Abstract
Purpose
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular complications represent significant cause of mortality in hemodialysis (HD) patients. The aims of this study were to: (a) investigate association of sICAM-1, sVCAM-1, omentin-1 and other non-traditional risk factors with subclinical atherosclerosis; (b) examine the diagnostic value of these specific markers in the early detection of subclinical atherosclerosis; and (c) examine their role as predictors of mortality in group of patients with subclinical atherosclerosis on regular HD.
Materials and methods
Starting from November 2011, a cohort of 210 HD patients participated in this 3-year follow-up study. The subjects were divided into three groups according to the presence of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerotic disease was assessed by measuring carotid intima-media thickness (IMT). Samplings were withdrawn at baseline and thereafter every 12 months until the end of follow-up.
Results
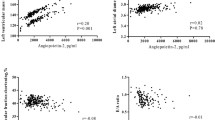
IMT showed weak correlation with sICAM-1 (r = 0.39, P = 0.001), sVCAM-1 (r = 0.27, P = 0.015) and omentin-1 (r = −0.25, P = 0.020), and also omentin-1 showed good correlation with parameters of systolic and diastolic function (r = 0.52, P = 0.001 and r = 0.51, P = 0.001). Multivariate analysis showed that sICAM-1 and sVCAM-1 concentrations were a strong independent correlate of IMT (P = 0.031 and P = 0.010, respectively). The Cox proportional analysis showed that sICAM-1 and omentin-1 concentrations were strong predictors of cardiovascular death (HR 1.85, CI 1.18–2.32, P = 0.021 and HR 4.14, CI 1.38–12.1, P = 0.004, respectively) and that serial measurements of these markers predict IMT progression (HR 1.98, 95 % CI 1.21–2.38, P < 0.002 and HR 2.91, 95 % CI 1.57–4.72, P < 0.001, respectively).
Conclusions
Our study demonstrated that sICAM-1 and omentin-1 levels are strong predictors of cardiovascular death in HD patients with subclinical atherosclerosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsimihodimos V, Dounousi E, Siamopoulos CK (2008) Dyslipidemia in chronic kidney disease: an approach to pathogenesis and treatment. Am J Nephrol 28:958–973. doi:10.1159/000144024
Yao Q, Filiho PR, Lindholm B, Stenvinkel P (2004) Traditional and non-traditional risk factors as contributors to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in end stage renal disease. Scand J Urol Nephrol 38:405–416. doi:10.1080/00365590410031715
Papagianni A, Kalovoulus M, Kirmizis D, Vainas A, Belechri AM, Alexopoulos E et al (2003) Carotid atherosclerosis is associated with inflammation and endothelia cell adhesion molecules in chronic haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18:113–119. doi:10.1093/ndt/18.1.113
Collado S, Coll E, Nicolau C, Pons M, Cruzado JM, Pascual J, Cases A (2015) Carotid atherosclerotic disease predicts cardiovascular events in hemodialysis patients: a prospective study. PLoS ONE 10:e0127344. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0127344
Davignon J, Ganz P (2004) Role of endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation 109:27–32. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000131515.03336.f8
Stoner L, Lucero AA, Palmer BR, Jones LM, Young JM, Faulkner J (2013) Inflammatory biomarkers for predicting cardiovascular disease. Clin Biochem 46:1353–1371. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2013.05.070
Kilic ID, Findikoglu G, Alihanoglu YI, Yildiz BS, Uslu S, Rota S et al (2014) Circulating adhesion molecules and arterial stiffness. Cardiovasc J Afr 26:21–24. doi:10.5830/CVJA-2014-060
Gross MD, Bielinski SJ, Suarez-Lopez JR, Reiner AP, Baily K, Thyagarajan B et al (2012) Circulating soluble intracellular adhesion molecule 1 and subclinical atherosclerosis: the coronary artery risk development in young adults study. Clin Chem 58:411–420. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2011.168559
Güray U, Erbay AR, Güray Y, Yilmaz MB, Boyaci AA, Samaz H et al (2004) Levels of soluble adhesion molecules in various clinical presentations of coronary atherosclerosis. Int J Cardiol 96:235–240. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2003.07.014
Tan KB, Adya R, Randeva SH (2010) Omentin: a novel link between inflammation, diabesity, and cardiovascular disease. Trends Cardiovasc Med 20:143–148. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2010.12.002
Moreno-Navarrete JM, Ortega F, Castro A, Sabater M, Ricart W, Fernandez-Real JM (2011) Circulating omentin as a novel marker of endothelial dysfunction. Obesity 19:1552–1559. doi:10.1038/oby.2010.351
Zhong X, Zhang HY, Tan H, Zhou Y, Liu FL, Chen FQ et al (2011) Association of serum omentin-1 levels with coronary artery disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32:873–878. doi:10.1038/aps.2011.26
