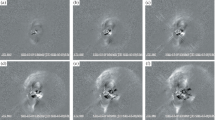
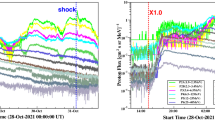
Abstract
It is well known that solar flares and shocks driven by coronal mass ejections (CMEs) are high-energy particle acceleration processes that might cause a high-energy particle event known as a ground-level enhancement (GLE). In this context, we have attempted to understand the processes responsible for the first GLE event (GLE71 17 May 2012 01:50 UT) of Solar Cycle 24. We studied the spatial and spectral data from the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) the Culgoora radio-heliograph, and Wind/WAVES instrument, and analyzed the temporal data of the solar-flare components, the solar radio-flux density, and the electron fluxes from the Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (RHESSI), the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES), the Radio Solar Telescope Network (RSTN), and Wind spacecraft. The flare had two ribbons separated by the neutral line between negative and positive magnetic polarity. Their structure was also almost consistent with the contours of some flare components, which were almost saturated during the flare-peak time. As indicated by the metric–kilometric Type-II burst, and because it extended over a wide heliolongitude (> ≈ 41∘) range, the CME-driven shock was fast enough to cause high-energy particle acceleration at a high altitude in the solar corona. Moreover, the CME and flare-flash phases were aligned along the same direction, which implies that if the CME-driven shock played the leading role in causing the GLE, preceding flare components may have contributed to the shock.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal, M., Jain, R., Mishra, A.P., Kulkarni, P.G., Vyas, C., Sahrma, R., Gupta, M.: 2008, J. Astrophys. Astron. 29, 195.
Andriopoulou, M., Mavromichalaki, H., Preka-Papadema, P., Plainaki, C., Belov, A., Eroshenko, E.: 2011, Astrophys. Space Sci. Trans. 7, 439.
Aschwanden, M.J.: 2006, Space Sci. Rev. 124, 361.
Aschwanden, M.J.: 2012, Space Sci. Rev. 171, 3.
Baisultanova, L.M., Belov, A.V., Dorman, L.I., Eroshenko, E.A., Gushchina, R.T., Ishkov, V.N., Yanke, V.G.: 1991, In: Cawley, M., Drury, L.OC., Fegan, D.J., O’Sullivan, D., Porter, N.A., Quenby, J.J., Watson, A.A. (eds.) Int’l. Cosmic Ray. Conf., Dublin 3, 105.
Belov, A.V., Blokh, Y.L., Eroshenko, E.A., Ishkov, V.N.: 1985, In: Jones, F.C., Adams, J., Mason, G.M. (eds.) 19th Int’l. Cosmic Ray Conf., SH 1.3 – 15, 118. archive.org/stream/nasa_techdoc_19850027753/19850027753_djvu.txt .
Bieber, J.W., Clem, J.M., Duldig, M.L., Evenson, P.A., Humble, J.E., Pyle, R.: 2004, J. Geophys. Res. 109, A12. DOI .
Bougeret, J.-L., Kaiser, M.L., Kellogg, P.J., Manning, R., Goetz, K., Monson, S.J., Monge, N., Friel, L., Meetre, C.A., Perche, C., Sitruk, L., Hoang, S.: 1995, Space Sci. Rev. 71, 231.
Cane, H.V., Richardson, I.G., von Rosenvinge, T.T.: 2007, Space Sci. Rev. 130, 301.
Chen, P.F.: 2008, J. Astrophys. Astron. 29, 179.
Chernov, G.P., Kaiser, M.L., Bougeret, J.-L., Fomichev, V.V., Gorgutsa, R.V.: 2007, Solar Phys. 241, 145. ADS . DOI .
Cramp, J.L., Duldig, M.L., Humble, J.E.: 1995, In: Iucci, N., Lamanna, E. (eds.) Int’l. Cosmic Ray. Conf. 4, 289.
Cramp, J.L., Duldig, M.L., Humble, J.E.: 1997, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 4919.
