Abstract
Background and aims
We investigated the effects of silicon (Si) on chlorophyll concentration, photosynthesis, leaf chloroplast ultrastructure, and expression of genes involved in photosynthesis to elucidate the mechanisms through which Si mediated alleviation of manganese (Mn) toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.).
Methods
Rice seedlings were grown hydroponically with normal Mn (6.7 μM) or high Mn (2 mM) concentrations, both with (1.5 mM) and without Si supplementation. Leaf chloroplast ultrastructure was observed by scanning and transmission electron microscopy. Differentially expressed genes relating to photosynthesis were identified by high-throughput sequencing, and their relative expression levels were evaluated by real-time quantitative PCR.
Results
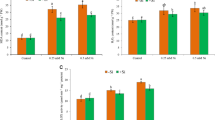
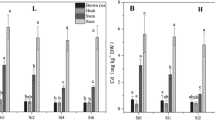
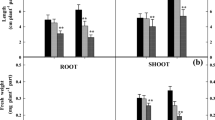
Chlorophyll and carotenoid concentrations and net photosynthesis decreased with chloroplast degradation under high Mn stress. High Mn concentrations may have inhibited photosynthesis through several mechanisms, including suppressing chlorophyll and ATP synthesis, decreasing light-harvesting processes, impairing photosystem I (PSI) stability and structure, and slowing activity of phosphoribulokinase. Si enhanced Mn tolerance efficiently by increasing chlorophyll concentration, light-use efficiency, and ATP concentration as well as by stabilizing the structure of PSI and promoting CO2 assimilation.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest active involvement of Si in Mn detoxification, ranging from physiological responses to gene expression.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADP:
-
Adenosine diphosphate
- ATP:
-
Adenosine-5′-triphosphate
- g s :
-
Stomatal conductance
- LHCII:
-
Light-harvesting complex proteins II
- OEC:
-
Oxygen-evolving complex
- Pi:
-
Inorganic phosphate
- P n :
-
Net photosynthesis
- PPi:
-
Pyrophosphate
- PRK:
-
Phosphoribulokinase
- PSI:
-
Photosystem I
- PSII:
-
Photosystem II
- RuBisCO:
-
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
- Tr:
-
Transpiration rate
References
Al-aghabary K, Zhu Z, Shi Q (2004) Influence of silicon supply on chlorophyll content, chlorophyll fluorescence, and antioxidative enzyme activities in tomato plants under salt stress. J Plant Nutr 27:2101–2115
Ali S, Farooq MA, Yasmeen T, Hussain S, Arif MS, Abbas F, Bharwana SA, Zhang GP (2013) The influence of silicon on barley growth, photosynthesis and ultra-structure under chromium stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 89:66–72
Audic S, Claverie JM (1997) The significance of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Res 7:986–995
Bokor B, Vaculik M, SlovákováL MD, Lux A (2014) Silicon does not always mitigate zinc toxicity in maize. Acta Physiol Plant 36:733–743
Bondarava N, Beyer P, Krieger-Liszkay A (2005) Function of the 23 kDa extrinsic protein of photosystem II as a manganese binding protein and its role in photoactivation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1708:63–70
Conyers MK, Uzen NC, Helyor KR, Poile GJ, Culist BR (1997) Temporal variation in soil acidity. Aust J Soil Res 35:1115–1129
Csatorday K, Gombos Z, Szalontai B (1984) Mn2+ and Co2+ toxicity in chlorophyll biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 81:476–478
da Cunha KPV, do Nascimento CWA (2009) Silicon effects on metal tolerance and structural changes in maize (Zea mays L.) grown on a cadmium and zinc enriched soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 197:323–330
Doncheva SN, Poschenrieder C, Zl S (2009) Silicon amelioration of manganese toxicity in Mn-sensitive and Mn-tolerant maize varieties. Environ Exp Bot 65:189–197
