Abstract
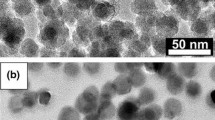
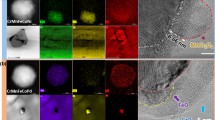
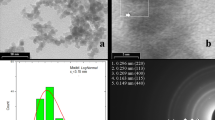
The near-surface oxidation-induced lattice relaxation and compositional changes of FeNi alloy nano-particles are investigated. Using a newly developed transfer system, the particle structure was characterised by means of aberration-corrected HR-TEM prior to exposing the particles to ambient air. This allows for a comparison of oxidised and un-oxidised particles, respectively. Independent of the oxidation, the surface-near and/or interface-near metal lattice was found to be expanded by up to 3%. EELS profiles clearly reveal an enrichment of Fe at the particle surfaces. MD simulations in combination with HR-TEM contrast simulations were conducted to investigate the effect of the Fe enrichment on the structural relaxation. The results show that a surface-near over-stoichiometric enrichment of Fe indeed causes a dilation that counteracts a compression of the lattice at the particle surface as obtained for homogeneously alloyed particles. Besides, the large lattice mismatch between the metallic cores and the NiFe2O4 shells causes the formation of step dislocations in the close vicinities of the interface. In essence, the surface-near lattice relaxation in oxide free particles is found to be due to a segregation of Fe to the surface, whereas in the case of shell–core particles, no systematic influence of the oxide on the lattice relaxation was found.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoniak C, Spasova M, Trunova A, Fauth K, Wilhelm F, Rogalev A, Minar J, Ebert H, Farle M, Wende H (2009) Inhomogeneous alloying in FePt nanoparticles as a reason for reduced magnetic moments. J Phys 21(33). doi:10.1088/0953-8984/21/33/336002
Baletto F, Ferrando R (2005) Structural properties of nanoclusters: energetic, thermodynamic, and kinetic effects. Rev Mod Phys 77:371
Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, Vangunsteren WF, Dinola A, Haak JR (1984) Molecular-dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys 81(8):3684
Colliex C, Manoubi T, Ortiz C (1991-II) Electron-energy-loss-spectroscopy near-edge fine structure in the iron-oxygen system. Phys Rev B 4(20):11402
D’Addato S, Pasquali L, Gazzadi G, Verucchi R, Capelli R, Nannarone S (2000) Growth of Fe ultrathin films on Ni(111): structure and electronic properties. Surf Sci 454-456:692
Danneberg A, Gruner ME, Hucht A, Entel P (2009) Surface energies of stoichiometric FePt and CoPt alloys and their implications for nanoparticle morphologies. Phys Rev B 80(24). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.80.245438
Dmitrieva O, Spasova M, Antoniak C, Acet M, Dumpich G, Kaestner J, Farle M, Fauth K, Wiedwald U, Boyen HG, Ziemann P (2007) Magnetic moment of Fe in oxide-free FePt nanoparticles. Phys Rev B 76(6). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.76.064414
Doerner MF, Nix WD (1988) Stresses and deformation processes in thin-films on substrates. CRC Crit Rev Solid State Mater Sci 14(3):225
Dumpich G, Wassermann E, Manns V, Keune W, Murayama S, Miyako Y (1987) Structural and magnetic properties of Ni x Fe1−x evaporated thin-films. J Magn Magn Mater 67(1):55
Egerton R (1996) Electron energy-loss spectroscopy in the electron microscope, 2nd edn. Plenum Publishers, New York
Flagan RC, Lunden MM (1995) Particle structure control in nanoparticle synthesis from the vapor phase. Mater Sci Eng A 204(1–2):113
Freund LB, Nix WD (1996) Critical thickness condition for a strained compliant substrate/epitaxial film system. Appl Phys Lett 69(2):173
Ghaly M, Nordlund K, Averback RS (1999) Molecular dynamics investigations of surface damage produced by kiloelectronvolt self-bombardment of solids. Philos Mag A 79(4):795
Gibbons DF (1957) Acoustic relaxations in ferrite single crystals. J Appl Phys 28(7):810
Haberland H, Mall M, Moseler M, Qian Y, Reiners T, Thurner Y (1994) Filling Of micron-sized contact holes with copper by energetic cluster-impact. J Vac Sci Technol A 12(5):2925
Leapman R, Grunes L, Fejes P (1982) Study od the L23 edges in the 3d transition metals and their oxides by electron-energy-loss spectroscopy with comparisons to theory. Phys Rev B 26(1):614
Leapman RD, Rez P, Mayers DF (1980) K-shell, L-shell and M-shell generalized oscillator-strenghts and Ionization cross-sections for fast electron collissions. J Chem Phys 72(2):1232
Lentzen M, Jahnen B, Jia CL, Thust A, Tillmann K, Urban K (2002) High-resolution imaging with an aberration-corrected transmission electron microscope. Ultramircroscopy 92(3–4):233
Massalski TB, Murray JL, Bennet LH, Baker H (1986) Binary phase diagrams. ASM International, Materials Park, p 1096
Methfessel M, Hennig D, Scheffler M (1992) Trends of the surface relaxations, surface energies, and work-functions of the 4D transition-metals. Phys Rev B 46(8):4816
Meyer R, Entel P (1998) Martensite-austenite transition and phonon dispersion curves of FeNi studied by molecular-dynamics simulations. Phys Rev B 57(9):5140
Nix WD (1989) Mechanical properties of thin-films. Metall Trans A 20(11):2217
Rellinghaus B, Stappert S, Acet M, Wassermann EF (2003) Magnetic properties of FePt nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 266(1-2):142–154
Stappert S, Rellinghaus B, Acet M, Wassermann EF (2003) Gas-phase preparation of l10 ordered fept nanoparticles. J Cryst Growth 252:440–450
Total Resolution (2010) MacTempasX. http://www.totalresolution.com
Verbeeck J, Van Aert S (2004) Model based quantification of EELS spectra. Ultramircroscopy 101(2–4):207
Vitos L, Ruban AV, Skriver HL, Kollar J (1998) The surface energy of metals. Surf Sci 411(1–2):186
Wang RM, Dmitrieva O, Farle M, Dumpich G, Ye HQ, Poppa H, Kilaas R, Kisielowski C (2008) Layer resolved structural relaxation at the surface of magnetic FePt icosahedral nanoparticles. Phys Rev Lett 100:017205
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to the facility department of the IFW Dresden for developing the transfer module and to A. Hartmann for his support with the EELS measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bieniek, B., Pohl, D., Schultz, L. et al. The effect of oxidation on the surface-near lattice relaxation in FeNi nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 13, 5935–5946 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0405-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0405-0