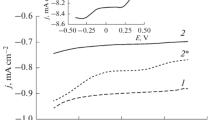
Abstract
We describe an atmospheric-pressure plasma process for the reduction of metal cation-containing polymer films to form electrically conductive patterns. Thin films of poly(acrylic) acid (PAA) containing silver ions (Ag+) were prepared by mixing the polymer with silver nitrate (AgNO3) in solution to produce a cross-linked precipitate, homogenizing, and depositing onto a substrate by doctor’s blade. Exposing the Ag–PAA films to a scanning microplasma resulted in reduction of the bulk dispersed Ag+ in a desired pattern at the film surface. The processed films were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, and current–voltage measurements. The resistances of the patterned features were found to depend on the thickness of the films, the microplasma scan rate, residual solvent in the film, and electric field created between the microplasma and the substrate. Together these results show that the formation of conductive features occurs via an electrodiffusion process where Ag+ diffuses from the film bulk to the surface to be reduced by the microplasma.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu X, Huo PP, Zhang YP, Liu CJ (2006) Ind Eng Chem Res 45(25):8604–8609
Crowther JM, Badyal JPS (1998) Adv Mater 10(5):407–411
Bromberg V, Ma S, Egittob FD, Singler TJ (2013) J Mater Chem C 1:6842–6849
Zou JJ, Zhang YP, Liu CJ (2006) Langmuir 22(26):11388–11394
Crowther JM, Badyal JPS (2012) Aust J Chem 65:1139–1144
Yu Y, Li Y, Pan Y, Liu CJ (2012) Nanoscale Res Lett 7(1):234–238
Fei X, Kuroda SI, Zhang G, Mori T, Hosoi K (2014) Key Eng Mater 596:60–64
Lee SW, Liang D, Gao XPA, Sankaran RM (2011) Adv Funct Mater 21(11):2155–2161
Ghosh S, Yang R, Kaumeyer M, Zorman CA, Rowan SJ, Feng PXL, Sankaran RM (2014) ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:3099–3104
Zou J, Zhang Y, Liu CJ (2006) Langmuir 22(26):11388–11394
Lahav M, Narovlyansky M, Winkleman A, Perez-Castillejos R, Weiss EA, Whitesides GM (2006) Adv Mater 18(23):3174–3178
Winkleman A, Perez-Castillejos R, Lahav M, Narovlyansky M, Rodriguez LNJ, Whitesides GM (2006) Soft Mater 3:108–116
Ahn BY, Walker SB, Slimmer SC, Russo A, Gupta A, Kranz S, Duoss EB, Malkowski TF, Lewis JA (2011) JoVE 58:3189
Sankaran RM, Giapis KP (2002) J Appl Phys 92:2406–2411
Machin D, Rogers CE (1972) Macromol Chem Phys 155(1):269–281
Cárdenas G, Muñoz C, Carbacho H (2000) Eur Polym J 36(6):1091–1099
Stern KH (1972) J Phys Chem Ref Data 1(3):747
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the National Science Foundation under Grant No. SNM-1246715 for support of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, S., Ostrowski, E., Yang, R. et al. Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma Reduction of Metal Cation-Containing Polymer Films to Produce Electrically Conductive Nanocomposites by an Electrodiffusion Mechanism. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 36, 295–307 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-015-9665-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-015-9665-2