Abstract
The transitional and well-developed regimes of turbulent shear flows exhibit a variety of remarkable scaling laws that are only now beginning to be systematically studied and understood. In the first part of this article, we summarize recent progress in understanding the friction factor of turbulent flows in rough pipes and quasi-two-dimensional soap films, showing how the data obey a two-parameter scaling law known as roughness-induced criticality, and exhibit power-law scaling of friction factor with Reynolds number that depends on the precise form of the nature of the turbulent cascade. These results hint at a non-equilibrium fluctuation-dissipation relation that applies to turbulent flows. The second part of this article concerns the lifetime statistics in smooth pipes around the transition, showing how the remarkable super-exponential scaling with Reynolds number reflects deep connections between large deviation theory, extreme value statistics, directed percolation and the onset of coexistence in predator-prey ecosystems. Both these phenomena reflect the way in which turbulence can be fruitfully approached as a problem in non-equilibrium statistical mechanics.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avila, K., Moxey, D., de Lozar, A., Avila, M., Barkley, D., Hof, B.: The onset of turbulence in pipe flow. Science 333(6039), 192–196 (2011)
Bardóczi, L., Bencze, A., Berta, M., Schmitz, L.: Experimental confirmation of self-regulating turbulence paradigm in two-dimensional spectral condensation. Phys. Rev. E 90(6), 063–103 (2014)
Barenblatt, G., Zel’Dovich, Y.B.: Self-similar solutions as intermediate asymptotics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 4(1), 285–312 (1972)
Barenblatt, G.I.: Scaling, self-similarity, and intermediate asymptotics. Scaling, Self-similarity, and Intermediate Asymptotics, by Grigory Isaakovich Barenblatt. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p. 408, ISBN 0521435226 (1996)
Barkley, D.: Simplifying the complexity of pipe flow. Phys. Rev. E 84(1), 016309 (2011)
Barkley, D.: Theoretical perspective on the route to turbulence in a pipe. J. Fluid Mech. 803, P1 (2016). doi:10.1017/jfm.2016.465
Bazant, M.Z.: Largest cluster in subcritical percolation. Phys. Rev. E 62(2), 1660–1669 (2000). doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.62.1660
Biancalani, T., Fanelli, D., Di Patti, F.: Stochastic Turing patterns in the Brusselator model. Phys. Rev. E 81(4), 046215 (2010)
Blasius, H.: Das Ähnlichkeitsgesetz bei Reibungsvorgängen in Flüssigkeiten. Forschg. Arb. Ing.-Wes 134 (1913)
Butler, T., Goldenfeld, N.: Robust ecological pattern formation induced by demographic noise. Phys. Rev. E 80(3), 030902 (2009)
Cao, T.Y., Schweber, S.S.: The conceptual foundations and the philosophical aspects of renormalization theory. Synthese 97(1), 33–108 (1993)
Cardy, J., Falkovich, G., Gawedzki, K.: Non-equilibrium Statistical Mechanics and Turbulence. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2008)
Cardy, J.L., Sugar, R.L.: Directed percolation and Reggeon field theory. J. Phys. A 13(12), L423–L427 (1980)
Chate, H., Manneville, P.: Transition to turbulence via spatiotemporal intermittency. Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 112–115 (1987)
Conway, G.D., Angioni, C., Ryter, F., Sauter, P., Vicente, J.: Mean and oscillating plasma flows and turbulence interactions across the L-H confinement transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 065001 (2011). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.065001
Crutchfield, J., Kaneko, K.: Are attractors relevant to turbulence? Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 2715–2718 (1988)
Cvitanović, P.: Recurrent flows: the clockwork behind turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 726, 1–4 (2013)
Diamond, P.H., Liang, Y.M., Carreras, B.A., Terry, P.W.: Self-regulating shear flow turbulence: a paradigm for the L-H transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 2565–2568 (1994). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.72.2565
Edwards, S.: The statistical dynamics of homogeneous turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 18(02), 239–273 (1964)
Estrada, T., Happel, T., Hidalgo, C., Ascasbar, E., Blanco, E.: Experimental observation of coupling between turbulence and sheared flows during L-H transitions in a toroidal plasma. EPL 92(3), 35001 (2010)
