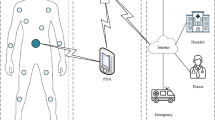
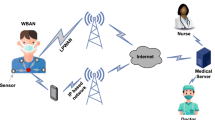
Wireless body area networks are captivating growing interest because of their suitability for wide range of applications. However, network lifetime is one of the most prominent barriers in deploying these networks for most applications. Moreover, most of these applications have stringent QoS requirements such as delay and throughput. In this paper, the modified superframe structure of IEEE 802.15.4 based MAC protocol is proposed which addresses the aforementioned problems and improves the energy consumption efficiency. Moreover, priority guaranteed CSMA/CA mechanism is used where different priorities are assigned to body nodes by adjusting the data type and size. In order to save energy, a wake-up radio based mechanism to control sleep and active modes of body sensors are used. Furthermore, a discrete time finite state Markov model to find the node states is used. Analytical expressions are derived to model and analyze the behavior of average energy consumption, throughput, packet drop probability, and average delay during normal and emergency data. Extensive simulations are conducted for analysis and validation of the proposed mechanism. Results show that the average energy consumption and delay are relatively higher during emergency data transmission with acknowledgment mode due to data collision and retransmission.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, A., Javaid, N., Khan, Z. A., Imran, M., & Alnuem, M. (2014). iA-MAC: improved Adaptive Medium Access Control protocol for Wireless Body Area Networks. In Proceedings of the 14th international symposium on communications and information technologies (pp. 156–160), Sept 26–26, 2014, Incheon, Korea.
Fang, G., & Dutkiewicz, E. (2009). BodyMAC: Energy efficient TDMA-based MAC protocol for wireless body area networks. In 9th International symposium on communications and information technology (pp. 1455–1459). IEEE, ISCIT, 2009.
Marinkovic, S., Spagnol, C., & Popovici, E. (2009). Energy-efficient TDMA-based MAC protocol for wireless body area networks In Third international conference on sensor technologies and applications. SENSORCOMM’09 (pp. 604–609). IEEE, 2009.
Semprebom, Tiago, Montez, C., & Vasques, F. (2013). (m, k)-firm pattern spinning to improve the GTS allocation of periodic messages in IEEE 802.15. 4 networks. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 1, 1–15.
Park, P., Marco, P. D., Fischione, C., & Johansson, K. H. (2013). Modeling and optimization of the IEEE 802.15. 4 protocol for reliable and timely communications. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 24(3), 550–564.
Pollin, S., Ergen, M., Ergen, S. C., Bougard, B., Perre, L., Moerman, I., et al. (2008). Performance analysis of slotted carrier sense IEEE 802.15.4 medium access layer. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communication, 7(9), 33593371.
Johansson, P., Kazantzidis, M., Kapoor, R., & Gerla, M. (2001). Bluetooth: An enabler for personal area networking. IEEE Network, 15(5), 28–37. doi:10.1109/65.953231.
Bangash, J. I., Abdullah, A. H., Anisi, M. H., & Khan, A. W. (2014). A survey of routing protocols in wireless body sensor networks. Sensors, 14(1), 1322–1357.
Cavallari, R., Martelli, F., Rosini, R., Buratti, C., & Verdone, R. (2014). A survey on wireless body area networks: Technologies and design challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 16(3), 1635–1657. doi:10.1109/SURV.2014.012214.00007.
Hayajneh, T., Almashaqbeh, G., Ullah, S., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2014). A survey of wireless technologies coexistence in WBAN: Analysis and open research issues. Wireless Networks, 20(8), 2165–2199. doi:10.1007/s11276-014-0736-8.
Ullah, S. (2013). RFID-enabled MAC protocol for WBAN. In IEEE international conference on communications (ICC) (pp. 6030–6034). IEEE, 2013.
Ullah, S., & Kwak, K. S. (2012). An ultra-low-power and traffic-adaptive medium access control protocol for wireless body area network. Journal of Medical Systems, 36(3), 1021–1030.
Ameen, M. A., Ullah, N., Chowdhury, M. S., Islam, S. R., & Kwak, K. (2012). A power efficient MAC protocol for wireless body area networks. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 1, 1–17.
Ullah, S., Higgins, H., Shen, B., & Kwak, K. S. (2010). On the implant communication and MAC protocols for WBAN. International Journal of Communication Systems, 23(8), 982–999.
Park, P., Marco, P. D., Fischione, C., & Johansson, K. H. (2013). Modeling and optimization of the IEEE 802.15.4 protocol for reliable and timely communications. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 24(3), 550–564. doi:10.1109/TPDS.2012.159.