Dragišić Maksimović J, Bogdanović J, Maksimović V, Nikolic M (2007) Silicon modulates the metabolism and utilization of phenolic compounds in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) grown at excess manganese. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 170:739–744
Feng JP, Shi QH, Wang XF (2009) Effects of exogenous silicon on photosynthetic capacity and antioxidant enzyme activities in chloroplast of cucumber seedlings under excess manganese. Agric Sci China 8:40–50
Feng JP, Shi QH, Wang XF, Wei M, Yang FJ, Xu HN (2010) Silicon supplementation ameliorated the inhibition of photosynthesis and nitrate metabolism by cadmium (Cd) toxicity in Cucumis sativus L. Sci Hortic 123:521–530
Fleck AT, Nye T, Repenning C, Stahl F, Zahn M, Schenk MK (2011) Silicon enhances suberization and lignification in roots of rice (Oryza sativa). J Exp Bot 62:2001–2011
Führs H, Hartwig M, Molina LEB, Heintz D, Dorsselaer AV, Braun HP, Horst WJ (2008) Early manganese-toxicity response in Vigna unguiculata L.—a proteomic and transcriptomic study. Proteomics 8:149–159
Führs H, Götze S, Specht A, Erban A, Gallien S, Heintz D, Van Dorsselaer A, Kopka J, Braun H-P, Horst WJ (2009) Characterization of leaf apoplastic peroxidases and metabolites in Vigna unguiculata in response to toxic manganese supply and silicon. J Exp Bot 60:1663–1678
Führs H, Behrens C, Gallien S, Heintz H, Van Dorsselaer A, Braun H-P, Horst WJ (2010) Physiological and proteomic characterization of manganese sensitivity and tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa) in comparison with barley (Hordeum vulgare). Ann Bot 105:1129–1140
Führs H, Specht A, Erban A, Kopka J, Horst WJ (2012) Functional associations between the metabolome and manganese tolerance in Vigna unguiculata. J Exp Bot 63:329–340
Gao X, Zou C, Wang L, Zhang F (2006) Silicon decreases transpiration rate and conductance from stomata of maize plants. J Plant Nutr 29:1637–1647
Ghanotakis DF, Topper JN, Babcock GT, Yocum CF (1984a) Water-soluble 17 and 23 kDa polypeptides restore oxygen evolution activity by creating a high-affinity binding site for Ca2+ on the oxidizing side of photosystem II. Febs Lett 170:169–173
Ghanotakis DF, Topper JN, Yocum CF (1984b) Structural organization of the oxidizing side of photosystem II: exogenous reductants reduce and destroy the Mn-complex in photosystem II membranes depleted of the 17 and 23 kDa polypeptides. Biochim Biophys Acta 767:524–531
González A, Lynch JP (1997) Effects of manganese toxicity on leaf CO2 assimilation of contrasting common bean genotypes. Physiol Plant 101:872–880
González A, Lynch JP (1999) Subcellular and tissue Mn compartmentation in bean leaves under Mn toxicity stress. Aust J Plant Physiol 26:811–822
González A, Steffen KL, Lynch JP (1998) Light and excess manganese: implications for oxidative stress in common bean. Plant Physiol 118:493–504
Hajduch M, Rakwal R, Agrawal GK, Yonekura M, Pretova A (2001) High-resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis separation of proteins from metal-stressed rice (Oryza sativa L.) leaves: Drastic reductions/fragmentation of ribulose-1,5- bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase and induction of stress-related proteins. Electrophoresis 22:2824–2831
Hao QN, Zhou XA, Sha AH, Wang C, Zhou R, Chen SL (2011) Identification of genes associated with nitrogen-use efficiency by genome-wide transcriptional analysis of two soybean genotypes. BMC Genomics 12:525
Hattori T, Inanaga S, Araki H, An P, Morita S, Luxová M, Lux A (2005) Application of silicon enhanced drought tolerance in Sorghum bicolor. Physiol Plant 123:459–466
He CW, Wang LJ, Liu J, Liu X, Li XL, Ma J, Lin YJ, Xu FS (2013) Evidence for ‘silicon’ within the cell walls of suspension-cultured rice cells. New Phytol 200:700–709