Estrada, T., Hidalgo, C., Happel, T., Diamond, P.H.: Spatiotemporal structure of the interaction between turbulence and flows at the L-H transition in a toroidal plasma. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 245004 (2011). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.245004
Eyink, G., Goldenfeld, N.: Analogies between scaling in turbulence, field theory and critical phenomena. Phys. Rev. E 50, 4679–4683 (1994)
Falkovich, G.: Interaction between mean flow and turbulence in two dimensions. Proc. R. Soc. A 472, 20160287 (2016)
Feigenbaum, M.J.: Quantitative universality for a class of nonlinear transformations. J. Stat. Phys. 19(1), 25–52 (1978)
Fisher, M.E.: Renormalization group theory: its basis and formulation in statistical physics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 70, 653–681 (1998)
Fisher, R.A., Tippett, L.H.C.: Limiting forms of the frequency distribution of the largest or smallest member of a sample. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 24, 180–190 (1928)
Gioia, G., Chakraborty, P.: Turbulent friction in rough pipes and the energy spectrum of the phenomenological theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 044502 (2006)
Gioia, G., Guttenberg, N., Goldenfeld, N., Chakraborty, P.: Spectral theory of the turbulent mean-velocity profile. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105(18), 184501 (2010)
Goldenfeld, N.: Lectures On Phase Transitions and the Renormalization Group. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1992)
Goldenfeld, N.: Roughness-induced critical phenomena in a turbulent flow. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 044503 (2006)
Goldenfeld, N., Guttenberg, N., Gioia, G.: Extreme fluctuations and the finite lifetime of the turbulent state. Phys. Rev. E 81(3), 035304 (2010). doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.81.035304
Goluskin, D., Johnston, H., Flierl, G.R., Spiegel, E.A.: Convectively driven shear and decreased heat flux. J. Fluid Mech. 759, 360–385 (2014)
Grassberger, P.: On phase transitions in Schlögl’s second model. Z. für Physik B Condens. Matter. 47(4), 365–374 (1982)
Gumbel, E.: Les valeurs extrêmes des distributions statistiques. Ann. de l’institut Henri Poincaré 5(2), 115–158 (1935)
Gumbel, E.: Statistics of Extremes. Columbia University Press, New York (1958)
Guttenberg, N., Goldenfeld, N.: Friction factor of two-dimensional rough-boundary turbulent soap film flows. Phys. Rev. E 79(6), 65306 (2009)
Harada, T., Sasa, S.I.: Equality connecting energy dissipation with a violation of the fluctuation-response relation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(13) (2005)
von Hardenberg, J., Goluskin, D., Provenzale, A., Spiegel, E.: Generation of large-scale winds in horizontally anisotropic convection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115(13), 134501 (2015)
Hinrichsen, H.: Non-equilibrium critical phenomena and phase transitions into absorbing states. Adv. Phys. 49(7), 815–958 (2000). doi:10.1080/00018730050198152
Hof, B., de Lozar, A., Kuik, D.J., Westerweel, J.: Repeller or attractor? Selecting the dynamical model for the onset of turbulence in pipe flow. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101(21), 214501 (2008). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.214501
Hof, B., Westerweel, J., Schneider, T., Eckhardt, B.: Finite lifetime of turbulence in shear flows. Nature 443, 59–62 (2006)
Itoh, K., Itoh, S.I., Diamond, P.H., Hahm, T.S., Fujisawa, A., Tynan, G.R., Yagi, M., Nagashima, Y.: Physics of zonal flows. Phys. Plasm. 13(5), 055502 (2006). doi:10.1063/1.2178779
Janssen, H.: On the nonequilibrium phase transition in reaction-diffusion systems with an absorbing stationary state. Z. für Physik B Condens. Matter. 42(2), 151–154 (1981). doi:10.1007/BF01319549
Kadanoff, L.P.: Scaling laws for Ising models near tc. Physics 2, 263–272 (1966)
Kadanoff, L.P.: More is the same; phase transitions and mean field theories. J. Stat. Phys. 137(5–6), 777–797 (2009)
Kadanoff, L.P.: Relating theories via renormalization. Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. Part B 44(1), 22–39 (2013)
Kampen, Nv: A power series expansion of the master equation. Can. J. Phys. 39(4), 551–567 (1961)
