Abstract
Background
The association of GHR-exon 3 and -202 A/C IGFBP3 polymorphisms with clinical presentation, biochemical measurements and response to therapies in acromegaly have been suggested.
Objective
To evaluate the presence of these polymorphisms in acromegaly and their influence on clinical and laboratorial characteristics of patients at diagnosis and after treatment in a large cohort of acromegalic patients.
Patients and methods
This is a cross-sectional study developed in a single tertiary reference center. Clinical data were obtained from the medical records of 186 acromegalic patients (116 women, age range 21–88 years). GH and IGF1 levels and GHR-exon 3 and -202 A/C IGFBP3 polymorphisms were evaluated in the same hospital.
Results
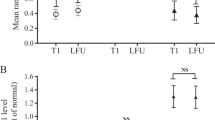
At diagnosis, serum GH concentrations were lower in patients with GHR-d3 genotype than those with GHR-fl, whereas an association of lower IGFBP3 levels with d3 allele was observed only after neurosurgical or medical treatments. However, these associations were not confirmed in posterior statistical analysis.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that GHR-exon 3 and -202 A/C IGFBP3 polymorphisms did not show any consistent association on clinical and laboratorial features of acromegalic patients even after treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dobrashian RD, O’Halloran DJ, Hunt A, Beardwell CG, Shalet SM (1993) Relationships between insulin-like growth factor-1 levels and growth hormone concentrations during diurnal profiles and following oral glucose in acromegaly. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 38:589–593
Parkinson C, Ryder WD, Trainer PJ, Group SAS (2001) The relationship between serum GH and serum IGF-I in acromegaly is gender-specific. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:5240–5244
Dimaraki EV, Jaffe CA, DeMott-Friberg R, Chandler WF, Barkan AL (2002) Acromegaly with apparently normal GH secretion: implications for diagnosis and follow-up. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:3537–3542
Freda PU, Nuruzzaman AT, Reyes CM, Sundeen RE, Post KD (2004) Significance of “abnormal” nadir growth hormone levels after oral glucose in postoperative patients with acromegaly in remission with normal insulin-like growth factor-I levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:495–500
Mercado M, Espinosa de los Monteros AL, Sosa E et al (2004) Clinical–biochemical correlations in acromegaly at diagnosis and the real prevalence of biochemically discordant disease. Horm Res 62:293–299
Alexopoulou O, Bex M, Abs R, T’Sjoen G, Velkeniers B, Maiter D (2008) Divergence between growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-i concentrations in the follow-up of acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:1324–1330
Machado EO, Taboada GF, Neto LV et al (2008) Prevalence of discordant GH and IGF-I levels in acromegalics at diagnosis, after surgical treatment and during treatment with octreotide LAR. Growth Horm IGF Res 18:389–393
Ho PJ, Jaffe CA, Friberg RD, Chandler WF, Barkan AL (1994) Persistence of rapid growth hormone (GH) pulsatility after successful removal of GH-producing pituitary tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 78:1403–1410
Walenkamp MJ, Wit JM (2006) Genetic disorders in the growth hormone—insulin-like growth factor-I axis. Horm Res 66:221–230
Pantel J, Machinis K, Sobrier ML, Duquesnoy P, Goossens M, Amselem S (2000) Species-specific alternative splice mimicry at the growth hormone receptor locus revealed by the lineage of retroelements during primate evolution. J Biol Chem 275:18664–18669
Buzi F, Mella P, Pilotta A, Prandi E, Lanfranchi F, Carapella T (2007) Growth hormone receptor polymorphisms. Endocr Dev 11:28–35
Dos Santos C, Essioux L, Teinturier C, Tauber M, Goffin V, Bougnères P (2004) A common polymorphism of the growth hormone receptor is associated with increased responsiveness to growth hormone. Nat Genet 36:720–724
Sobrier ML, Duquesnoy P, Duriez B, Amselem S, Goossens M (1993) Expression and binding properties of two isoforms of the human growth hormone receptor. FEBS Lett 319:16–20
Urbanek M, Russell JE, Cooke NE, Liebhaber SA (1993) Functional characterization of the alternatively spliced, placental human growth hormone receptor. J Biol Chem 268:19025–19032
