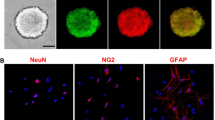
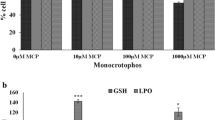
Abstract
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have the potential to differentiate into neural lineages. Salvianolic acid B (Sal B) is a commonly used, traditional Chinese medicine for enhancing neuroprotective effects, and has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic properties. Here, we explore the potential mechanism of Sal B in protecting iPSC-derived neural stem cells (NSCs) against H2O2-induced injury. iPSCs were induced into NSCs, iPSC-derived NSCs were treated with 50 μM Sal B for 24.5 h and 500 μM H2O2 for 24 h. The resulting effects were examined by flow cytometry analysis, quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction, and western blotting. Upon H2O2 exposure, Sal B significantly promoted cell viability and stabilization of the mitochondrial membrane potential. Sal B also visibly decreased the cell apoptotic ratio. In addition, Sal B markedly reduced expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and -9, and phosphospecific signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (p-STAT3), and increased the level of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-2 in iPSC-derived NSCs induced by H2O2. These results suggest that Sal B protects iPSC-derived NSCs against H2O2-induced oxidative stress. The mechanisms of this stress tolerance may be attributed to modulation of the MMP/TIMP system and inhibition of the STAT3 signaling pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shu T, Pang M, Rong L, Zhou W, Wang J, Liu C, Wang X (2014) Effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza on neural differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells. J Ethnopharmacol 153:233–241
Yuan T, Liao W, Feng NH, Lou YL, Niu X, Zhang AJ, Wang Y, Deng ZF (2013) Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural stem cells survive, migrate, differentiate, and improve neurological function in a rat model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stem Cell Res Ther 4:73
Szymczak P, Wojcik-Stanaszek L, Sypecka J, Sokolowska A, Zalewska T (2010) Effect of matrix metalloproteinases inhibition on the proliferation and differentiation of HUCB-NSCs cultured in the presence of adhesive substrates. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 70:325–336
Jung JS, Ahn JH, Le TK, Kim DH, Kim HS (2013) Protopanaxatriol ginsenoside Rh1 inhibits the expression of matrix metalloproteinases and the in vitro invasion/migration of human astroglioma cells. Neurochem Int 63:80–86
Sinno M, Biagioni S, Ajmone-Cat MA, Pafumi I, Caramanica P, Medda V, Tonti G, Minghetti L, Mannello F, Cacci E (2013) The matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor marimastat promotes neural progenitor cell differentiation into neurons by gelatinase-independent TIMP-2-dependent mechanisms. Stem Cells Dev 22:345–358
Lee JH, Cui HS, Shin SK, Kim JM, Kim SY, Lee JE, Koo BN (2013) Effect of propofol post-treatment on blood-brain barrier integrity and cerebral edema after transient cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurochem Res 38:2276–2286
Zhang K, McQuibban GA, Silva C, Butler GS, Johnston JB, Holden J, Clark-Lewis I, Overall CM, Power C (2003) HIV-induced metalloproteinase processing of the chemokine stromal cell derived factor-1 causes neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci 6:1064–1071
Noble LJ, Donovan F, Igarashi T, Goussev S, Werb Z (2002) Matrix metalloproteinases limit functional recovery after spinal cord injury by modulation of early vascular events. J Neurosci 22:7526–7535
Bai X, Zhang X, Chen L, Zhang J, Zhang L, Zhao X, Zhao T, Zhao Y (2014) Protective effect of naringenin in experimental ischemic stroke: down-regulated NOD2, RIP2, NF-kappaB, MMP-9 and up-regulated claudin-5 expression. Neurochem Res 39:1405–1415
Lin YH, Liu AH, Wu HL, Westenbroek C, Song QL, Yu HM, Ter Horst GJ, Li XJ (2006) Salvianolic acid B, an antioxidant from Salvia miltiorrhiza, prevents Abeta(25-35)-induced reduction in BPRP in PC12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348:593–599
Li K, Li SZ, Zhang YL, Wang XZ (2011) The effects of dan-shen root on cardiomyogenic differentiation of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 415:147–151
Kim DH, Park SJ, Kim JM, Jeon SJ, Kim DH, Cho YW, Son KH, Lee HJ, Moon JH, Cheong JH, Ko KH, Ryu JH (2011) Cognitive dysfunctions induced by a cholinergic blockade and Abeta 25–35 peptide are attenuated by salvianolic acid B. Neuropharmacology 61:1432–1440
Wang SX, Hu LM, Gao XM, Guo H, Fan GW (2010) Anti-inflammatory activity of salvianolic acid B in microglia contributes to its neuroprotective effect. Neurochem Res 35:1029–1037
Wu HL, Li YH, Lin YH, Wang R, Li YB, Tie L, Song QL, Guo DA, Yu HM, Li XJ (2009) Salvianolic acid B protects human endothelial cells from oxidative stress damage, a possible protective role of glucose-regulated protein 78 induction. Cardiovasc Res 81:148–158
Zhou J, Qu XD, Li ZY, Wei J, Liu Q, Ma YH, He JJ (2014) Salvianolic acid B attenuates toxin-induced neuronal damage via Nrf2-dependent glial cells-mediated protective activity in Parkinson’s disease models. PLoS One 9:e101668
Nicolas CS, Amici M, Bortolotto ZA, Doherty A, Csaba Z, Fafouri A, Dournaud P, Gressens P, Collingridge GL, Peineau S (2013) The role of JAK-STAT signaling within the CNS. JAKSTAT 2:e22925
Fang S, Xu H, Lu J, Zhu Y, Jiang H (2013) Neuroprotection by the kappa-opioid receptor agonist, BRL52537, is mediated via up-regulating phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Neurochem Res 38:2305–2312