Deeley, K.M., Duldig, M.L., Humble, J.E.: 2002, Adv. Space Res. 30, 1049.
Dennis, B.R.: 2002, Bull. Am. Astron. Soc. 34, 76.03.
Dennis, B.R., Pernak, R.L.: 2009, Astrophys. J. 698, 2131.
Dorman, L.I., Belov, A.V., Eroshenko, E.A., Gushchina, R.T., Iucci, N., Mavromichalaki, H., Parisi, M., et al.: 2001 In: Proc. of 27th Int’l Cosmic Ray Conf., Hamburg, 3469.
Dorotovič, I., Kudela, K., Lorenc, M., Rybanský, M.: 2008, Solar Phys. 250, 339. ADS . DOI .
Duldig, M.L., Humble, J.E.: 1999, In: Kieda, D., Salamon, M., Dingus, B. (eds.) Proc. 26th Int’l. Cosmic Ray Conf., Utah, USA 6, 403. ADS .
Firoz, K.A., Cho, K.-S., Hwang, J., Kumar, P.D.V., Lee, J.J., Oh, S.Y., Kaushik, S.C., Kudela, K., Milan, R., Dorman, L.I.: 2010, J. Geophys. Res. 115, A09105. DOI .
Firoz, K.A., Moon, Y.-J., Park, S.H., Kudela, K., Islam, J.N., Dorman, L.I.: 2011, Astrophys. J. 743, 190.
Firoz, K.A., Gan, W.Q., Moon, Y.J., Li, C.: 2012, Astrophys. J. 758, 119.
Firoz, K.A., Gan, W.Q., Li, Y.P., Rodríguez-Pacheco, J.: 2014a, Geophys. Res. Abstr. 16, EGU2014-1920, EGU General Assembly 2014.
Firoz, K.A., Gan, W.Q., Li, Y.P., Rodríguez-Pacheco, J.: 2014b, Astrophys. Space Sci. 350, 21. DOI . ISSN 0004-640X.
Flückiger, E.O.: 2009, In: Caballero, R., D’Olivo, J.C., Medina-Tanco, G., Valdes-Galicia, J.F. (eds.) Proc. 30th Int’l. Cosmic Ray Conf. 6, 239.
Gómez-Herrero, R., Rodríguez Frias, M.D., del Peral, L., Sequeiros, J., Müller-Mellin, R., Kunow, H.: 2000, In: Wilson, A. (ed.) Proc. 1st Solar & Space Weather Euroconference: The Solar Cycle and Terrestrial Climate SP-463, ESA, Noordwijk, 325.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A., Reames, D.V., Leske, R., von Rosenvinge, T.: 2002, Astrophys. J. 572, L103.
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Usoskin, I.G., Davila, J.M.: 2013, Astrophys. J. Lett. 765, L30.
Hock, R.A., Chamberlin, P.C., Woods, T.N., Crotser, D., Eparvier, F.G., Woodraska, D.L., Woods, E.C.: 2012, Solar Phys. 275, 145. ADS . DOI .
Holman, G.D., Aschwanden, M.J., Aurass, H., Battaglia, M., Grigis, P.C., Kontar, E.P., Liu, W., Saint-Hilaire, P., Zharkova, V.V.: 2011, Space Sci. Rev. 159, 107. DOI .
Kahler, S.W.: 1994, Astrophys. J. 428, 837.
Kallenrode, M.-B.: 1993, J. Geophys. Res. 98(A11), 19037.
Kocharov, L., Torsti, J.: 2002, Solar Phys. 207, 149. ADS . DOI .
Kumar, P., Srivastava, A.K., Somov, B.V., Manoharan, P.K., Erdelyi Uddin, W.: 2010, Astrophys. J. 723, 1651.
Kurt, V.G., Yushkov, B.Y., Belov, A.V.: 2010, Astron. Lett. 36, 520.
Kuznetsov, S.N., Kurt, V.G., Yushkov, B.Y., Myagkova, I.N., Kudela, K., Kassovicova, J., Slivka, M.: 2006, Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skaln. Pleso 360, 85.
