Abstract
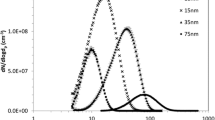
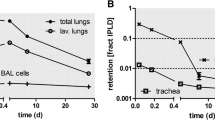
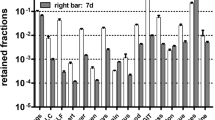
The intensive use of nano-sized particles in many different applications necessitates studies on their risk assessment as there are still open questions on their safe handling and utilization. For reliable risk assessment, the interaction of nanoparticles (NP) with biological systems after various routes of exposure needs to be investigated using well-characterized NP. We report here on the generation of gold-NP (Au-NP) aerosols for inhalation studies with the spark ignition technique, and their characterization in terms of chemical composition, physical structure, morphology, and specific surface area, and on interaction with lung tissues and lung cells after 1 h inhalation by mice. The originally generated agglomerated Au-NP were converted into compact spherical Au-NP by thermal annealing at 600 °C, providing particles of similar mass, but different size and specific surface area. Since there are currently no translocation data available on inhaled Au-NP in the 10–50 nm diameter range, the emphasis was to generate NP as small as 20 nm for inhalation in rodents. For anticipated in vivo systemic translocation and dosimetry analyses, radiolabeled Au-NP were created by proton irradiating the gold electrodes of the spark generator, thus forming gamma ray emitting 195Au with 186 days half-life, allowing long-term biokinetic studies. The dissolution rate of 195Au from the NP was below detection limits. The highly concentrated, polydisperse Au-NP aerosol (1–2 × 107 NP/cm3) proved to be constant over several hours in terms of its count median mobility diameter, its geometric standard deviation and number concentration. After collection on filters particles can be re-suspended and used for instillation or ingestion studies.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessandrini F, Semmler-Behnke M, Jakob T, Schulz H, Behrendt H, Kreyling W (2008) Total and regional deposition of ultrafine particles in a mouse model of allergic inflammation of the lung. Inhal Toxicol 20(6):585–593
Arvizo R, Bhattacharya R, Mukherjee P (2010) Gold nanoparticles: opportunities and challenges in nanomedicine. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 7(6):753–763. doi:10.1517/17425241003777010
Baron PA, Willeke K (2001) Aerosol measurement: principles, techniques, and applications, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Baumeister W (2002) Electron tomography: towards visualizing the molecular organization of the cytoplasm. Curr Opin Struct Biol 12(5):679–684
Buffat P, Borel JP (1976) Size effect on the melting temperature of gold particles. Phys Rev A 13(6):2287–2298
Doane TL, Burda C (2012) The unique role of nanoparticles in nanomedicine: imaging, drug delivery and therapy. Chem Soc Rev 41(7):2885–2911. doi:10.1039/C2cs15260f
Donaldson K, Stone V, Tran CL, Kreyling W, Borm PJA (2004) Nanotoxicology. Occup Environ Med 61(9):727–728
Ferin J, Oberdörster G, Penney DP (1992) Pulmonary retention of ultrafine and fine particles in rats. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 6(5):535–542
Fierz M, Kaegi R, Burtscher H (2007) Theoretical and experimental evaluation of a portable electrostatic TEM sampler. Aerosol Sci Technol 41(5):520–528
Firestone RB, Ekström LP (2004) WWW table of radioactive isotopes. LBNL Isotopes Project—LUNDS Universitet, vol 2.1. Lund University, Lund, Sweden
Geiser M, Kreyling W (2010) Deposition and biokinetics of inhaled nanoparticles. Part Fibre Toxicol 7(1):2
