Abstract
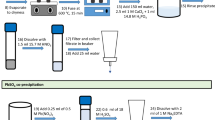
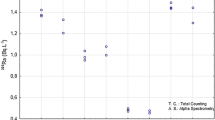
A new rapid method for the determination of 226Ra in environmental samples has been developed at the Savannah River Site Environmental Lab (Aiken, SC, USA) that can be used for emergency response or routine sample analyses. The need for rapid analyses in the event of a Radiological Dispersive Device or Improvised Nuclear Device event is well-known. In addition, the recent accident at Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant in March, 2011 reinforces the need to have rapid analyses for radionuclides in environmental samples in the event of a nuclear accident. 226Ra (T1/2 = 1,620 years) is one of the most toxic of the long-lived alpha-emitters present in the environment due to its long life and its tendency to concentrate in bones, which increases the internal radiation dose of individuals. The new method to determine 226Ra in environmental samples utilizes a rapid sodium hydroxide fusion method for solid samples, calcium carbonate precipitation to preconcentrate Ra, and rapid column separation steps to remove interferences. The column separation process uses cation exchange resin to remove large amounts of calcium, Sr Resin to remove barium and Ln Resin as a final purification step to remove 225Ac and potential interferences. The purified 226Ra sample test sources are prepared using barium sulfate microprecipitation in the presence of isopropanol for counting by alpha spectrometry. The method showed good chemical recoveries and effective removal of interferences. The determination of 226Ra in environmental samples can be performed in less than 16 h for vegetation, concrete, brick, soil, and air filter samples with excellent quality for emergency or routine analyses. The sample preparation work takes less than 6 h. 225Ra (T1/2 = 14.9 day) tracer is used and the 225Ra progeny 217At is used to determine chemical yield via alpha spectrometry. The rapid fusion technique is a rugged sample digestion method that ensures that any refractory radium particles are effectively digested. The preconcentration and column separation steps can also be applied to aqueous samples with good results.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larivière D, Cumming T, Kiser S, Li C, Cornett R (2008) Automated flow injection system using extraction chromatography for the determination of plutonium in urine by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom 23:352
Stricklin DL, Tjarnhage A, Nygren U (2002) Application of low energy gamma-spectrometry in rapid actinide analysis for emergency preparedness. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 251(1):69
Maxwell S, Culligan B, Noyes G (2010) Rapid separation method for actinides and radiostrontium in vegetation samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 286(1):273–282
Wardaszko T, Grzybowska D, Nidecka J (1986) 222Rn and 226Ra in fresh waters: measurement method and results. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 17(5–6):530–534
Escobar VG, Tome F, Lozano J, Sanchez A (1996) Determination of 222Ra and 226Ra in aqueous samples using a low level liquid scintillation counter. Appl Radiat Isot 47(9/10):861–867
Benkhedda K, Larivière D, Scott S, Evans D (2005) Hyphenation of flow injection on-line preconcentration and ICP-MS for the rapid determination of 226Ra in natural waters. J Anal At Spectrom 20:523–528
Chabaux F, Othman B, Birck JL (1994) A new Ra–Ba chromatographic separation and its application to Ra mass-spectrometric measurement in volcanic rocks. Chem Geol 114(3–4):191–197
Larivière D, Brownell DK, Epov VN, Cornett RJ, Evans RD (2007) Determination of 226Ra in sediments by ICP-MS: a comparative study of three sample preparation approaches. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 273(2):337–344
Crespo MT (2000) On the determination of 226Ra in environmental and geological samples by alpha-spectrometry using 225Ra as yield tracer. Appl Radiat Isot 53(1–2):109–114
Maxwell SL (2006) Rapid method for 226Ra and 228Ra analysis in water samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 270(3):651–655
Burnett WC (2004) Radium-228 determination of natural waters via concentration on manganese dioxide and separation using Diphonix ion exchange resin. Appl Radiat Isot 61:1173
Burnett WC, Moon DS, Nour S, Horwitz P, Bond A (2003) Preconcentration of radium isotopes from natural waters using MnO2 resin. Appl Radiat Isot 59:255–262
Sharabia G, Lazarb B, Kolodny Y, Teplyakov N, Halicz L (2010) High precision determination of 228Ra and 228Ra/226Ra isotope ratio in natural waters by MC-ICPMS. Int J Mass Spectrom 294(2–3):112–115
Currie LA (1968) Limits for qualitative and quantitative determination. Anal Chem 40:586
Acknowledgment
This work was performed under the auspices of the Department of Energy, DOE Contract No. DE-AC09-96SR18500. The authors wish to acknowledge Staci Britt, Jack Herrington and Becky Chavous for their assistance with this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maxwell, S.L., Culligan, B.K. Rapid determination of 226Ra in environmental samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 293, 149–156 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-1627-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-1627-z