Kellay, H., Tran, T., Goldburg, W., Goldenfeld, N., Gioia, G., Chakraborty, P.: Testing a missing spectral link in turbulence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109(25), 254502 (2012)
Kim, E.J., Diamond, P.H.: Zonal flows and transient dynamics of the L-H transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 185006 (2003). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.185006
Kraichnan, R.H.: The structure of isotropic turbulence at very high reynolds numbers. J. Fluid Mech. 5(04), 497–543 (1959)
Landau, L.D.: On the problem of turbulence. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 44, 339–349 (1944)
Lemoult, G., Shi, L., Avila, K., Jalikop, S.V., Avila, M., Hof, B.: Directed percolation phase transition to sustained turbulence in Couette flow. Nat. Phys. 12, 254–258 (2016)
Lotka, A.J.: Contribution to the theory of periodic reactions. J. Phys. Chem. 14(3), 271–274 (1910)
Manneville, P.: On the transition to turbulence of wall-bounded flows in general, and plane Couette flow in particular. Eur. J. Mech. -B/Fluids 49, 345–362 (2015)
McComb, W.: Theory of turbulence. Rep. Prog. Phys. 58, 1117–1205 (1995)
McKane, A.J., Newman, T.J.: Predator-prey cycles from resonant amplification of demographic stochasticity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(21), 218102 (2005)
Mehrafarin, M., Pourtolami, N.: Intermittency and rough-pipe turbulence. Phys. Rev. E 77, 055304 (2008)
Mobilia, M., Georgiev, I.T., Täuber, U.C.: Phase transitions and spatio-temporal fluctuations in stochastic lattice Lotka-Volterra models. J. Stat. Phys. 128(1–2), 447–483 (2007). doi:10.1007/s10955-006-9146-3
Nikuradze, J.: Stromungsgesetze in rauhen Rohren. VDI Forschungsheft 361(1) (1933). [English translation available as National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics, Tech. Memo. 1292 http://hdl.handle.net/2060/19930093938] (1950)
Parker, J.B., Krommes, J.A.: Generation of zonal flows through symmetry breaking of statistical homogeneity. New J. Phys. 16(3), 035006 (2014)
Polyakov, A.: Kenneth Wilson in Moscow. (2015) arXiv:1502.03502
Pomeau, Y.: Front motion, metastability and subcritical bifurcations in hydrodynamics. Physica 23D, 3–11 (1986)
Pomeau, Y.: The long and winding road. Nat. Phys. 12, 198–199 (2016)
Prost, J., Joanny, J.F., Parrondo, J.: Generalized fluctuation-dissipation theorem for steady-state systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103(9), 90601 (2009)
Renshaw, E.: Modelling Biological Populations in Space and Time. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1993)
Reynolds, O.: An experimental investigation of the circumstances which determine whether the motion of water shall be direct or sinuous and the law of resistance in parallel channel. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 174, 935 (1883)
Reynolds, O.: An experimental investigation of the circumstances which determine whether the motion of water shall be direct or sinuous, and of the law of resistance in parallel channels. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 174, 935–982 (1883)
Ruelle, D.: Non-equilibrium statistical mechanics of turbulence. J. Stat. Phys. 157, 205–218 (2014)
Ruelle, D., Takens, F.: On the nature of turbulence. Commun. Math. Phys. 20(3), 167–192 (1971)
Sano, M., Tamai, K.: A universal transition to turbulence in channel flow. Nat. Phys. 12, 249–253 (2016)
Schmitz, L., Zeng, L., Rhodes, T.L., Hillesheim, J.C., Doyle, E.J., Groebner, R.J., Peebles, W.A., Burrell, K.H., Wang, G.: Role of zonal flow predator-prey oscillations in triggering the transition to H-mode confinement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 155002 (2012). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.155002
Schneider, T., Eckhardt, B.: Lifetime statistics in transitional pipe flow. Phys. Rev. E 78(4), 46310 (2008)
Seifert, U.: Stochastic thermodynamics, fluctuation theorems and molecular machines. Rep. Prog. Phys. 75(12), 6001 (2012)
Shih, H.Y., Goldenfeld, N.: Extreme value statistics and critical exponents at the laminar-turbulence transition in pipes (2016). Unpublished
Shih, H.Y., Hsieh, T.L., Goldenfeld, N.: Ecological collapse and the emergence of travelling waves at the onset of shear turbulence. Nat. Phys. 12, 245–248 (2016)
Sipos, M., Goldenfeld, N.: Directed percolation describes lifetime and growth of turbulent puffs and slugs. Phys. Rev. E 84(3), 035304 (2011)