Geiser M, Rothen-Rutishauser B, Kapp N, Schurch S, Kreyling W, Schulz H, Semmler M, Hof VI, Heyder J, Gehr P (2005) Ultrafine particles cross cellular membranes by nonphagocytic mechanisms in lungs and in cultured cells. Environ Health Perspect 113(11):1555–1560
Geiser M, Casaulta M, Kupferschmid B, Schulz H, Semmler-Behnke M, Kreyling W (2008) The role of macrophages in the clearance of inhaled ultrafine titanium dioxide particles. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 38(3):371–376
George S, Pokhrel S, Xia T, Gilbert B, Ji Z, Schowalter M, Rosenauer A, Damoiseaux R, Bradley KA, Madler L, Nel AE (2010) Use of a rapid cytotoxicity screening approach to engineer a safer zinc oxide nanoparticle through iron doping. ACS Nano 4(1):15–29. doi:10.1021/nn901503q
Gibson PN, Özsan ME, Lincot D, Cowache P, Summa D (2000) Modelling of the structure of CdS thin films. Thin Solid Films 361–362:34–40. doi:10.1016/s0040-6090(99)00833-0
Hainfeld JF, Slatkin DN, Focella TM, Smilowitz HM (2006) Gold nanoparticles: a new X-ray contrast agent. Br J Radiol 79(939):248–253
Holzwarth U, Bulgheroni A, Gibson N, Kozempel J, Cotogno G, Abbas K, Simonelli F, Cydzik I (2012) Radiolabelling of nanoparticles by proton irradiation: temperature control in nanoparticulate powder targets. J Nanopart Res 14(6):1–15. doi:10.1007/s11051-012-0880-y
Kreuter J (2004) Influence of the surface properties on nanoparticle-mediated transport of drugs to the brain. J Nanosci Nanotech 4(5):484–488
Kreyling W, Biswas P, Messing M, Gibson N, Geiser M, Wenk A, Sahu M, Deppert K, Cydzik I, Wigge C, Schmid O, Semmler-Behnke M (2011) Generation and characterization of stable, highly concentrated titanium dioxide nanoparticle aerosols for rodent inhalation studies. J Nanopart Res 13(2):511–524. doi:10.1007/s11051-010-0081-5
Kreyling WG, Semmler-Behnke M, Takenaka S, Möller W (2013) Differences in the biokinetics of inhaled nano-versus micrometer-sized particles. Accounts Chem Res (in press). doi:10.1021/ar300043r
Kuehl PJ, Anderson TL, Candelaria G, Gershman B, Harlin K, Hesterman JY, Holmes T, Hoppin J, Lackas C, Norenberg JP, Yu H, McDonald JD (2012) Regional particle size dependent deposition of inhaled aerosols in rats and mice. Inhal Toxicol 24(1):27–35. doi:10.3109/08958378.2011.632787
Liu Z, Kim SC, Wang J, Shin WG, Fissan H, Pui DYH (2012) Measurement of metal nanoparticle agglomerates generated by spark discharge using the universal nanoparticle analyzer (UNPA). Aerosol Sci Technol 46(3):333–346. doi:10.1080/02786826.2011.626002
Ma-Hock L, Gamer AO, Landsiedel R, Leibold E, Frechen T, Sens B, Linsenbuehler M, van Ravenzwaay B (2007) Generation and characterization of test atmospheres with nanomaterials. Inhal Toxicol 19(10):833–848
Maynard AD, Aitken RJ, Butz T, Colvin V, Donaldson K, Oberdörster G, Philbert MA, Ryan J, Seaton A, Stone V, Tinkle SS, Tran L, Walker NJ, Warheit DB (2006) Safe handling of nanotechnology. Nature 444(7117):267–269
Moghimi SM, Hunter AC, Murray JC (2005) Nanomedicine: current status and future prospects. FASEB J 19(3):311–330
Nel A, Xia T, Madler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311(5761):622–627
Nel AE, Mädler L, Velegol D, Xia T, Hoek EMV, Somasundaran P, Klaessig F, Castranova V, Thompson M (2009) Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano-bio interface. Nat Mater 8(7):543–557
Oberdörster G, Oberdörster E, Oberdörster J (2005) Nanotoxicology: an emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ Health Perspect 113:823–839
