Abstract
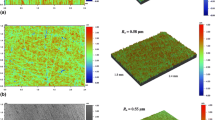
Friction influences the nature of transfer layer formed at the interface between tool and metal during sliding. In the present investigation, experiments were conducted using “Inclined Scratch Tester” to understand the effect of surface texture of hard surfaces on coefficient of friction and transfer layer formation. EN8 steel flats were ground to attain surfaces of different textures with different roughness. Then super purity aluminium pins were scratched against the prepared steel flats. Scanning electron micrographs of the contact surfaces of pins and flats were used to reveal the morphology of transfer layer. It was observed that the coefficient of friction and the formation of transfer layer depend primarily on the texture of hard surfaces, but independent of surface roughness of hard surfaces. It was observed that on surfaces that promote plane strain conditions near the surface, the transfer of material takes place due to the plowing action of the asperities. But, on a surface that promotes plane stress conditions the transfer layer was more due to the adhesion component of friction. It was observed that the adhesion component increases for surfaces that have random texture but was constant for the other surfaces.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rymuza Z. (1996) Wear 199: 187
Kato K. (2000) Wear 241: 151
Bello D.O., Walton S. (1987) Tribol. Int. 20: 59
Rasp W., Wichern C.M. (2002) J. Mater. Process. Tech. 125–126: 379
Schedin E. (1994) Wear 179: 123
Kim D.E., Suh N.P. (1991) Wear 149: 199
Hu Z.M., Dean T.A. (2000) Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manu. 40: 1637
Lanzon J.M., Cardew-Hall M.J., Hodgson P.D. (1998) J. Mater. Process. Tech. 80–81: 251
Saha P.K., Wilson W.R.D., Timsit R.S. (1996) Wear 197: 123
Lovell M.R., Deng Zhi, Khonsari M.M. (2000) Trans. of ASME 122: 856
Lakshmipathy R., Sagar R. (1992) Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manu. 32: 685
Wang L.Y., Yin Z.F., Zhang J., Chen C., Hsu S. (2000) Wear 237: 155–162
Feder J. (1988) Fractals Plenum Press, New York
Hasegawa M., Liu J., Okuda K., Nunobiki M. (1996) Wear 192: 40
Bowden F.P., Tabor D. (1954) The Friction and Lubrication of Solids, Clarendon, Oxford
George E. Dieter (2000) Mechanical Metallurgy. McGraw-Hill, New York
Faulkner A., Arnell R.D. (2000) Wear 242: 114
Satish V. Kailas and Pradeep Lancy Menezes, Proceedings of International Seminar on Metal Forming–Process Design and Optimization, (Indian Institute of Science, India, 2003) pp. 124–143
Challen J.M., Oxley P.L.B. (1979) Wear 53: 229–243
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menezes, P., Kishore & Kailas, S. Studies on friction and transfer layer: role of surface texture. Tribol Lett 24, 265–273 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-006-9129-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-006-9129-1