Sivashinsky, G., Yakhot, V.: Negative viscosity effect in large-scale flows. Phys. Fluids (1958–1988) 28(4), 1040–1042 (1985)
Song, B., Hof, B.: Deterministic and stochastic aspects of the transition to turbulence. J. Stat. Mech. 2014(2), P02001 (2014)
Sreenivasan, K.R., Eyink, G.L.: Sam Edwards and the turbulence theory. In: Goldbart, P., Goldenfeld, N., Sherrington, D. (eds.) Stealing the Gold: A Celebration of the Pioneering Physics of Sam Edwards, pp. 66–85. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2005)
Strickler, A.: Beitrage zur frage der geschwindigkeitsformel und der rauhigkeitszahlen fur strome, kanale und geschlossene leitungen (1923). Mitteilungen des Eidgenössischen Amtes für Wasserwirtschaft 16, Bern, Switzerland. Translated as “ Contributions to the question of a velocity formula and roughness data for streams, channels and closed pipelines.” by T. Roesgan and W. R. Brownie, Translation T-10, W. M. Keck lab of hydraulics and water resources, Calif. Inst. Tech., Pasadena, CA. January (1981)
Täuber, U.C.: Population oscillations in spatial stochastic Lotka-Volterra models: a field-theoretic perturbational analysis. J. Phys. A 45(40), 405002 (2012)
Tél, T., Lai, Y.: Chaotic transients in spatially extended systems. Phys. Rep. 460(6), 245–275 (2008)
Tran, T., Chakraborty, P., Guttenberg, N., Prescott, A., Kellay, H., Goldburg, W., Goldenfeld, N., Gioia, G.: Macroscopic effects of the spectral structure in turbulent flows. Nat. Phys. 4, 438–441 (2010)
Van Kampen, N.: Stochastic Processes in Physics and Chemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2011)
Volterra, V.: Variazioni e fluttuazioni del numero d’individui in specie animali conviventi. C. Ferrari (1927)
Widom, B.: Equation of state in the neighbourhood of the critical point. J. Chem. Phys. 43, 3898–3905 (1965)
Widom, B.: Laboring in the vineyard of physical chemistry. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 62, 1–18 (2011)
Willis, A.P., Kerswell, R.R.: Turbulent dynamics of pipe flow captured in a reduced model: puff relaminarisation and localised ‘edge’ states. J. Fluid Mech. 619, 213–233 (2009)
Wilson, K.G.: Renormalization group and critical phenomena. I. renormalization group and the Kadanoff scaling picture. Phys. Rev. B 4, 3174–3183 (1971)
Wilson, K.G.: The renormalization group and critical phenomena. Rev. Mod. Phys. 55, 583–600 (1983)
Wyld, H.W.: Formulation of the theory of turbulence in an incompressible fluid. Ann. Phys. 14, 143–165 (1961)
Xu, G.S., Wan, B.N., Wang, H.Q., Guo, H.Y., Zhao, H.L., Liu, A.D., Naulin, V., Diamond, P.H., Tynan, G.R., Xu, M., Chen, R., Jiang, M., Liu, P., Yan, N., Zhang, W., Wang, L., Liu, S.C., Ding, S.Y.: First evidence of the role of zonal flows for the L-H transition at marginal input power in the east tokamak. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 125001 (2011). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.125001
Yakhot, V., Orszag, S.A.: Renormalization group analysis of turbulence. I. Basic theory. J. Sci. Comput. 1(1), 3–51 (1986)
Zamalloa, Z.C., Ng, H.C.H., Chakraborty, P., Gioia, G.: Spectral analogues of the law of the wall, the defect law and the log law. J. Fluid Mech. 757, 498–513 (2014)
Acknowledgements
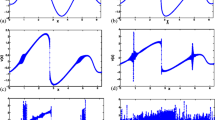
NG wishes to express his gratitude to Leo P. Kadanoff for his scientific inspiration, support, collaboration and friendship over many decades. NG also wishes to thank P. Chakraborty, G. Gioia, W. Goldburg, T. Tran, H. Kellay and N. Guttenberg for collaboration on the topics in Sect. 2. We thank T.-L. Hsieh and M. Sipos for collaboration on the topics in Sect. 3. We acknowledge helpful discussions with L.P. Kadanoff, B. Hof, J. Wesfreid, P. Manneville, D. Barkley and Y. Pomeau. We thank N. Guttenberg for technical assistance with Fig. 1. This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation through grant NSF-DMR-1044901.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: The equation 23 is incorrect. This has been corrected in this version.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10955-016-1713-7.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goldenfeld, N., Shih, HY. Turbulence as a Problem in Non-equilibrium Statistical Mechanics. J Stat Phys 167, 575–594 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-016-1682-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-016-1682-x