Abstract
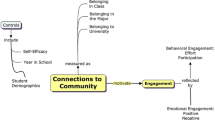
This explanatory sequential mixed methods study examined how belonging perceptions, academic motivation, and engagement might mediate the relationship between academic contextual characteristics and achievement using structural equation modeling and qualitative follow-up interviews with college students from a large, Midwestern university. In the first, quantitative phase, two hypothesized models of student belonging and motivation were tested. In line with the Self-System Model of Classroom Support for Motivation (Connell and Wellborn, in: Gunnar and Sroufe (eds.) Minnesota Symposium on Child Psychology: Self-processes and Development, 1991), Model 1 hypothesized student belonging and motivation to be directly predicted by supportive classroom environment perceptions, and to directly predict engagement, which was hypothesized to predict achievement. Model 2 elaborated on the traditional self-system model and hypothesized student belonging to mediate the relationship between supportive classroom environment perceptions and student motivation. Quantitative findings revealed support for Model 2. Supportive classroom environment perceptions predicted students’ belonging beliefs, which in turn predicted students’ motivation, engagement, and achievement in the course. The second, follow-up qualitative phase suggested ways in which contextual characteristics might influence student belonging beliefs in the classroom. Taken together, the quantitative and qualitative data illustrate the influential role of classroom contextual characteristics on student outcomes, as well as the role student belonging plays in college student motivation and success.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, W., Minnaert, A., van der Werf, G., & Kuyper, H. (2010). Perceived social support and early adolescents’ achievement: the meditational roles of motivational beliefs and emotions. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 39, 36–46.
Anderman, E. M. (2002). School effects on psychological outcomes during adolescence. Journal of Educational Psychology, 94, 795–809.
Anderman, L. H. (2003). Academic and social perceptions as predictors of change in middle school students’ sense of school belonging. The Journal of Experimental Education, 72(1), 5–22.
Anderman, L. H., & Freeman, T. M. (2004). Students’ sense of belonging in school. In P. R. Pintrich & M. L. Maehr (Eds.), Advances in motivation and achievement (Vol. 13, pp. 27–63). Oxford: Elsevier.
Anderman, L., & Kaplan, A. (2008). The role of interpersonal relationships in student motivation: introduction to the special issue. Journal of Experimental Education, 76, 115–119.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Barnes, D. C., Engelland, B. T., Matherine, C. F., Martin, W. C., Orgeron, C. P., Ring, J. K., et al. (2008). Developing a psychometrically sound measure of collegiate teaching proficiency. College Student Journal, 42, 199–213.
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51, 1173–1182.
Battistich, V., Solomon, D., Watson, M., & Schaps, E. (1997). Caring school communities. Educational Psychologist, 32, 137–151.
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1995). The need to belong: desire for interpersonal attachments as a fundamental human motivation. Psychological Bulletin, 117, 497–529.
Bentler, P. M. (1990). Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin, 88, 238–246.
Betts, L., & Rotenberg, K. (2007). Trustworthiness, friendships, and self-control: factors that contribute to young children’s school adjustment. Infant and Child Development, 16, 491–508.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). The ecology of human development. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Buhs, E. (2005). Peer rejection, negative peer treatment, and school adjustment: Self-concept and classroom engagement as mediating processes. Journal of School Psychology, 43, 407–424.
Castellanos, J., & Jones, L. (2003). Latina/o undergraduate experience in American higher education. In J. Castellanos & L. Jones (Eds.), The majority in the minority: expanding representation of Latina/o faculty, administrators, and students in higher education (pp. 1–14). Sterling: Stylus Publishing.
Catalano, R. F., Oesterle, S., Fleming, C. B., & Hawkins, J. D. (2004). The importance of bonding to school for healthy development: Findings from the Social Development Research Group. Journal of School Health, 74(7), 252–261.
Cleary, M., Walter, G., & Jackson, D. (2011). “Not always smooth sailing”: mental health issues associated with the transition from high school to college. Issues in Mental Health Nursing, 32(4), 250–254.
Connell, J. P., Spencer, M. B., & Aber, J. L. (1994). Educational risk and resilience in African American youth: context, self, action, and outcomes in school. Child Development, 65, 493–506.
