Abstract
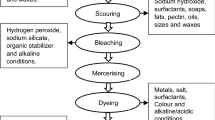
The contamination of soils and waters by dye-containing effluents is of environmental concern. Due to the increasing awareness and concern of the global community over the discharge of synthetic dyes into the environment and their persistence there, much attention has been focused on the remediation of these pollutants. Among the current pollution control technologies, biodegradation of synthetic dyes by different microbes is emerging as an effective and promising approach. The bioremediation potentials of many microbes for synthetic dyes have been demonstrated and those of others to be explored in future. The biodegradation of synthetic dyes is an economic, effective, biofriendly, and environmentally benign process. Bioremediation of xenobiotics including synthetic dyes by different microbes will hopefully prove a green solution to the problem of environmental soil and water pollution in future. This review paper discusses comprehensively the science and arts of biodegradation of synthetic dyes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedin, R. M. A. (2009). Decolorization and biodegradation of crystal violet and malachite green by Fusarium solani (Martius) Saccardo. A comparative study on biosorption of dyes by the dead fungal biomass. American-Eurasian Journal of Botany, 2, 01–15.
Ali, H., Ahmad, W., & Haq, T. (2009). Decolorization and degradation of malachite green by Aspergillus flavus and Alternaria solani. African Journal of Biotechnology, 8, 1574–1576.
An, S. Y., Min, S. K., Cha, I. H., Choi, Y. L., Cho, Y. S., Kim, C. H., et al. (2002). Decolorization of triphenylmethane and azo dyes by Citrobacter sp. Biotechnology Letters, 24, 1037–1040.
Annuar, M. S. M., Adnan, S., Vikineswary, S., & Chisti, Y. (2009). Kinetics and energitics of azo dye decolorization by Pycnoporus sanguineus. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 202, 179–188.
Bafana, A., Krishnamurthi, K., Devi, S. S., & Chakrabarti, T. (2008). Biological decolorization of C. I. Direct Black 38 by E. gallinarum. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 157, 187–193.
Bafana, A., Chakrabarti, T., Muthal, P., & Kanade, G. (2009). Detoxification of benzidine-based azo dye by E. gallinarum: Time-course study. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72, 960–964.
Chander, M., & Arora, D. S. (2007). Evaluation of some white-rot fungi for their potential to decolorize industrial dyes. Dyes and Pigments, 72, 192–198.
Chang, J. S., Kuo, T. S., Chao, Y. P., Ho, J. Y., & Lin, P. J. (2000). Azo dye decolorization with a mutant Escherichia coli strain. Biotechnology Letters, 22, 807–812.
Chen, H. (2006). Recent advances in azo dye degrading enzyme research. Current Protein and Peptide Science, 7, 101–111.
Chen, K. C., Wu, J. Y., Liou, D. J., & Huang, S. C. J. (2003). Decolorization of the textile dyes by newly isolated bacterial strains. Journal of Biotechnology, 101, 57–68.
Chen, C. C., Liao, H. J., Cheng, C. Y., Yen, C. Y., & Chung, Y. C. (2007). Biodegradation of crystal violet by Pseudomonas putida. Biotechnology Letters, 29, 391–396.
Chen, C. H., Chang, C. F., Ho, C. H., Tsai, T. L., & Liu, S. M. (2008). Biodegradation of crystal violet by a Shewanella sp. NTOU1. Chemosphere, 72, 1712–1720.
Couto, S. R. (2009). Dye removal by immobilized fungi. Biotechnology Advances, 27, 227–235.
Dafale, N., Rao, N. N., Meshram, S. U., & Wate, S. R. (2008). Decolorization of azo dyes and simulated dye bath wastewater using acclimatized microbial consortium-Biostimulation and halo tolerance. Bioresource Technology, 99, 2552–2558.
Dawkar, V. V., Jadhav, U. U., Ghodake, G. S., & Govindwar, S. P. (2009). Effect of inducers on the decolorization and biodegradation of textile azo dye Navy blue 2GL by Bacillus sp. VUS. Biodegradation, 20, 777–787.
Eichlerova, I., Homolka, L., & Nerud, F. (2006). Synthetic dye decolorization capacity of white rot fungus Dichomitus squalens. Bioresource Technology, 97, 2153–2159.
Enayatzamir, K., Tabandeh, F., Yakhchali, B., Alikhani, H. A., & Couto, S. R. (2009). Assessment of the joint effect of laccase and cellobiose dehydrogenase on the decoloration of different synthetic dyes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 169, 176–181.
Environmental Protection Agency. (1997). Profile of the textile industry. Washington: EPA.
