Abstract
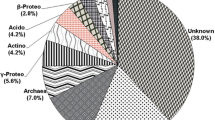
The present study aimed to investigate variations in the diversity of the indigenous bacterial and fungal populations in contaminated soil. Soil samples were collected from highly contaminated agricultural soil adjacent to an industrial drain in the Nile Delta named the “Defsho” drain, located at the city of Kafr El-Dawar, 20 km south of Alexandria (Longitude 30.12917 and Latitude 31.13972). PCR has become a popular tool for the retrieval of the natural environmental rRNA genes that represent native microbial species. Soil DNA was extracted and the 16S and 18S rRNA genes were amplified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and gene cloning. About 5,000 clones were obtained and genotyped using denaturing high performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC) to fingerprinting the biodiversity in the soil. Clones, which give different peaks with DHPLC, were then subjected to partial sequencing. Five prokaryotic and two eukaryotic out of 1,000 recombinant clones were randomly selected and further studied by DNA sequencing analysis. These clones were designated PT and ET for prokaryotes and eukaryotes, respectively. Results confirmed the hazardous effects of pollution on the distribution and biodiversity of soil microorganisms where most of the native beneficial microorganisms were disappeared or non-cultured under these stressed conditions compared to the normal non-polluted soils in the same governorate which is certainly affecting soil fertility and productivity. Five prokaryotic (PT) and two eukaryotic (ET) recombinant clones were randomly selected and further studied by DNA sequence analysis. DNA sequencing revealed that most of the identified bacteria are members of the class Proteobacteria; subdivision Gammaproteobacteria; order Enterobacteriales and family Enterobacteriaceae. Two PT clones (PT2 and PT4) were identified as Shigella flexneri 301-AF499895; members of PT1 and PT3 were related to Escherichia sp. and the uncultured bacterium S000009863 while PT5 was uncultured bacterium-S000331457 in addition to unclassified member of Desulfobacteriaceae, subdivision Deltaproteobacteria. ET1 was uncultured Trichocomaceae clone HC-B1/1-AF548306 and ET2 represents uncultured fungus clone SBS8w47f-AY681463, respectively. In conclusion, the significant decline in the genetic diversity in Defsho soil emphasized the hazardous effect of the industrial pollution on the biodiversity, stability and functioning of the native microbial population. Results also proved the efficiency of molecular characterization as precise and fast techniques for determining soil biodiversity compared to the traditional cultivation methods.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Salam H, Shameseldin A, Hafez EE (2006) PAH degradation by two native Egyptian strains Flavobacterium sp. and Pseudomonas putida. J Appl Sci Res 2:1092–1098
Bååth E, Diaz-Ravina M, Frostegard A, Campbell CD (1998) Effect of metal-rich sludge amendments on the microbial community. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:238–245
Bater JE (1996) Micro- and macro-arthropods. In: Hall GS (ed) Methods for the examination of organismal diversity in soils and sediments. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 163–174
Betancourt DA, Loveless TM, Brown JW, Bishop PE (2008) Characterization of diazotrophs containing Mo-independent nitrogenases, isolated from diverse natural environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(11):3471–3480. doi:10.1128/AEM.02694-07
Black CA (ed) (1965) Methods of soil analysis. Part 1 and 2. Agronomy 9. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, Wisconsin, USA
Brookes PC, Heijnen CE, McGrath SP, Vance ED (1986) Soil microbial biomass estimates in soils contaminated with metals. Soil Biol Biochem 18:383–388. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(86)90042-8
Brussaard L (1998) Soil fauna, guilds, functional groups and ecosystem processes. Appl Soil Ecol 263:1–13
Caruso T, Pigino G, Bernini F, Bargagli R, Migliorini M (2008) Biodiversity and conservation in Europe. In: Hawksworth DL, Bull AT (eds) vol 7. Springer, Netherlands, pp 35–43. ISBN 978-1-4020-6864-5 (Print) 978-1-4020-6865-2 (Online)
Chaudri AM, McGrath SP, Giller KE (1992) Survival of the indigenous population of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii in soil spiked with Cd, Zn Cu and Ni salts. Soil Biol Biochem 24:625–632. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(92)90040-5
Chaudri AM, McGrath SP, Giller KE, Rietz E, Sauerbeck D (1993) Enumeration of indigenous Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii in soils previously treated with metal sewage sludge. Soil Biol Biochem 25:301–309. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(93)90128-X
Claassens S, Jansen PJ, Van Rensburg L (2006) Soil microbial community structure of coal mine discard under rehabilitation. Water Air Soil Pollut 174:355–366. doi:10.1007/s11270-006-9125-y
Colles FM, Dingle KE, Cody AJ, Maiden MCJ (2008) Comparison of Campylobacter populations in wild geese with those in starlings and free-range poultry on the same farm. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(11):3583–3590. doi:10.1128/AEM.02491-07