Yoo HJ, Hwang SY, Hong HC, Choi HY, Yang SJ, Seo JA et al (2001) Association of circulating omentin-1 level with arterial stiffness and carotid plaque in type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol 10:103–110. doi:10.1186/1475-2840-10-103
Toth PP (2008) Subclinical atherosclerosis: what it is, what it means and what we can do about it. Int J Clin Pract 62:1246–1254. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2008.01804.x
Singh S, Nagra A, Maheshwari P, Panwar R, Hecht H, Fukumoto T et al (2013) Rapid screening for subclinical atherosclerosis by carotid ultrasound examination. Glob Heart 8:83–89. doi:10.1016/j.gheart.2013.05.001
Narumi T, Watanabe T, Kadowaki S, Kinoshita D, Yokoyama M, Honda Y et al (2014) Impact of serum omentin-1 levels on cardiac prognosis in patients with heart failure. Cardiovasc Diabetol 13:84–91. doi:10.1186/1475-2840-13-84
Shibata R, Ouchi N, Kikuchi R, Takahashi R, Takeshita K, Kataoka Y et al (2011) Circulating omentin is associated with coronary artery disease in men. Atherosclerosis 219:811–814. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.08.017
Qureshi AR, Alvestrand A, Divino-Filho JC, Gutierrez A, Heimbürger O, Lindholm B et al (2001) Inflammation, malnutrition, and cardiac disease as predictors of mortality in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:S28–S36
Tripepi G, Raso FM, Sijbrands E, Seck MS, Maas R, Boger R et al (2001) Inflammation and asymmetric dimethylarginine for predicting death and cardiovascular events in ESRD patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6:1714–1721. doi:10.2215/CJN.11291210
Bazeley JK, Bieber B, Li Y, Morgenstern H, de Sequera P, Combe C et al (2001) C-reactive protein and prediction of 1-year mortality in prevalent hemodialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6:2452–2461. doi:10.2215/CJN.00710111
Kanda E, Bieber BA, Pisoni RL, Robinson BM, Fuller DS (2015) Importance of simultaneous evaluation of multiple risk factors for hemodialysis patients’ mortality and development of a novel index: dialysis outcomes and practice patterns study. PLoS ONE 10:e0128652. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0128652
Kwan BCH, Kronenberg F, Beddhu S, Cheung AK (2007) Lipoprotein metabolism and lipid management in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:1246–1261. doi:10.1681/ASN.2006091006
Mallamaci F, Zoccali C, Tripei G, Fermo I, Benedetto FA, Cataliotti A et al (2002) Hyperhomocysteinemia predicts cardiovascular outcomes in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 61:609–614. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00144.x
Ulusoy S, Özkan G (2013) Lipid abnormalities in hemodialysis patients. In: Suzuki H (ed) Hemodialysis. http://www.intechopen.com/books/hemodialysis/lipid-abnormalities-in-hemodialysis-patients
Chang JF, Hsu SP, Pai MF, Yang JY, Wu HY et al (2013) High soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 concentrations predict long-term mortality in hemodialysis patients. Int Urol Nephrol 45:1693–1701. doi:10.1007/s11255-013-0425-z
Alcelik A, Tosun M, Ozlu MF, Eroglu M, Aktas G, Kemahli E et al (2012) Serum levels of omentin in end stage renal disease patients. Kidney Blood Press Res 35:511–516. doi:10.1159/000338796
Tawfeeka HM, Maghrapyb HM, Elsaidb FM, Eliazeedc HA (2014) Relationship between omentin-1 and carotid intima thickness in type 2 diabetes mellitus Egypt. J Intern Med 26:68–74. doi:10.4103/1110-7782.139547
Shibata R, Takahashi R, Kataoka Y, Ohashi K, Ikeda N, Kihara S et al (2011) Association of fat-derived plasma protein omentin with carotid artery intima-media thickness in apparently healthy men. Hypertens Res 34:1309–1312. doi:10.1038/hr.2011.130
Yamawaki H, Tsubaki N, Mukohda M, Okada M, Hara Y (2010) Omentin, a novel adipokine, induces vasodilation in rat isolated blood vessels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 393:668–672. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.053
Acknowledgments
In this study, the reagents kit for adhesion molecules were provided free of charge by H.K.O. medical systems, Zagreb, and MEDiLAB, Zagreb. Reagents for homocysteine were provided free of charge by Abbott laboratories, Zagreb, and reagents for Lp (a) were provided free of charge by Beckman Coulter, Zagreb.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication. All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kocijancic, M., Cubranic, Z., Vujicic, B. et al. Soluble intracellular adhesion molecule-1 and omentin-1 as potential biomarkers of subclinical atherosclerosis in hemodialysis patients. Int Urol Nephrol 48, 1145–1154 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1275-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1275-2