Connell, J. P., & Wellborn, J. G. (1991). Competence, autonomy and relatedness: a motivational analysis of self-system processes. In M. Gunnar & L. A. Sroufe (Eds.), Minnesota symposium on child psychology: self-processes and development. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Creswell, J., & Plano Clark, V. (2010). Designing and conducting mixed methods research. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (1985). Intrinsic motivation and self-determination in human behavior. New York: Plenum.
Eccles, J. S., & Wigfield, A. (2002). Motivational beliefs, values, and goals. Annual Review of Psychology, 53, 109–132.
Eccles, J.S., Wigfield, A., & Schiefele, U. (1998). Motivation to succeed. In W. Damon (Series E.) & N. Eisenberg (Vol. Ed.), Handbook of child psychology; Vol 3. Social, emotional, and personality development (5th edn., pp. 1017–1095). New York: Wiley.
Engstrom, C., & Tinto, V. (2008). Access without support is not opportunity. Change, 40(1), 46–50.
Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., & Paris, A. H. (2004). School engagement: potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Review of Educational Research, 74, 59–109.
Freeman, T. M., Anderman, L. H., & Jensen, J. M. (2007). Sense of belongingness of college freshmen at the classroom and campus levels. Journal of Experimental Education, 75, 203–220.
Furrer, C., & Skinner, E. (2003). Sense of relatedness as a factor in children’s academic engagement and performance. Journal of Educational Psychology, 95, 148–161.
Garcia, T., & Pintrich, P. R. (1996). Assessing students’ motivation and learning strategies in the classroom context: the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire. In M. Birenbaum & F. J. R. C. Dochy (Eds.), Alternatives in assessment of achievements, learning processes, and prior knowledge (pp. 319–339). Boston: Kluwer Academic Press.
Goodenow, C. (1993). Classroom belonging among early adolescent students: relationships to motivation and achievement. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 13, 21–43.
Goodenow, C., & Grady, K. (1993). The relationship of school belonging and friends’ values to academic motivation among urban adolescent students. Journal of Experimental Education, 62, 60–71.
Hamre, B. K., & Pianta, R. C. (2005). Can instructional and emotional support in the first grade classroom make a difference for children at risk of school failure? Child Development, 76, 949–967.
Harris, B. A. (2001). The power of creating a spiritual learning community. Adult Learning, 12(3), 22–23.
Hausmann, L. M., Schofield, J. W., & Wood, R. L. (2007). Sense of belonging as a predictor of intentions to persist among African American and White first-year college students. Research in Higher Education, 48, 803–839.
Hoffman, M., Richmond, J., Morrow, J., & Salamone, K. (2002). Investigating “sense of belonging” in first-year college students. Journal of College Student Retention, 4(3), 227–256.
Hu, L., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6, 1–55.
Hulleman, C. S., Durik, A. M., Schweigert, S. B., & Harackiewicz, J. M. (2008). Task values, achievement goals, and interest: an integrative analysis. Journal of Educational Psychology, 100, 398–416.
Hurtado, S., & Carter, D. F. (1997). Effects of college transition and perceptions of campus racial climate on Latino college students’ sense of belonging. Sociology of Education, 70(4), 324–345.
Jacobs, J. E., Lanza, S., Osgood, D. W., Eccles, J. S., & Wigfield, A. (2002). Changes in children’s self-competence and values: Gender and domain differences across grades one through twelve. Child Development, 73(2), 509–527.
Kim, C., & Keller, J. M. (2008). Effects of motivation and volitional email messages (MVEM) with personal messages on undergraduate students’ motivation, study habits and achievement. British Journal of Educational Technology, 39, 36–51.
Kuh, G. D. (2003). What we’re learning about student engagement from NSSE: benchmarks for effective educational practices. Change, 35(2), 24–32.
Linnenbrink, E. A., & Pintrich, P. R. (2002). Motivation as an enabler for academic success. School Psychology Review, 31, 313–327.
McKeachie, W. (2012). McKeachie’s teaching tips. Independence: Cengage Learning.
McKinney, J. P., McKinney, K. G., Franiuk, R., & Schweitzer, J. (2006). The college classroom as a community: Impact on student attitudes and learning. College Teaching, 54(3), 281–284.
McNeely, C. A., Nonnemaker, J. M., & Blum, R. W. (2002). Promoting school connectedness: evidence from the national longitudinal study of adolescent health. Journal of School Health, 72(4), 138–146.
Merriam, S. B. (2009). Qualitative research: a guide to design and implementation. San Francisco: Wiley.
