Abstract
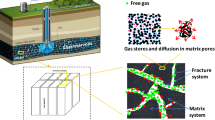
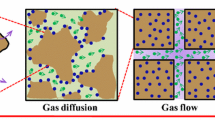
The sorbed gas diffuses in a coal matrix, where diffusion varies considerably with pore structure and pressure. The diffusion is an essential factor due to high sorption affinity of \(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) on coal grain surface. The sorption within the matrix causes swelling or shrinkage of matrix, in which the amount of sorbed gas affects gas diffusion. In this study, in order to observe permeability change occurred when the sorbed gas diffuses in a coal matrix, experiments were conducted with a bituminous coal sample. Firstly, gas partial pressure was measured through a diffusion experiment with a transient flow method. Secondly, flowing experiments were conducted to examine the permeability reduction yielded by sorption phenomena according to the various pore pressures. The results were then analyzed for the effect of diffusion coefficient on permeability change. The diffusion coefficient of \(\hbox {CH}_{4}\) in low-pressure section was greater than that of \(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) owing to the difference in their molecular weight. However, as pressure increased, the diffusion coefficient of \(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) became greater because of higher sorption affinity of \(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) compared to \(\hbox {CH}_{4}\). Finally, it was revealed that the gas diffused instantaneously in the case of crushed coal in which its diffusion coefficient had infinite value due to the destroyed pore structure. Meanwhile, in the coal core sample in which pore structure was preserved as original state, it was ascertained that diffusional flow occurred gradually corresponding to concentration gradient, and hence, the permeability was reduced accordingly. This phenomenon was also confirmed through pore images obtained from X-ray CT.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Pounds per square inch absolute (psia):
-
6.894757 kPa
- Atmosphere (atm):
-
101.325 kPa
- Millidarcy (mD):
-
\(0.9869 \times 10^{-15}\,\hbox {m}^{2}\)
- Centipoise (cp):
-
0.001 Pa s
References
Anggara, F., Sasaki, K., Sugai, Y.: Experimental and analytical studies on permeability reduction of coal seam by \({\rm CO}_{2}\) injection. Paper IPTC 14165 Presented at the International Petroleum Technology Conference held in Bangkok, Thailand, 7–9, Feb 2012
Cui, X., Bustin, R.M., Dipple, G.: Selective transport of \({\rm CO}_{2}\), \({\rm CH}_{4}\), and \({\rm N}_{2}\) in coals: insights from modeling of experimental gas adsorption data. Fuel 83(3), 293–303 (2004)
Fathi, E., Akkutlu, I.Y.: Counter-diffusion and competitive adsorption effects during \({\rm CO}_{2}\) injection and coalbed methane production. Paper SPE 115482 Presented at the Society of Petroleum Engineers Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition Held in Denver, CO, 21–24 Sep 2008
Guo, R., Mannhardt, K., Kantzas, A.: Laboratory investigation on the permeability of coal during primary and enhanced coalbed methane production. J. Can. Petrol. Technol. 47(10), 27–32 (2008)
Harpalani, S., Mitra, A.: Impact of \({\rm CO}_{2}\) injection on flow behavior of coalbed methane reservoirs. Trans. Porous Media 82(1), 141–156 (2010)
Jessen, K., Tang, G.-Q., Kovscek, A.R.: Laboratory and simulation investigation of enhanced coalbed methane recovery by gas injection. Trans. Porous Media 73(2), 141–159 (2008)
Jian, X., Guan, P., Zhang, W.: Carbon dioxide sorption and diffusion in coals: experimental investigation and modeling. Sci. China Earth Sci. 55(4), 633–643 (2011)
Lee, Y.S., Kim, K.H., Lee, T.H., Sung, W.M., Park, Y.C., Lee, J.H.: Analysis of \({\rm CO}_{2}\) endpoint relative permeability and injectivity by change in pressure, temperature, and phase in saline aquifer. Energy Source Part A 32(1), 83–99 (2009)
Lee, Y.S., Kim, K.H., Sung, W.M., You, I.H.: Analysis of the leakage possibility of injected \({\rm CO}_{2}\) in a saline aquifer. Energy Fuel 24(5), 3292–3298 (2010)
Li, W., Cheng, Y., Wang, L., Mo, J.: A study of coal swelling-controlled \({\rm CO}_{2}\) diffusion processes. Paper Presented at the 13th Coal Operators’ Conference held in Wollongong, Australia, 14–15 Feb 2013
Lin, W., Tang, G.Q., Kovscek, A.R.: Sorption-induced permeability change of coal during gas-injection processes. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 11(4), 792–802 (2008)
Palmer, I., Mansoori, J.: How permeability depends on stress and pore pressure in coalbeds: a new model. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 1(6), 539–544 (1998)
Pillalamarry, M., Harpalani, S., Liu, S.: Gas diffusion behavior of coal and its impact on production from coalbed methane reservoirs. Int. J. Coal Geol. 86(4), 342–348 (2011)
Sabir, A., Chalaturnyk, R.J.: Adsorption characteristics of coal in constant-pressure tests. Can. Geotech. J. 46(10), 1165–1176 (2009)
Smith, D.H., Bromhal, G., Sams, W.N., Jikich, S., Ertekin, T.: Simulating carbon dioxide sequestration/ECBM production in coal seams: effects of permeability anisotropies and the diffusion-time constant. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 8(2), 156–163 (2005)
Smith, D.M., Williams, F.L.: Diffusional effects in the recovery of methane from coalbeds. Soc. Petrol. Eng. J. 24(5), 529–535 (1984)
Tang, G.Q., Jessen, K., Kovscek, A.R.: Laboratory and simulation investigation of enhanced coalbed methane recovery by gas injection. Paper SPE 95947 Presented at the Society of Petroleum Engineers Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition held in Dallas, TX, 9–12 Oct 2005
Thimons, E.D., Kissell, F.N.: Diffusion of methane through coal. Fuel 52(4), 274–280 (1973)
Wang, G.X., Massarotto, P., Rudolph, V.: An improved permeability model of coal for coalbed methane recovery and \({\rm CO}_{2}\) geosequestration. Int. J. Coal Geol. 77(1–2), 127–136 (2009)
Yang, Y., Zoback, M.D.: The effects of gas adsorption on swelling, visco-plastic creep and permeability of sub-bituminous coal. Paper ARMA 11–433 Presented at the 45th US Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium held in San Francisco, CA, 26–29 Jun 2011
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology Grant from the Korean Government’s Ministry of Knowledge Economy (No. 10039231).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seomoon, H., Lee, M. & Sung, W. Analysis of Sorption-Induced Permeability Reduction Considering Gas Diffusion Phenomenon in Coal Seam Reservoir. Transp Porous Med 108, 713–729 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-015-0498-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-015-0498-5