Papasani MR, Wang G, Hill RA (2012) Gold nanoparticles: the importance of physiological principles to devise strategies for targeted drug delivery. Nanomedicine (Lond). doi:10.1016/j.nano.2012.01.008
Peters A, Veronesi B, Calderon-Garciduenas L, Gehr P, Chen L, Geiser M, Reed W, Rothen-Rutishauser B, Schurch S, Schulz H (2006) Translocation and potential neurological effects of fine and ultrafine particles a critical update. Part Fibre Toxicol 3(1):13
Porter D, Sriram K, Wolfarth M, Jefferson A, Schwegler-Berry D, Andrew ME, Castranova V (2008) A biocompatible medium for nanoparticle dispersion. Nanotoxicology 2(3):144–154
Rand D, Ortiz V, Liu Y, Derdak Z, Wands JR, Tatíček M, Rose-Petruck C (2011) Nanomaterials for X-ray imaging: gold nanoparticle enhancement of X-ray scatter imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nano Lett 11(7):2678–2683. doi:10.1021/nl200858y
Seaton A, Donaldson K (2005) Nanoscience, nanotoxicology, and the need to think small. Lancet 365(9463):923–924
Semmler-Behnke M, Kreyling WG, Lipka J, Fertsch S, Wenk A, Takenaka S, Schmid G, Brandau W (2008) Biodistribution of 1.4- and 18-nm gold particles in rats. Small 4(12):2108–2111. doi:10.1002/smll.200800922
Stoeger T, Reinhard C, Takenaka S, Schroeppel A, Karg E, Ritter B, Heyder J, Schulz H (2006) Instillation of six different ultrafine carbon particles indicates a surface area threshold dose for acute lung inflammation in mice. Environ Health Perspect 114(3):328–333
Takenaka S, Karg E, Kreyling WG, Lentner B, Möller W, Behnke-Semmler M, Jennen L, Walch A, Michalke B, Schramel P, Heyder J, Schulz H (2006) Distribution pattern of inhaled ultrafine gold particles in the rat lung. Inhal Toxicol 18(10):733–740
Takenaka S, Möller W, Semmler-Behnke M, Karg E, Wenk A, Schmid O, Stoeger T, Jennen L, Aichler M, Walch A, Pokhrel S, Mädler L, Eickelberg O, Kreyling WG (2012) Efficient internalization and intracellular translocation of inhaled gold nanoparticles in rat alveolar macrophages. Nanomedicine (Lond) 7:855–865. doi:10.2217/nnm.11.152
Wilson BJ (1966) The radiochemical manual, 2nd edn. Radiochemical Centre, Amersham
Zhang H, Ji Z, Xia T, Meng H, Low-Kam C, Liu R, Pokhrel S, Lin S, Wang X, Liao Y-P, Wang M, Li L, Rallo R, Damoiseaux R, Telesca D, Mädler L, Cohen Y, Zink JI, Nel AE (2012) Use of metal oxide nanoparticle band gap to develop a predictive paradigm for oxidative stress and acute pulmonary inflammation. ACS Nano 6(5):4349–4368. doi:10.1021/nn3010087
Acknowledgments
This work was partially funded by HMGU: EU FP7 Projects NeuroNano, NMP4-SL-2008-214547; ENPRA, NMP4-SL-2009-228789; InLiveTox, NMP4-SL-2009-228625; UBern: Swiss National Science Foundation Project 310030-120763; UBremen: S.P. and L.M. would like to thank National Science Foundation and the Environmental Protection Agency under Cooperative Agreement Number DBI-0830117 for supporting this work. Key support was also provided by the US Public Health Service Grants U19 ES019528 (UCLA Center for NanoBiology and Predictive Toxicology), RO1 ES016746, and RC2 ES018766. S.P. and L.M. would also like to thank Prof. A. Rosenauer and M. Schowalter, Department of Physics, University of Bremen, for TEM and EDX analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Möller, W., Gibson, N., Geiser, M. et al. Gold nanoparticle aerosols for rodent inhalation and translocation studies. J Nanopart Res 15, 1574 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1574-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1574-9