Micari, M., & Pazos, P. (2012). Connecting to the professor: impact of the student–faculty relationship in a highly challenging course. College Teaching, 60(2), 41–47.
Midgley, C., Feldlaufer, H., & Eccles, J. (1989). Change in teacher efficacy and student self- and task-related beliefs in mathematics during the transition to junior high school. American Psychological Association, 81, 247–258.
Moustakas, C. (1994). Phenomenological research methods. Los Angeles: SAGE Publications.
Murdock, T. B., Anderman, L. H., & Hodge, S. A. (2000). Middle-grade predictors of students’ motivation and behavior in high school. Journal of Adolescent Research, 15(3), 327–351.
Muthén, B. (2011). Applications of causally defined direct and indirect effects in mediation analysis using SEM in Mplus. Retrieved Sep 1, 2012 from http://www.statmodel.com/download/causalmediation.pdf.
Muthén, L.K. & Muthén, B.O. (1998–2010). Mplus User’s Guide. 6th edition. Los Angeles: Muthén & Muthén.
Nichols, L. (2008). An exploration of students’ belongingness beliefs in one middle school. The Journal of Experimental Education, 76, 145–169.
Nunez, A. (2009). Latino students’ transitions to college: a social and intercultural capital perspective. Harvard Educational Review, 79(1), 22–48.
Pajares, F. (1996). Self-efficacy beliefs in achievement settings. Review of Educational Research, 66, 543–578.
Pajares, F., & Valiante, G. (2001). Gender differences in writing motivation and achievement of middle school students: A function of gender orientation? Contemporary Educational Psychology, 26(3), 366–381.
Pascarella, E. T., & Terenzini, P. T. (1980). Predicting freshman persistence and voluntary dropout decisions from a theoretical model. The Journal of Higher Education, 51, 60–75.
Pascarella, E. T., & Terenzini, P. T. (1983). Predicting voluntary freshman year persistence/withdrawal behavior in a residential university: a path analytic validation of Tinto’s model. Journal of Educational Psychology, 75, 215–226.
Patrick, H., Hicks, L., & Ryan, A. M. (1997). Relations of perceived social efficacy and social goal pursuit to self-efficacy for academic work. Journal of Early Adolescence, 17, 109–128.
Pintrich, P. R. (1999). The role of motivation in promoting and sustaining self-regulated learning. International Journal of Educational Research, 31, 459–470.
Pintrich, P. R., Smith, D. A., García, T., & McKeachie, W. J. (1993). Reliability and predictive validity of the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ). Educational and Psychological Measurement, 53(3), 801–813.
Pittman, L. D., & Richmond, A. (2008). University belonging, friendship quality, and psychological adjustment during the transition to college. The Journal of Experimental Education, 76, 343–361.
Roeser, R. W., Midgley, C., & Urdan, T. C. (1996). Perceptions of the school psychology environment and early adolescents’ psychological and behavioral functioning in school: The mediating role of goals and belonging. Journal of Educational Psychology, 88, 408–422.
Ryan, A. M., & Patrick, H. (2001). The classroom social environment and changes in adolescents’ motivation and engagement during middle school. American Educational Research Journal, 38(2), 437–460.
Saldaña, J. (2013). The coding manual for qualitative researchers (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Schunk, D. H. (1995). Self-efficacy and education and instruction. In J. E. Maddux (Ed.), Self-efficacy, adaptation, and adjustment: Theory, research, and application. The Plenum series in social/clinical psychology (pp. 281–303). New York: Plenum Press.
Skinner, E. A., Zimmer-Gembeck, M. J., & Connell, J. P. (1998). Individual differences and the development of perceived control. Monographs of the Society of Research in Child Development, 63, 2–3.
Steiger, J. H. (1990). A structural model evaluation and modification: an interval estimation approach. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 25, 173–180.
Strayhorn, T. L. (2008a). Fittin’ in: Do diverse interactions with peers affect sense of belonging for Black men at predominantly White institutions? Journal of Student Affairs Research and Practice, 45(4), 501–527.
Strayhorn, T. L. (2008b). The role of supportive relationships in facilitating African American males’ success in college. NASPA Journal, 45(1), 26–48.
Strayhorn, T. L. (2010). Majority as temporary minority: examining the influence of faculty-student relationship on satisfaction among white undergraduates at historically black colleges and universities. Journal of College Student Development, 51(5), 509–524.