Fernando, T., & Aust, S. D. (1994). Biodegradation of toxic chemicals by white rot fungi. In G. R. Chaudhry (Ed.), Biological degradation and bioremediation of toxic chemicals (pp. 386–402). London: Chapman and Hall.
Forgacs, E., Cserhati, T., & Oros, G. (2004). Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: a review. Environment International, 30, 953–971.
Forss, J., & Welander, U. (2009). Decolorization of reactive azo dyes with microorganisms growing on soft wood chips. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 63, 752–758.
Fu, Y., & Viraraghavan, T. (2001). Fungal decolorization of dye wastewaters: A review. Bioresource Technology, 79, 251–262.
Gopinath, K. P., Sahib, H. A. M., Muthukumar, K., & Velan, M. (2009). Improved biodegradation of Congo red by Bacillus sp. Bioresource Technology, 100, 670–675.
Hai, F. I., Yamamoto, K., Nakajima, F., & Fukushi, K. (2008). Removal of structurally different dyes in submerged membrane fungi reactor-biosorption/PAC-adsorption, membrane retention and biodegradation. Journal of Membrane Science, 325, 395–403.
Hu, T. L. (1998). Degradation of azo dye RP2B by Pseudomonas luteola. Water Science and Technology, 38, 299–306.
Husseiny, S. M. (2008). Biodegradation of the reactive and direct dyes using Egyptian isolates. Journal of Applied Science and Research, 4, 599–606.
Jadhav, S. U., Kalme, S. D., & Govindwar, S. P. (2008). Biodegradation of Methyl red by Galactomyces geotrichum MTCC 1360. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 62, 135–142.
Jin, X., Liu, G., Xu, Z., & Yao, W. (2007). Decolorization of a dye industry effluent by Aspergillus fumigatus XC6. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 74, 239–243.
Jirasripongpun, K., Nasanit, R., Niruntasook, J., & Chotikasatian, B. (2007). Decolorization and degradation of C. I. Reactive Red 195 by Enterobacter sp. Thammasat. International Journal of Science and Technology, 12, 6–11.
Kalyani, D. C., Telke, A. A., Dhanve, R. S., & Jadhav, J. P. (2009). Ecofriendly biodegradation and detoxification of Reactive Red 2 textile dye by newly isolated Pseudomonas sp. SUK1. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163, 735–742.
Kaushik, P., & Malik, A. (2009). Fungal dye decolorization: Recent advances and future potential. Environment International, 35, 127–141.
Khalid, A., Arshad, M., & Crowley, D. E. (2008). Decolorization of azo dyes by Shewanella sp. under saline conditions. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 79, 1053–1059.
Khehra, M. S., Saini, H. S., Sharma, D. K., Chadha, B. S., & Chimni, S. S. (2005). Decolorization of various azo dyes by bacterial consortium. Dyes and Pigments, 67, 55–61.
Kilic, N. K., Nielson, J. P., Yuce, M., & Donmez, G. (2007). Characterization of a simple bacterial consortium for effective treatment of wastewaters with reactive dyes and Cr (VI). Chemosphere, 67, 826–831.
King, B. R., Long, G. M., & Sheldon, H. K. (1997). Practical environmental bioremediation: The field guide. Boca Raton: CRC.
Knackmuss, H. J. (1996). Basic knowledge and perspectives of bioelimination of xenobiotic compounds. Journal of Biotechnology, 51, 287–295.
Kuhad, R. C., Sood, N., Tripathi, K. K., Singh, A., & Ward, O. P. (2004). Developments in microbial methods for the treatment of dye effluents. Advances in Applied Microbiology, 56, 185–213.
Lodato, A., Alfieri, F., Olivieri, G., Donato, A. D., Marzocchella, A., & Salatino, P. (2007). Azo-dye conversion by means of Pseudomonas sp. OX1. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 41, 646–652.
Lu, L., Zhao, M., Liang, S. C., Zhao, L. Y., Li, D. B., & Zhang, B. B. (2009). Production and synthetic dyes decolorization capacity of a recombinant laccase from Pichia pastoris. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 107, 1149–1156.
Luo, H., Liu, G., Zhang, R., & Jin, R. (2009). Phenol degradation in microbial fuel cells. Chemical Engineering Journal, 147, 259–264.
Machado, K. M. G., Compart, L. C. A., Morais, R. O., Rosa, L. H., & Santos, M. H. (2006). Biodegradation of reactive textile dyes by basidiomycetous fungi from Brazilian ecosystems. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 37, 481–487.
McMullan, G., Meehan, C., Conneely, A., Kirby, N., Robinson, T., Nigam, P., et al. (2001). Microbial decolorization and degradation of textile dyes. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 56, 81–87.
Melgoza, M. R., Cruz, A., & Buitron, G. (2004). Anaerobic/aerobic treatment of colorants present in textile effluent. Water Science and Technology, 50, 149–155.