Manickam M, Tulsawani R (2014) Survival response of hippocampal neurons under low oxygen conditions induced by Hippophae rhamnoides is associated with JAK/STAT signaling. PLoS One 9:e87694
Zhu H, Zou L, Tian J, Du G, Gao Y (2013) SMND-309, a novel derivative of salvianolic acid B, protects rat brains ischemia and reperfusion injury by targeting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 714:23–31
Przybyla LM, Theunissen TW, Jaenisch R, Voldman J (2013) Matrix remodeling maintains embryonic stem cell self-renewal by activating Stat3. Stem Cells 31:1097–1106
Kreitzer FR, Salomonis N, Sheehan A, Huang M, Park JS, Spindler MJ, Lizarraga P, Weiss WA, So PL, Conklin BR (2013) A robust method to derive functional neural crest cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Am J Stem Cells 2:119–131
Nori S, Okada Y, Yasuda A, Tsuji O, Takahashi Y, Kobayashi Y, Fujiyoshi K, Koike M, Uchiyama Y, Ikeda E, Toyama Y, Yamanaka S, Nakamura M, Okano H (2011) Grafted human-induced pluripotent stem-cell-derived neurospheres promote motor functional recovery after spinal cord injury in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:16825–16830
Zhang N, Kang T, Xia Y, Wen Q, Zhang X, Li H, Hu Y, Hao H, Zhao D, Sun D, Yan Y, Zhang GX, Yang J (2012) Effects of salvianolic acid B on survival, self-renewal and neuronal differentiation of bone marrow derived neural stem cells. Eur J Pharmacol 697:32–39
Bi XB, Deng YB, Gan DH, Wang YZ (2008) Salvianolic acid B promotes survival of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells in spinal cord-injured rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29:169–176
Sun LQ, Zhao J, Zhang TT, Qu L, Wang X, Xue B, Li XJ, Mu YM, Lu JM (2012) Protective effects of Salvianolic acid B on Schwann cells apoptosis induced by high glucose. Neurochem Res 37:996–1010
Fu Q, Gao N, Yu J, Ma G, Du Y, Wang F, Su Q, Che F (2014) Diazoxide pretreatment prevents Abeta1-42 induced oxidative stress in cholinergic neurons via alleviating NOX2 expression. Neurochem Res 39:1313–1321
Mannello F, Tonti GA, Bagnara GP, Papa S (2006) Role and function of matrix metalloproteinases in the differentiation and biological characterization of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 24:475–481
Mannello F, Luchetti F, Falcieri E, Papa S (2005) Multiple roles of matrix metalloproteinases during apoptosis. Apoptosis 10:19–24
Dzwonek J, Rylski M, Kaczmarek L (2004) Matrix metalloproteinases and their endogenous inhibitors in neuronal physiology of the adult brain. FEBS Lett 567:129–135
Lee K, Lee JS, Jang HJ, Kim SM, Chang MS, Park SH, Kim KS, Bae J, Park JW, Lee B, Choi HY, Jeong CH, Bu Y (2012) Chlorogenic acid ameliorates brain damage and edema by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2 and 9 in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol 689:89–95
Hahn-Dantona E, Ruiz JF, Bornstein P, Strickland DK (2001) The low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein modulates levels of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) by mediating its cellular catabolism. J Biol Chem 276:15498–15503
Anelli T, Mannello F, Salani M, Tonti GA, Poiana G, Biagioni S (2007) Acetylcholine induces neurite outgrowth and modulates matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 362:269–274
Njiee G, Kantorovich S, Astary GW, Green C, Zheng T, Semple-Rowland SL, Steindler DA, Sarntinoranont M, Streit WJ, Borchelt DR (2012) A preclinical assessment of neural stem cells as delivery vehicles for anti-amyloid therapeutics. PLoS One 7:e34097
Wang L, Zhang ZG, Zhang RL, Gregg SR, Hozeska-Solgot A, LeTourneau Y, Wang Y, Chopp M (2006) Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2) and MMP9 secreted by erythropoietin-activated endothelial cells promote neural progenitor cell migration. J Neurosci 26:5996–6003
Ben-Hur T, Ben-Yosef Y, Mizrachi-Kol R, Ben-Menachem O, Miller A (2006) Cytokine-mediated modulation of MMPs and TIMPs in multipotential neural precursor cells. J Neuroimmunol 175:12–18
Wu JP, Kuo JS, Liu YL, Tzeng SF (2000) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha modulates the proliferation of neural progenitors in the subventricular/ventricular zone of adult rat brain. Neurosci Lett 292:203–206
Song Y, Zeng Z, Jin C, Zhang J, Ding B, Zhang F (2013) Protective effect of ginkgolide B against acute spinal cord injury in rats and its correlation with the Jak/STAT signaling pathway. Neurochem Res 38:610–619
Garza JC, Guo M, Zhang W, Lu XY (2008) Leptin increases adult hippocampal neurogenesis in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem 283:18238–18247
Cheng X, Jin G, Zhang X, Tian M, Zou L (2011) Stage-dependent STAT3 activation is involved in the differentiation of rat hippocampus neural stem cells. Neurosci Lett 493:18–23
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (31170947), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014M552272), the Guangdong Natural Sciences Foundation of China (S2012020011099 and S2013010016413), the Guangzhou Science and Technology Project of China (2013J4100062), and the New Teachers’ Fund for Doctor Stations of Ministry of Education of China (20100171120088).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Tao Shu and Mao Pang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, T., Pang, M., Rong, L. et al. Protective Effects and Mechanisms of Salvianolic Acid B Against H2O2-Induced Injury in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neural Stem Cells. Neurochem Res 40, 1133–1143 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1573-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1573-6