Cragg RG, Bardgett RD (2001) How changes in soil faunal diversity and composition within a trophic group influence decomposition processes. Soil Biol Biochem 33:2073–2081. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(01)00138-9
Crowley DE, Dungan RS (2002) Encyclopedia of environmental microbiology, 4. Interscience, Gabriel Bitton Wiley, pp 1878–1892
De Deyn GB, Raaijmakers CE, Zoomer HR, Berg MP, Rulter PC, Verhoef HA, Bezemer TM, Van der Putten WH (2003) Soil invertebrate fauna enhances grassland succession and diversity. Nature 422:711–713. doi:10.1038/nature01548
Del Val C, Barea JM, Azcón-Aguilar C (1999) Assessing the tolerance to heavy metals of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi isolated from sewage sludge-contaminated soils. Appl Soil Ecol 11:261–269. doi:10.1016/S0929-1393(98)00153-X
El-Sokkary IH, Låg J (1980) Status of trace elements in Egyptian soils on wheat grains. Beitr Trop Landwirtsch Veterinarmed 18:35–47
Franco CMM, McClure NC (1998) Isolation of microorganisms for biotechnological application. J Microbiol Biotechnol 8:101–110. doi:10.1159/000030634
Frey B, Stemmer M, Widmer F, Luster J, Sperisen C (2006) Microbial activity and community structure of a soil after heavy metal contamination in a model forest ecosystem. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1745–1756. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.11.032
Frostegård A, Tunlid A, Bååth E (1996) Changes in microbial community structure during long-term incubation of two soils experimentally contaminated with metals. Soil Boil Biochem 28:55–63. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(95)00100-X
Gadd GM (1993) Interaction of fungi with toxic metals. New Phytol 124:25–60. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1993.tb03796.x
Giller KE, Witter E, MacGrath SP (1998) Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1389–1414. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(97)00270-8
Harris S, Morris P, Wray S, Yalden D (1995) A review of British mammals: population estimates and conservation status of British mammals other than Cetaceans. Joint Nature Conservation Committee, Peterborough
Hatamoto M, Imachi H, Yashiro Y, Ohashi A, Harada H (2008) Detection of active butyrate-degrading microorganisms in methanogenic sludges by RNA-based stable isotope probing. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(11):3610–3614. doi:10.1128/AEM.00045-08
Heywood VH (1995) Global biodiversity assessment. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hughes MN, Poole RK (1989) The functions of metals in microorganisms. Metals and microorganisms. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 22–27
Jones CG, Lawton JH, Shachak M (1994) Organisms as ecosystem engineers. Oikos 69:373–386. doi:10.2307/3545850
Joynt J, Bischoff M, Turco R, Konopka A, Nakatsu CH (2006) Microbial community analysis of soils contaminated with lead, chromium and petroleum hydrocarbons. Microbial Ecol 51:209–219. doi:10.1007/s00248-005-0205-0
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (1992) Trace element in soils and plants, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boston, USA
Keanel B, Collier MH, Rogstad SH (2005) Pollution and genetic structure of North American populations of the common dandelion (Taraxacum Officinale). Environ Monit Assess 105:341–357. doi:10.1007/s10661-005-4333-2c_Springer
Lynch JM, Benedetti A, Insam H, Nuti MP, Smalla K, Torsvik V, Nannipieri P (2004) Microbial diversity in soil: ecological theories, the contribution of molecular techniques and the impact of transgenic plants and transgenic microorganisms. Biol Fertil Soils 40:363–385. doi:10.1007/s00374-004-0784-9
Martino E, Turnau K, Girlanda M, Bonfante P, Perroto S (2000) Ercoid mycorrhizal fungi from heavy metal polluted soils: their identification and growth in the presence of zinc ions. Mycol Res 104:338–344. doi:10.1017/S0953756299001252
McGrath SP, Chaudri AM, Giller KE (1995) Long term effects of metals in sewage sludge on soils, microorganisms and plants. J Ind Microbiol 14:94–104. doi:10.1007/BF01569890
Mocali S, Paffetti D, Emiliani G, Benedetti A, Fani R (2008) Diversity of heterotrophic aerobic cultivable microbial communities of soils treated with fumigants and dynamics of metabolic, microbial, and mineralization quotients. Biol Fertil Soils 44:557–569. doi:10.1007/s00374-007-0235-5
Negraa C, Rossa DS, Lanzirottib A (2005) Oxidizing behavior of soil manganese: interactions among abundance, oxidation state, and pH. J Soil Sci Soc Am 1(69):95–97
Norton JM, Klotz MG, Stein LY, Arp DJ, Bottomley PJ, Chain PSG, Hauser LJ, Land ML, Larimer FW, Shin MW, Starkenburg SR (2008) Complete genome sequence of Nitrosospira multiformis, an ammonia-oxidizing bacterium from the soil environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(11):3559–3572. doi:10.1128/AEM.02722-07
Ogram A, Sayler GS, Barkay T (1987) The extraction and purification of microbial DNA from sediments. J Microbiol Methods 7:57–66. doi:10.1016/0167-7012(87)90025-X
Pace NR (1997) A molecular view of microbial diversity and the biosphere. Science 272:734–740. doi:10.1126/science.276.5313.734