Meyer, U. (1981). Biodegradation of synthetic organic colorants. FEMS Symposium, 12, 371–385.
Morris, J. M., Jin, S., Crimid, B., & Prudend, A. (2009). Microbial fuel cell in enhancing anaerobic biodegradation of diesel. Chemical Engineering Journal, 146, 161–167.
Nigam, P., McMullan, G., Banat, I. M., & Merchant, R. (1996). Decolorization of effluent from the textile industry by a microbial consortium. Biotechnology Letters, 18, 117–120.
Novotny, C., Svobodova, K., Erbanova, P., Cajthaml, T., Kasinath, A., Lang, E., et al. (2004a). Ligninolytic fungi in bioremediation: extracellular enzyme production and degradation rate. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 36, 1545–1551.
Novotny, C., Svobodova, K., Kasinath, A., & Erbanova, P. (2004b). Biodegradation of synthetic dyes by Irpex lacteus under various growth conditions. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 54, 215–223.
Nozaki, K., Beh, C. H., Mizuno, M., Isobe, T., Shiroishi, M., Kanda, T., et al. (2008). Screening and investigation of dye decolorization activities of basidiomycetes. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 105, 69–72.
O’Neill, C., Hawkes, F. R., Hawkes, D. L., Lourenco, N. D., Pinheiro, H. M., & Delee, W. (1999). Color in textile effluents sources, measurement, discharge consents and simulation: a review. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 74, 1009–1018.
Pandey, A., Singh, P., & Iyengar, L. (2007). Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 59, 73–84.
Parikh, A., & Madamwar, D. (2005). Textile dye decolorization using cyanobacteria. Biotechnology Letters, 27, 323–326.
Park, C., Lee, M., Lee, B., Kim, S. W., Chase, H. A., Lee, J., et al. (2007). Biodegradation and biosorption for decolorization of synthetic dyes by Funalia trogii. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 36, 59–65.
Parshetti, G., Kalme, S., Saratale, G., & Govindwar, S. (2006). Biodegradation of Malachite green by Kocuria rosea MTCC 1532. Acta Chimica Slovenica, 53, 492–498.
Pinheiro, H. M., Touraud, E., & Thomas, O. (2004). Aromatic amines from azo dye reduction: status review with emphasis on direct UV spectrophotometric detection in textile industry wastewaters. Dyes and Pigments, 61, 121–139.
Pointing, S. B. (2001). Feasibility of bioremediation by white-rot fungi. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 57, 20–33.
Pourbabaee, A. A., Malekzadeh, F., Sarbolouki, M. N., & Najafi, F. (2006). Aerobic decolorization and detoxification of a disperse dye in textile effluent by a new isolate of Bacillus sp. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 93, 631–635.
Rafii, F., Fraeankalin, W., & Cerniglia, C. E. (1990). Azo reductase activity of anaerobic bacteria isolated from human intestinal microflora. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 56, 2146–2151.
Raghukumar, C. (2000). Fungi from marine habitats: An application in bioremediation. Mycology Research, 104, 1222–1226.
Raghukumar, C., Chandramohan, D., Michel, F. C., Jr., & Reddy, C. A. (1996). Degradation of lignin and decolorization of paper mill bleach plant effluent (BPE) by marine fungi. Biotechnology Letters, 18, 105–106.
Ramalho, P. A. (2005). Degradation of dyes with microorganisms—Studies with ascomycete yeasts. PhD thesis, Biology Department, University of Minho.
Ramsay, J. A., & Nguyen, T. (2002). Decoloration of textile dyes by Trametes versicolor and its effect on dye toxicity. Biotechnology Letters, 24, 1757–1761.
Reddy, C. A. (1995). The potential of white rot fungi in the treatment of pollutants. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 6, 320–328.
Ren, S., Guo, J., Zeng, G., & Sun, G. (2006). Decolorization of triphenylmethane, azo and anthraquinone dyes by a newly isolated Aeromonas hydrophila strain. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 72, 1316–1321.
Robinson, T., McMullan, G., Marchant, R., & Nigam, P. (2001). Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresource Technology, 77, 247–255.
Saratale, R. G., Saratale, G. D., Kalyani, D. C., Chang, J. S., & Govindwar, S. P. (2009a). Enhanced decolorization and biodegradation of textile azo dye Scarlet R by using developed microbial consortium-GR. Bioresource Technology, 100, 2493–2500.
Saratale, R. G., Saratale, G. D., Chang, J. S., & Govindwar, S. P. (2009b). Decolorization and biodegradation of textile dye Navy blue HER by Trichosporon beigelii NCIM-3326. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166, 1421–1428.