Bass SH, Mulkerrin MG, Wells JA (1991) A systematic mutational analysis of hormone-binding determinants in the human growth hormone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:4498–4502
Schmid C, Krayenbuehl PA, Bernays RL, Zwimpfer C, Maly FE, Wiesli P (2007) Growth hormone (GH) receptor isoform in acromegaly: lower concentrations of GH but not insulin-like growth factor-1 in patients with a genomic deletion of exon 3 in the GH receptor gene. Clin Chem 53:1484–1488
Mercado M, González B, Sandoval C et al (2008) Clinical and biochemical impact of the d3 growth hormone receptor genotype in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:3411–3415
Costalonga EF, Antonini SR, Guerra-Junior G, Mendonca BB, Arnhold IJ, Jorge AA (2009) The -202 A allele of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP3) promoter polymorphism is associated with higher IGFBP-3 serum levels and better growth response to growth hormone treatment in patients with severe growth hormone deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:588–595
van der Kaay DC, Hendriks AE, Ester WA et al (2009) Genetic and epigenetic variability in the gene for IGFBP-3 (IGFBP3): correlation with serum IGFBP-3 levels and growth in short children born small for gestational age. Growth Horm IGF Res 19:198–205
Jernström H, Deal C, Wilkin F et al (2001) Genetic and nongenetic factors associated with variation of plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 in healthy premenopausal women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 10:377–384
Deal C, Ma J, Wilkin F et al (2001) Novel promoter polymorphism in insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3: correlation with serum levels and interaction with known regulators. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:1274–1280
Bianchi A, Giustina A, Cimino V et al (2009) Influence of growth hormone receptor d3 and full-length isoforms on biochemical treatment outcomes in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:2015–2022
Bianchi A, Mazziotti G, Tilaro L et al (2009) Growth hormone receptor polymorphism and the effects of pegvisomant in acromegaly. Pituitary 12:196–199
Kamenicky P, Dos Santos C, Espinosa C et al (2009) D3 GH receptor polymorphism is not associated with IGF1 levels in untreated acromegaly. Eur J Endocrinol 161:231–235
Montefusco L, Filopanti M, Ronchi CL et al (2010) d3-Growth hormone receptor polymorphism in acromegaly: effects on metabolic phenotype. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 72:661–667
Bernabeu I, Alvarez-Escolá C, Quinteiro C et al (2010) The exon 3-deleted growth hormone receptor is associated with better response to pegvisomant therapy in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:222–229
Filopanti M, Olgiati L, Mantovani G et al (2012) Growth hormone receptor variants and response to pegvisomant in monotherapy or in combination with somatostatin analogs in acromegalic patients: a multicenter study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:E165–E172
Wassenaar MJ, Biermasz NR, Pereira AM et al (2009) The exon-3 deleted growth hormone receptor polymorphism predisposes to long-term complications of acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:4671–4678
Turgut S, Akın F, Ayada C, Topsakal S, Yerlikaya E, Turgut G (2012) The growth hormone receptor polymorphism in patients with acromegaly: relationship to BMI and glucose metabolism. Pituitary 15:374–379
Akin F, Turgut S, Cirak B, Kursunluoglu R (2010) IGF(CA)19 and IGFBP-3-202A/C gene polymorphism in patients with acromegaly. Growth Horm IGF Res 20:399–403
Acknowledgments
We thanks to Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) for the financial support. This study was funded by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo—FAPESP (Grant Number 2010/11718-1).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jallad, R.S., Trarbach, E.B., Duarte, F.H. et al. Influence of growth hormone receptor (GHR) exon 3 and -202A/C IGFBP-3 genetic polymorphisms on clinical and biochemical features and therapeutic outcome of patients with acromegaly. Pituitary 18, 666–673 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-014-0629-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-014-0629-y