Page AL, Keeney DR, Miller RH (1982) Method of soil analysis, Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn, No. 9 in the series Agronomy ASA, SSSA. Pub. Madison, Wisconsin, USA
Pearson A, Pi Y, Zhao W, Li W, Li Y, Inskeep W, Perevalova A, Romanek C, Li S, Zhang CL (2008) Factors controlling the distribution of archaeal tetraethers in terrestrial hot springs. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(11):3523–3532. doi:10.1128/AEM.02450-07
Presing M, Balogh K, Salanki J (1993) Cadmium uptake and depuration in different organs of Lymnaea stagnalis L. and the effect of cadmium on the natural zinc level. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 24:28–34. doi:10.1007/BF01061086
Ranjard L, Brothier E, Nazaret S (2000) Sequencing bands of ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis fingerprints for characterization and microscale distribution of soil bacterium populations responding to mercury spiking. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5334–5339. doi:10.1128/AEM.66.12.5334-5339.2000
Sallam A, Steinbüchel A (2008) Anaerobic and aerobic degradation of Cyanophycin by the denitrifying bacterium Pseudomonas alcaligenes strain DIP1 and role of three other coisolates in a mixed bacterial consortium. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(11):3434–3443. doi:10.1128/AEM.02575-07
Sánchez-Moreno S, Camargol JA, Navas A (2006) Ecotoxicological assessment of the impact of residual heavy metals on soil nematodes in the Guadiamar River Basin (Southern Spain). Environ Monit Assess 116:245–262. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-7398-7
Sims JT, Kline JS (1991) Chemical fractionation and plant uptake of heavy metals in soils amended with sewage sludge. J Environ Qual 20:387–395
Stegmann R (2001) Treatment of contaminated soil: fundamentals, analysis, applications. Springer Verlag, Berlin
Sun Q, He ZL, Yang XE, Shentu JL (2007) Microbiological response to copper contamination of a paddy soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 78:469–473. doi:10.1007/s00128-007-9213-8
Swift MJ (1999) Towards the second paradigm: integrated biological management of soil. In: Siqueira JO, Moreira FMS, Lopes AS, Guilherme LRG, Faquin V, Furtani Neto AE, Carvalho JG (eds) Interrelação Fertilidade Biologia do Solo e Nutrição de Plantas. UFLA, Lavras, Brazil, pp 11–24
Thompson JD, Higgins D, Gibson TJ (1994) ClustalW: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680. doi:10.1093/nar/22.22.4673
Tobor-Kaplon MA, Bloem J, Ro¨ Mkensi PFAM, De Rutter PC (2006) Functional stability of microbial communities in contaminated soils near a zinc smelter (Budel, The Netherlands). Ecotoxicol 15:187–197. doi:10.1007/s10646-005-0050-4
Van der Heijden MGA, Klinonomos JN, Ursic M, Moutoglis P, Streitwolf-Engel R, Boller T, Wiemken A, Sanders IR (1998) Mycorrhizal fungal diversity determines plant biodiversity, ecosystem variability and productivity. Nature 396:69–72. doi:10.1038/23932
Vargha B, Otvos E, Tuba Z (2002) Investigations on ecological effects of heavy metal pollution in Hungary by moss-dwelling water bears (Tardigrada), as bioindicators. Ann Agric Environ Med 9:141–146
Wang J, Ma T, Zhao L, Lv J, Li G, Zhang H, Zhao B, Liang F, Liu R (2008) Monitoring exogenous and indigenous bacteria by PCR-DGGE technology during the process of microbial enhanced oil recovery. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:619–628. doi:10.1007/s10295-008-0326-9
Ward RD, Morton IE, Brazil RP, Trumper S, Falcão AL (1990) Preliminary laboratory and field trials of a heated pheromone trap for the sand fly Lutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera: Psychodidae). Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 85:445–452
Wilson SM, Rakhit S, Murdoch R et al (1996) Activation of apical P2U purine receptors permits inhibition of adrenaline-evoked cyclic AMP accumulation in cultured equine sweat gland epithelial cells. J Exp Biol 199:2153–2160
Wolters V (2001) Biodiversity of soil animals and its function. Eur J Soil Biol 37:221–227. doi:10.1016/S1164-5563(01)01088-3
Yin H, Cao L, Qiu G, Wang D, Kellogg L, Zhou J, Liu X, Dai Z, Ding J, Liu X (2008) Molecular diversity of 16S rRNA and gyrB genes in copper mines. Arch Microbiol 189:101–110. doi:10.1007/s00203-007-0298-6
Zhang Y, Dong J, Yang Z, Zhang S, Wang Y (2008) Phylogenetic diversity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in mangrove sediments assessed by PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Arch Microbiol 190(1):19–28. doi:10.1007/s00203-008-0359-5
Zhao X, Yang L, Chen C et al (2006) Microbial diversity in lake sediments detected by PCR-DGGE. Front Biol China 26(11):3610–3616. doi 10.1007/s11515-008-0044-8. Translated from Acta Ecologica Sinica
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the NSF; BIO8-001-004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hafez, E.E., Elbestawy, E. Molecular characterization of soil microorganisms: effect of industrial pollution on distribution and biodiversity. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25, 215–224 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9881-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9881-5