Lemen, J.R., Title, A.M., Akin, D.J., Boerner, P.F., Chou, C., Drake, J.F., Duncan, D.W., Edwards, C.G., et al.: 2012, Solar Phys. 275, 17. ADS . DOI .
Lin, R.P., Anderson, K.A., Ashford, S., Carlson, C., Curtis, D., Ergun, R., Larson, D., McFadden, J., McCarthy, M., Parks, G.K., et al.: 1995, Space Sci. Rev. 71, 125.
Lin, R.P., Dennis, B.R., Hurford, G.J., Smith, D.M., Zehnder, A., Harvey, P.R., Curtis, D.W., Pankow, D., Turin, P., et al.: 2002, Solar Phys. 210, 3. ADS . DOI .
Liu, W., Chen, Q., Petrosian, V.: 2013, Astrophys. J. 767, 168.
Liu, Y., Luhmann, J.G., Bale, S.D., Lin, R.P.: 2009, Astrophys. J. Lett. 691, L151.
Lovell, J.L., Duldig, M.L., Humble, J.E.: 1998, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 23733.
Mavromichalaki, H., Papaioannou, A., Plainaki, C., Sarlanis, C., Souvatzoglou, G., Gerontidou, M., Papailiou, M., Eroshnenko, E., Belov, A., Yanke, V., et al.: 2011, Adv. Space Res. 47, 2210. DOI .
Moraal, H., McCracken, K.G.: 2012, Space Sci. Rev. 1717, 85.
Müller, D., Fleck, B., Dimitoglou Caplins, B.W., Amadigwe, D.E., Ortiz, J.P.G., Wamsler, B., Alexanderian, A., Hughitt, V.K., Ireland, J.: 2009, Comput. Sci. Eng. 11, 38.
Prestage, N.P.: 1995, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 57, 1815.
Prestage, N.P., Luckhurst, R.G., Paterson, B.R., Bevins, C.S., Yuile, C.G.: 1994, Solar Phys. 150, 393. ADS . DOI .
Reames, D.V.: 2009, Astrophys. J. 693, 812.
Reeves, K.K., Golub, L.: 2011, Astrophys. J. Lett. 727, L52.
Ryan, J.M., Lockwood, J.A., Debrunner, H.: 2000, Space Sci. Rev. 93, 35.
Scherrer, P.H., Schou, J., Bush, R.I., Kosovichev, A.G., Bogart, R.S., Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Duvall, T.L. Jr., Zhao, J., Title, A.M., Schrijver, C.J., Tarbell, T.D., Tomczyk, S.: 2012, Solar Phys. 275, 207. ADS . DOI .
Schrijver, C.J., De Rosa, M.L.: 2003, Solar Phys. 212, 165. ADS . DOI .
Shanmugaraju, A., Moon, Y.J., Cho, K.S., Dryer, M., Umapathy, S.: 2006, Solar Phys. 233, 117. ADS . DOI .
Shea, M.A., Smart, D.F.: 2012, Space Sci. Rev. 171, 161.
Shea, M.A., Smart, D.F., Humble, J.E., Fluckiger, E.O., Gentile, L.C., Nichol, M.R.: 1987, In: Kozyvarivsky, V.A., Lidvansky, A.S., Tulupova, T.I., Tsyabuk, A.L., Voevdovsky, A.V., Volgemut, N.S. (eds.) Int’l. Cosmic Ray Conf. 3, 171S, SH 3.2 – 17.
Shen, Y., Liu, Y.: 2012, Astrophys. J. 754, 7.
Simnett, G.M.: 2006, Astron. Astrophys. 445, 715.
Stoker, P.H., Makgamathe, S.: 1990, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 73, 263.
Struminsky, A.B.: 2005, In: Acharya, B.S., Gupta, S., Iyer, A., Jagadeesan, P., Jain, A., Karthikeyan, S., Morris, S., Tonwar, S. (eds.) 29th Int’l. Cosmic Ray Conf., Pune 1, 201.