Sarnthima, R., Khammuang, S., & Svasti, J. (2009). Extracellular ligninolytic enzymes by Lentinus polychrous Lev. under solid-state fermentation of potential agro-industrial wastes and their effectiveness in decolorization of synthetic dyes. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 14, 513–522.
Selvam, K., Swaminathan, K., & Chae, K. S. (2003). Decolorization of azo dyes and a dye industry effluent by a white rot fungus Thelephora sp. Bioresource Technology, 88, 115–119.
Semple, K. T., Cain, R. B., & Schmidt, S. (1999). Biodegradation of aromatic compounds by microalgae. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 170, 291–300.
Shedbalkar, U., Dhanve, R., & Jadhav, J. (2008). Biodegradation of triphenylmethane dye Cotton blue by Penicillium ochrochloron MTCC 517. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 157, 472–479.
Singh, H. (2006). Fungal decolorization and degradation of dyes. In H. Singh (Ed.), Mycoremediation: Fungal bioremediation (pp. 420–483). Hoboken: Wiley.
Steffan, S., Bardi, L., & Marzona, M. (2005). Azo dye biodegradation by microbial cultures immobilized in alginate beads. Environment International, 31, 201–205.
Stolz, A. (2001). Basic and applied aspects in the microbial degradation of azo dyes. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 56, 69–80.
Sugano, Y., Matsushima, Y., Tsuchiya, K., Aoki, H., Hirai, M., & Shoda, M. (2009). Degradation pathway of an anthraquinone dye catalyzed by a unique peroxidase DyP from Thanatephorus cucumeris Dec 1. Biodegradation, 20, 433–440.
Sun, J., Hu, Y. Y., Bi, Z., & Cao, Y. Q. (2009). Simultaneous decolorization of azo dye and bioelectricity generation using a microfiltration membrane air-cathode single-chamber microbial fuel cell. Bioresource Technology, 100, 3185–3192.
Tatarko, M., & Bumpus, J. A. (1998). Biodegradation of Congo red by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Water Research, 32, 1713–1717.
Van der Zee, F. P., & Villaverde, S. (2005). Combined anaerobic-aerobic treatment of azo dyes—A short review of bioreactor studies. Water Research, 39, 1425–1440.
Verma, P., & Madamwar, D. (2003). Decolorization of synthetic dyes by a newly isolated strain of Serratia marcescens. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 19, 615–618.
Wang, H., Zheng, X. W., Su, J. Q., Tian, Y., Xiong, X. J., & Zheng, T. L. (2009). Biological decolorization of the reactive dye Reactive Black 5 by a novel isolated bacterial strain Enterobacter sp. EC3. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171, 654–659.
Wesenberg, D., Kyriakides, I., & Agathos, S. N. (2003). White-rot fungi and their enzymes for the treatment of industrial dye effluents. Biotechnology Advances, 22, 161–187.
Wong, Y., & Yu, J. (1999). Laccase-catalyzed decolorization of synthetic dyes. Water Research, 33, 3512–3520.
Yang, X. Q., Zhao, X. X., Liu, C. Y., Zheng, Y., & Qian, S. J. (2009). Decolorization of azo, triphenylmethane and anthraquinone dyes by a newly isolated Trametes sp. SQ01 and its laccase. Process Biochemistry, 44, 1185–1189.
Yatome, C., Yamada, S., Ogawa, T., & Matsui, M. (1993). Degradation of crystal violet by Nocardia corallina. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 38, 565–569.
Youssef, A. S., El-Sherif, M. F., & El-Assar, S. A. (2008). Studies on the decolorization of Malachite green by the local isolate Acremonium kiliense. Biotechnology, 7, 213–223.
Yu, Z., & Wen, X. (2005). Screening and identification of yeasts for decolorizing synthetic dyes in industrial wastewater. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 56, 109–114.
Zhang, F. M., Knapp, J. S., & Tapley, K. N. (1999). Development of bioreactor systems for decolorization of Orange II using white rot fungus. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 24, 48–53.
Zhao, X., & Hardin, I. (2007). HPLC and spectrophotometric analysis of biodegradation of azo dyes by Pleurotus ostreatus. Dyes and Pigments, 73, 322–325.
Zhou, W., & Zimmermann, W. (1993). Decolorization of industrial effluents containing reactive dyes by actinomycetes. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 107, 157–162.
Acknowledgements
I am grateful to Dr. Muhammad Ali, Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry and Chairman, Department of Biotechnology, University of Malakand, for the encouragement and to my student Mr. Shah Khalid Muhammad for the help in establishing the environmental biotechnology research section at the department.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, H. Biodegradation of Synthetic Dyes—A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut 213, 251–273 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0382-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0382-4