Strayhorn, T. L. (2012). College students’ sense of belonging: a key to educational success for all students. New York: Sage.
Strayhorn, T. L., & Saddler, T. N. (2009). Gender differences in the influence of faculty–student mentoring relationships on satisfaction with college among African Americans. Journal of African American Studies, 13(4), 476–493.
Strayhorn, T. L., & Terrell, M. C. (2007). Mentoring and satisfaction with college for Black students. Negro Educational Review, 58(1), 69–83.
Tebben, S. L. (1995). Community and caring in a college classroom. Journal for a Just and Caring Education, 1(3), 335–344.
Tinto, V. (1993). Leaving college: rethinking the causes and cures of student attrition (2nd ed.). Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Umbach, P. D., & Wawrzynski, M. R. (2005). Faculty do matter: the role of college faculty in student learning and engagement. Research in Higher Education, 46, 153–184.
Usher, E. L., & Pajares, F. (2009). Sources of self-efficacy in mathematics: a validation study. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 34, 89–101.
Vallerand, R. J., Pelletier, L. G., & Koestner, R. (2008). Reflections on self-determination theory. Canadian Psychology, 49, 257–262.
Van Ryzin, M., Gravely, A., & Roseth, C. (2009). Autonomy, belongingness, and engagement in school as contributors to adolescent psychological well-being. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 38, 1–12.
Walker, C. O., Greene, B. A., & Mansell, R. A. (2006). Identification with academics, intrinsic/extrinsic motivation, and self-efficacy as predictors of cognitive engagement. Learning and individual differences, 16, 1–12.
Walton, G. M., & Cohen, G. L. (2007). A question of belonging: race, social fit, and achievement. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 92(1), 82–96.
Walton, G. M., & Cohen, G. L. (2011). A brief-social belonging intervention improves academic and health outcomes of minatory students. Science, 331, 1447–1451.
Wentzel, K. R. (1991). Social and academic goals at school: motivation and achievement in context. In M. L. Maehr & P. R. Pintrich (Eds.), Advances in motivation and achievement, a research annual (Vol. 7, pp. 185–212). Greenwich: JAI Press.
Wentzel, K. R. (1997). Student motivation in middle school: the role of perceived pedagogical caring. Journal of Educational Psychology, 89, 411–419.
Wentzel, K. R. (1998). Student motivation in middle school: the role of parents, teachers, and peers. Journal of Educational Psychology, 90, 202–209.
Wheeless, V. E., Witt, P. L., Maresh, M., Bryand, M. C., & Schrodt, P. (2011). Instructor credibility as a mediator of instructor communication and students’ intent to persist in college. Communication Education, 60, 314–339.
Wigfield, A., & Cambria, J. (2010). Students’ achievement values, goal orientations, and interest: definitions, development, and relations to achievement outcomes. Developmental Review, 30, 1–35.
Wigfield, A., & Eccles, J. (2002). The development of achievement motivation. San Diego: Academic Press.
Willis, J. W. (2007). Foundations of qualitative research: interpretive and critical approaches. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Qualitative phase interview protocol
-
Describe your experience in this class.
-
Probe: Was it good? Bad? So-So? Why?
-
-
On a scale from 0 – 100, how much would you say that you fit in and belong in this class? Why?
-
Follow-up: Did you know the instructor or any of your classmates before this class?
-
Follow-up: In what ways do you feel that you do or don’t fit in?
-
-
What does it mean “to belong” in the classroom?
-
Probe: Define belonging in the classroom.
-
-
Give a specific example of a time in this class when you felt like you did or didn’t belong.
-
Describe a specific example of your experiences with your peers in this class.
-
Follow-up: Based on those experiences, do you feel accepted/supported by your peers? Why do you feel this way?
-
Probe: In what ways do you feel that you are or are not supported?
-
-
-
Describe your experiences with your instructor in this class.
-
Follow-up: Do you feel supported by your instructor? Why do you feel this way?
-
Probe: In what ways do you feel that you are/are not supported?
-
-
Follow-up: What instructional practices are used that are supportive?
-
Follow-up: What instructional practices are used that are not particularly supportive?
-
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zumbrunn, S., McKim, C., Buhs, E. et al. Support, belonging, motivation, and engagement in the college classroom: a mixed method study. Instr Sci 42, 661–684 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-014-9310-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-014-9310-0