Vashenyuk, E.V., Fischer, S., Gvozdevsky, B.B.: 1993, In: Leahy, D.A., Hickws, R.B., Venkatesan, D. (eds.) Int’l. Cosmic Ray Conf. 3, World Scientific, Singapore, 266.
White, S.M., Benz, A.O., Christe, S., Farnik, F., Kundu, M.R., Mann, G., Ning, Z., Raulin, J.-P., Silva-Valio, A.V.R., Saint-Hilaire, P., Vilmer, N., Warmuth, A.: 2011, Space Sci. Rev. 159, 225.
Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N., Michalek, G., St. Cyr, O.C., Plunkett, S.P., Rich, N.B., Howard, R.A.: 2004, J. Geophys. Res. 109, A07105. DOI .
Yue, X., Schreiner, W.S., Kuo, Y.-H., Zhao, B., Wan, W., Ren, Z., Liu, L., Wei, Y., Lei, J., Solomon, S., Rocken, C.: 2013, J. Geophys. Res. 118, 5906. DOI .
Zhang, J., Dere, K.P., Howard, R.A., Kundu, M.R., White, S.M.: 2001, Astrophys. J. 559, 452.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the anonymous referee for the constructive comments and valuable suggestions that greatly helped us to improve the manuscript. We used NM data from NMDB funded by European Union’s FP7 program (contract No. 213007). To study possible causes of GLEs, data provided by NOAA’s National Geophysical Data Center (NGDC), NASA’s Wind/WAVES, and RHESSI have been used. We acknowledge discussions with David J. Thompson (NASA), Y.-J. Moon (KHU), Z. Ning (PMO/CAS), Q.M. Zhang (PMO/CAS), and R. Gómez-Herrero (EPD/ESA). WQG acknowledges the projects of MSTC (2011CB811402) and NNSFC (11233008 and 11427803). JRP acknowledges the projects of Solar Orbiter-Energetic Particle Detector (EPD): Ciencia y Gestión de Sistemas (AYA2012-39810-C02-01) funded by the Ministerio de Economia y Competitividad, the Solar Orbiter Energetic Particle Detector System Management (AYA2011-29727-C02-01), and DETECTOR DE PARTÍCULAS ENERGÉTICAS PARA SOLAR ORBITER II (ESP2013-48346-C2-1-R). We have used data provided by NOAA’s National Geophysical Data Center (NGDC), NASA’s Wind/WAVES, SDO, RHESSI missions, and the ESA/NASA SOHO mission. SOHO is a mission of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. The SDO/HMI and EVE data are available by courtesy of NASA/SDO and the AIA and EVE science teams.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
If reconnection of magnetic fields takes place more than once at different heights of the corona, and the shock wave is produced low in the corona, there might be a possibility that the shock would be turned into a blast wave (see cartoons in, e.g., Aschwanden 2006; Chen 2008; Kumar et al. 2010; Liu, Chen, and Petrosian 2013). If the shock were a freely propagating blast wave, it would decay before reaching the interplanetary medium (because it does not have any driver to back it up). In contrast, the CME-driven shocks continuously receive energy from the driver, so the CME-driven shock is more energetic and long-lived (e.g., Liu et al. 2009). Although there is a possibility of blast waves during CME-less shock events (e.g., Shanmugaraju et al. 2006), we did not find any evidence of a blast wave for the GLE71 event, which is associated with a very fast CME (≈ 1582 km s−1). In practice, the low frequency of Type-II bursts corresponds to densities typical of the upper corona. Since the possible time line exists within the Type-II burst (Figure 2), we can therefore assume for the GLE71 event that the CME-driven shock naturally has a leading role in accelerating the particles (Figure 3).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Firoz, K.A., Gan, W.Q., Li, Y.P. et al. An Interpretation of a Possible Mechanism for the First Ground-Level Enhancement of Solar Cycle 24. Sol Phys 290, 613–626 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-014-0619-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-014-0619-2