He CW, Ma J, Wang LJ (2015) A hemicellulose-bound form of silicon with potential to improve the mechanical properties and regeneration of the cell wall of rice. New Phytol 206:1051–1062
Hoffmann H, Schenk MK (2011) Arsenite toxicity and uptake rate of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in vivo. Environ Pollut 159:2398–2404
Horiguchi T (1988) Mechanism of manganese toxicity and tolerance of plants. IV. Effect of silicon on alleviation of manganese toxicity of rice plants. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 34:65–73
Houtz RL, Nable RO, Cheniae GM (1988) Evidence for effects on the in vivo activity of ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase during development of Mn toxicity in tobacco. Plant Physiol 86:1143–1149
Hussain I, Ashraf MA, Rasheed R, Asghar A, Sajid MA, Iqbal M (2015) Exo-genous application of silicon at the boot stage decreases accumulation of cadmium in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grains. Braz J Bot. doi:10.1007/s40415-014-0126-6
Ifuku K, Yamamoto Y, Ono T, Ishihara S, Sato F (2005) PsbP protein, but not PsbQ protein, is essential for the regulation and stabilization of photosystem II in higher plants. Plant Physiol 139:1175–1184
Iwasaki K, Matsumura A (1999) Effect of silicon on alleviation of manganese toxicity in pumpkin (Cucurbita moschtaa Duch cv. Shintosa). Soil Sci Plant Nutr 45:909–920
Iwasaki K, Maier P, Fecht M, Horst WJ (2002a) Effects of silicon supply on apoplastic manganese concentrations in leaves and their relation to manganese tolerance in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.)Walp.). Plant Soil 238:281–288
Iwasaki K, Maier P, Fecht M, Horst WJ (2002b) Leaf apoplastic silicon enhances manganese tolerance of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). J Plant Physiol 159:167–173
Jensen PE, Bassi R, Boekema EJ, Dekker JP, Jansson S, Leister D, Robinson C, Scheller HV (2007) Structure, function and regulation of plant photosystem I. Biochim Biophys Acta 1767:335–352
Júnior LAZ, Fontes RLF, Neves JCL, Korndörfer GH, Ávila VTD (2010) Rice grown in nutrient solution with doses of manganese and silicon. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 34:1629–1639
Kaufman PB, Takeoka Y, Carlson TJ, Bigelow WC, Jones JD, Moore PH, Ghosheh NS (1979) Studies on silica deposition in sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) using scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray analysis, neutron activation analysis and light microscopy. Phytomorphology 29:185–193
Kim YH, Khan AL, SY Lee KDH, Kim KM, Waqas M, Jung HY, Shin JH, Kim JG, Lee IJ (2014) Silicon mitigates heavy metal stress by regulating P-type heavy metal ATPases, Oryza sativa low silicon genes, and endogenous phytohormones. BMC Plant Biol 14:13
Kitao M, Lei TT, Koike T (1997) Effects of manganese toxicity on photosynthesis of white birch (Betula platyphylla var. japonica) seedlings. Physiol Plant 101:249–256
Li Q, Ma C, Shang Q (2007) Effects of silicon on photosynthesis and antioxidant enzymes of maize under drought stress. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 18:531–536
Li Q, Chen LS, Jiang HX, Tang N, Yang LT, Lin ZH, Li Y, Yang GH (2010) Effects of manganese-excess on CO2 assimilation ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, carbohydrates and photosynthetic electron transport of leaves, and antioxidant systems of leaves and roots in Citrus grandis seedlings. BMC Plant Biol 10:42
Li P, Song AL, Li ZJ, Fan FL, Liang YC (2012) Silicon ameliorates manganese toxicity by regulating manganese transport and antioxidant reactions in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Soil 354:407–419
Liang YC, Wong JWC, Wei L (2005) Silicon-mediated enhancement of cadmium tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.) grown in cadmium contaminated soil. Chemosphere 58:475–483