Javaid, N., Ahmad, A., Rahim, A., Khan, Z. A., Ishfaq, M., & Qasim, U. (2014). Adaptive medium access control protocol for wireless body area networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks. doi:10.1155/2014/254397.
Rahim, A., Javaid, N., Aslam, M., Rahman, Z., Qasim, U., & Khan, Z. A. (2012) A comprehensive survey of MAC protocols for wireless body area networks. In Seventh international conference on broadband, wireless computing, communication and applications (BWCCA) (pp. 434–439), 12–14. doi:10.1109/BWCCA.2012.77.
Ullah, S., Imran, M., & Alnuem, M. (2014). A hybrid and secure priority-guaranteed MAC protocol for wireless body area network. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2014, 481761. doi:10.1155/2014/481761.
Liu, B., Yan, Z., & Chen, C. W. (2013). MAC protocol in wireless body area networks for E-health: Challenges and a context-aware design. IEEE Wireless Communications, 20(4), 64–72.
Park, P., Marco, P. D., Fischione, C., & Johansson, K. H. (2013). Modeling and optimization of the IEEE 802.15. 4 protocol for reliable and timely communications. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 24(3), 550–564.
Park, P., Fischione, C., & Johansson, K. H. (2013). Modeling and stability analysis of hybrid multiple access in the IEEE 802.15.4 protocol. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN), 9(2), 13–30.
Almashaqbeh, G., Hayajneh, T., Vasilakos, A. V., & Mohd, B. J. (2014). QoS-aware health monitoring system using cloud-based WBANs. Journal of Medical Systems, 38(121), 1–20. doi:10.1007/s10916-014-0121-2.
Almashaqbeh, G., Hayajneh, T., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2014) A cloud-based interference-aware remote health monitoring system for non-hospitalized patients. In Proceedings of the IEEE 12th global communication conference (IEEE Globecom’14), Austin, TX, USA, 2014.
Khan, Z. A., Rasheed, M. B., Javaid, N., & Robertson, B. (2014). Effect of packet interarrival time on the energy consumption of beacon enabled MAC protocol for body area networks. Procedia Computer Science, 32, 579–586.
Pletcher, N., Gambini, S., & Rabaey, J. M. (2008). A 2 GHz 52 W wake-up receiver with 72 dBm sensitivity using uncertain-IF architecture. In Conference proceedings, IEEE international solidstate circuits conference, San Francisco, CA (pp 525–526), 2008.
Ansari, J., Pankin, D., & Mhnen, P. (2009). Radio-triggered wake-ups with addressing capabilities for extremely low power sensor network applications. International Journal of Wireless Information Networks, 16(3), 118–130.
Gu, L., & Stankovic, J. A. (2004) Radio-triggered wake-up capability for sensor networks. In Proceedings of 10th IEEE Real-time and embedded technology and applications symposium, RTAS (pp. 27–36), 25–28. doi:10.1109/RTTAS.2004.1317246.
Bas, V. D., Kavelaars, W., & Langendoen, K. (2009). A prototype low-cost wakeup radio for the 868 MHz band. International Journal of Sensor Networks, 5(1), 22–32.
Zhu, J., Chunfend, L., & Tao, Z. (2013). Performance analyses and improvements for IEEE 802.15.4 CSMA/CA scheme in wireless multihop sensor networks based on HTC algorithm. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2013, 452423. doi:10.1155/2013/452423.
Enz, C. C., Hoiydi, A. E., Decotignie, J. D., & Peiris, V. (2004). WiseNET: An ultralow power wireless sensor network solution. Computer, 37(8), 62–70. doi:10.1109/MC.2004.109.
Levy, Y., & Yechiali, U. (1975). Utilization of idle time in an M/G/1 queueing system. Management Science, 22(2), 202–211.
Hayes, J. F., & Babu, T. V. J. G. (2004). Modeling and analysis of telecommunications networks. New York: Wiley.
Pletcher, N., Gambini, S., & Rabaey, J. (2007). A 65 μW, 1.9 GHz RF to digital baseband wakeup receiver for wireless sensor nodes. In Custom integrated circuits conference (CICC), Sep 16–19, San Jose, CA.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this research through Research Group Project NO. (RG#1435-051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rasheed, M.B., Javaid, N., Imran, M. et al. Delay and energy consumption analysis of priority guaranteed MAC protocol for wireless body area networks. Wireless Netw 23, 1249–1266 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-016-1199-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-016-1199-x