Liang YC, Sun WC, Zhu YG, Christie P (2007) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of abiotic stresses in higher plants: a review. Environ Pollut 147:422–428
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellbum AR (1983) Determination of total carotenoids and chlorophylls A and B of leaf in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 11:591–592
Lidon FC (2001) Tolerance of rice to excess manganese in the early stages of vegetative growth. Characterization of manganese accumulation. J Plant Physiol 158:1341–1348
Lidon FC, Teixeira MG (2000) Rice tolerance to excess Mn: implications in the chloroplast lamellae and synthesis of a novel Mn protein. Plant Physiol Biochem 38:969–978
Lidon FC, Barreiroc MG, Ramalhob JC (2004) Manganese accumulation in rice: implications for photosynthetic functioning. J Plant Physiol 161:1235–1244
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−△△CT method. Methods 225:402–408
Ma JF, Takahashi E (2002) Functions of silicon in plant growth. In: Ma JF, Takahashi E (eds) Soil, fertilizer, and plant silicon research in Japan. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 107–180
Ma J, Cai H, He C, Zhang W, Wang L (2015) A hemicellulose-bound form of silicon inhibits cadmium ion uptake in rice (Oryza sativa) cells. New Phytol 206:1063–1074
Macfie SM, Taylor GJ (1992) The effects of excess manganese on photosynthetic rate and concentration of chlorophyll in Triticum aestivum grown in solution culture. Physiol Plant 85:67–475
Malčovská SM, Dučaiová Z, Maslaňáková I, Bačkor M (2014) Effect of silicon on growth, photosynthesis, oxidative status and phenolic compounds of maize (Zea mays L.) grown in cadmium excess. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:1–11
Millaleo R, Reyes-Diaz M, Alberdi M, Ivanov AG, Krol M, Huner NP (2013) Excess manganese differentially inhibits photosystem I versus II in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 64:343–354
Monni S, Uhlig C, Hansen E, Magel E (2001) Ecophysiological responses of Empetrum nigrum to heavy metal pollution. Environ Pollut 112:121–129
Moroni JS, Briggs KG, Taylor GJ (1991) Chlorophyll content and leaf elongation rate in wheat seedlings as a measure of manganese tolerance. Plant Soil 136:1–9
Nable RO, Houtz RL, Cheniae GM (1988) Early inhibition of photosynthesis during development of Mn toxicity in tobacco. Plant Physiol 86:136–1142
Nwugo CC, Huerta AJ (2008) Effects of silicon nutrition on cadmium uptake, growth and photosynthesis of rice plants exposed to low-level cadmium. Plant Soil 311:73–86
Nwugo CC, Huerta AJ (2011) The effect of silicon on the leaf proteome of rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants under cadmium-stress. J Proteome Res 10(2):518–528
Ohki K (1985) Manganese deficiency and toxicity effects on photosynthesis, chlorophyll, and transpiration in wheat. Crop Sci 25:187–191
Papadakis IE, Giannakoula A, Therios IN, Bosabalidis AM, Moustakas M, Nastou A (2007) Mn-induced changes in leaf structure and chloroplast ultrastructure of Citrus volkameriana(L) plants. J Plant Physiol 164:100–103
Rezai K, Farboodnia T (2008) Manganese toxicity effects on chlorophyll content and antioxidant enzymes in pea plant (Pisum sativum L.c.v qazvin). Agric J 3:454–458
Rizwan M, Meunier JD, Miche H, Keller C (2012) Effect of silicon on reducing cadmium toxicity in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio W.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. J Hazard Mater 209–210:326–334
Rogalla and Römheld (2002) Role of leaf apoplast in silicon mediated manganese tolerance of Cucumis sativus L. Plant Cell Environ 25:549–555
Romero-Aranda MR, Jurado O, Cuartero J (2006) Silicon alleviates the deleterious salt effect on tomato plant growth by improving plant water status. J Plant Physiol 163:847–855
Rosa-Ibara MDL, Maiti RK (1995) Biochemical mechanism in Glossay sorgum lines for resistance to salinity stress. Plant Physiol 146:515–519
Sanglard LMVP, Martins SCV, Detmann KC, Silva PEM, Lavinsky AO, Silva MM, Detmann E, Araújo WL, DaMatta FM (2014) Silicon nutrition alleviates the negative impacts of arsenic on the photosynthetic apparatus of rice leaves: an analysis of the key limitations of photosynthesis. Physiol Plant. doi:10.1111/ppl.12178
Schlichting E, Sparrow L (1988) Distribution and amelioration of manganese toxic soils. In: Graham RD, Hannam RJ, Uren NC, HP-UTAH Minerals International (Corporation) (eds) Manganese in soils and plants. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 277–288
Shi QH, Bao ZY, Zhu ZJ, He Y, Qian QQ, Yu JQ (2005a) Silicon-mediated alleviation of Mn toxicity in Cucumis sativus in relation to activities of superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase. Phytochemistry 66:1551–1559
Shi XH, Zhang CH, Wang H, Zhang FS (2005b) Effect of Si on the distribution of Cd in rice seedlings. Plant Soil 272:53–60
Shi T, Gao Z, Wang L, Zhang Z, Zhuang W, Sun H, Zhong W (2012) Identification of differentially-expressed genes associated with pistil abortion in Japanese apricot by genome-wide transcriptional analysis. PLoS One 7, e47810
Singh VP, Tripathi DK, Kumar D, Chauhan DK (2011) Influence of exogenous silicon addition on aluminium tolerance in rice seedlings. Biol Trace Elem Res 144:1260–1274
Sinha S, Mukherji S, Dutta J (2002) Effect of manganese toxicity on pigment content, Hill activity and photosynthetic rate of Vigna radiata L. Wilczek seedlings. J Environ Biol 23:253–257
Song AL, Li P, Li ZJ, Fan FL, Liang YC (2014) The effect of silicon on photosynthesis and expression of its relevant genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under high-zinc stress. PLoS One 9(11), e113782
Subrahmanyam D, Rathore VS (2000) Influence of manganese toxicity on photosynthesis in ricebean (Vigna umbellate) seedlings. Photosynthetica 38:449–453
Tripathi DK, Singh VP, Prasad SM, Chauhan DK, Dubey NK, Rai AK (2015) Silicon-mediated alleviation of Cr(VI) toxicity in wheat seedlings as evidenced by chlorophyll florescence, laser induced break down spectroscopy and anatomical changes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 113:133–144
Acknowledgments
This work was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China entitled “The quantitative study of influence of straw returning on silicon releasing in major types of paddy soils in South China” (41301310), Shanxi Agricultural University Doctoral Scientific Research Fund (2012YJ05), The 12th Five Year Key Programs entitled “Techniques for agricultural use of steel and iron slag: Research and demonstration” (2013BAB03B02), National Nonprofit Institute Research Grant of CAAS entitled “The studies on the mechanism and the potential of phytolith carbon sequestration” (IARRP-2015-20) and Natural Science Fund Projects of Shanxi Province (No. 2013011039–3). Thanks are given to Professor Hans Lambers for his critical reading of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Hans Lambers.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Figure 1
(DOC 129 kb)
Supplemental Table 1
(DOC 49 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Song, A., Li, Z. et al. Silicon ameliorates manganese toxicity by regulating both physiological processes and expression of genes associated with photosynthesis in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Soil 397, 289–301 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2626-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2626-y