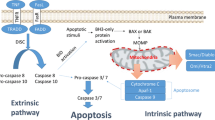
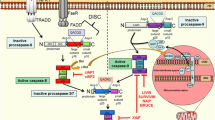
Abstract
Apoptosis resistance is a hallmark of human cancer. Research in the last two decades has identified key regulators of apoptosis, including inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs). These critical apoptosis regulators have been targeted for the development of new cancer therapeutics. In this article, we will discuss three members of IAP proteins, namely XIAP, cIAP1 and cIAP2, as cancer therapeutic targets and the progress made in developing new cancer therapeutic agents to target these IAP proteins.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AIF:
-
Apoptosis-Inducing Factor
- Apaf-1:
-
Apoptotic protease activating factor 1
- Apo2L:
-
Apo2 ligand
- Apo3L:
-
Apo3 ligand
- Bcl-2:
-
B-cell lymphoma 2
- BIR:
-
Baculoviral IAP Repeat domain
- CARD:
-
Caspase Recruitment Domain
- CD95:
-
Cluster of Differentiation 95
- cFLIP:
-
cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein
- cIAP1:
-
cellular Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein 1
- cIAP2:
-
cellular Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins 2
- dATP:
-
Deoxyadenosine triphosphate
- DIABLO:
-
Direct IAP-Binding protein with Low PI
- DISC:
-
Death-Inducing Signaling Complex
- DR:
-
Death Receptor
- FADD:
-
Fas-Associated protein with Death Domain
- FasR:
-
Fas Receptor
- IAPs:
-
Inhibitors of Apoptosis Proteins
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- LRIG1:
-
Leucine-Rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains protein 1
- ML-IAP:
-
Melanoma Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein
- NCI:
-
National Cancer Institute
- NFκB:
-
Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- PMBC:
-
Peripheral Mononuclear Blood cells
- RING:
-
Really Interesting New Gene
- RIPK1:
-
Receptor-Interacting serine/threonine-protein Kinase 1
- RTK:
-
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase
- Smac:
-
Second Mitochondria-derived Activator of Caspases
- TNF:
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor
- TNF-alpha:
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
- TNFR:
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor
- TRADD:
-
TNFR Associated DEATH Domain
- TRAF:
-
TNF Receptor Associated Factor
- TRAIL:
-
TNF Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand
- UBA:
-
Ubiquitin-Associated domain
References
Lowe SW, Lin AW. Apoptosis in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:485–95.
Nicholson DW. From bench to clinic with apoptosis-based therapeutic agents. Nature. 2000;407:810–6.
Reed JC. Apoptosis-based therapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2002;1:111–21.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74.
Fulda S, Debatin K-M. Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene. 2005;25:4798–811.
Candé CVN, Garrido C, Kroemer G. Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): caspase-independent after all. Cell Death Differ. 2004;11:591–5.
Deveraux QL, Reed JC. IAP family proteinssuppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1999;13:239–52.
Shiozaki EN, Shi Y. Caspases, IAPs and Smac/DIABLO: mechanisms from structural biology. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004;29:486–94.
Schimmer AD. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: translating basic knowledge into clinical practice. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7183–90.
Salvesen GS, Duckett CS. IAP proteins: blocking the road to death’s door. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:401–10.
Fulda S, Vucic D. Targeting IAP proteins for therapeutic intervention in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012;11:109–24.
Crook NE, Clem RJ, Miller LK. An apoptosis inhibiting baculovirus gene with a zinc finger-like motif. J Virol. 1993;67:2168–74.
Vucic D, Stennicke HR, Pisabarro MT, Salvesen GS, Dixit VM. ML-IAP, a novel inhibitor of apoptosis that is preferentially expressed in human melanomas. Curr Biol. 2000;10:1359–66.
Gyrd-Hansen M, Meier P. IAPs: from caspase inhibitors to modulators of NF-kappaB, inflammation and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:561–74.
Tamm I, Kornblau SM, Segall H, Krajewski S, Welsh K, Kitada S, Scudiero DA, Tudor G, Qui YH, Monks A, Andreeff M, Reed JC. Expression and prognostic significance of IAP-family genes in human cancers and myeloid leukemias. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:1796–803.
Jaffer S, Orta L, Sunkara S, Sabo E, Burstein DE. Immunohistochemical detection of antiapoptotic protein X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis in mammary carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2007;38:864–70.
Wang J, Liu Y, Ji R, Gu Q, Zhao X, Sun B. Prognostic value of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein for invasive ductal breast cancer with triple-negative phenotype. Hum Pathol. 2010;41:1186–95.
Foster FM, Owens TW, Tanianis-Hughes J, Clarke RB, Brennan K, Bundred NJ, Streuli CH. Targeting inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in combination with ErbB antagonists in breast cancer. Breast Canc Res. 2009;11:R41.
Parton M, Krajewski S, Smith I, Krajewska M, Archer C, Naito M, Ahern R, Reed J, Dowsett M. Coordinate expression of apoptosis-associated proteins in human breast cancer before and during chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:2100–8.
Yang L, Cao Z, Yan H, Wood WC. Coexistence of high levels of apoptotic signaling and inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in human tumor cells: implication for cancer specific therapy. Cancer Res. 2003;63:6815–24.
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L, Wang X. Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell. 2000;102:33–42.
Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, Silke J, Connolly LM, Reid GE, Moritz RL, Simpson RJ, Vaux DL. Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell. 2000;102:43–53.
Chai J, Du C, Wu JW, Kyin S, Wang X, Shi Y. Structural and biochemical basis of apoptotic activation by Smac/DIABLO. Nature. 2000;406:855–62.
Liu Z, Sun C, Olejniczak ET, Meadows RP, Betz SF, Oost T, Herrmann J, Wu JC, Fesik SW. Structural basis for binding of Smac/DIABLO to the XIAP BIR3 domain. Nature. 2000;408:1004–8.
Wang S. Design of small-molecule Smac mimetics as IAP antagonists. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2011;348:89–113.
Oost TK, Sun C, Armstrong RC, Al-Assaad AS, Betz SF, Deckwerth TL, Ding H, Elmore SW, Meadows RP, Olejniczak ET, Oleksijew A, Oltersdorf T, Rosenberg SH, Shoemaker AR, Tomaselli KJ, Zou H, Fesik SW. Discovery of potent antagonists of the antiapoptotic protein XIAP for the treatment of cancer. J Med Chem. 2004;47:4417–26.
Cai Q, Sun H, Peng Y, Lu J, Nikolovska-Coleska Z, McEachern D, Liu L, Qiu S, Yang C-Y, Miller R, Yi H, Zhang T, Sun D, Kang S, Guo M, Leopold L, Yang D, Wang S. A potent and orally active antagonist (SM-406/AT-406) of multiple inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) in clinical development for cancer treatment. J Med Chem. 2011;54:2714–26.
Flygare JA, Beresini M, Budha N, Chan H, Chan IT, Cheeti S, Cohen F, Deshayes K, Doerner K, Eckhardt SG, Elliott LO, Feng B, Franklin MC, Reisner SF, Gazzard L, Halladay J, Hymowitz SG, La H, LoRusso P, Maurer B, Murray L, Plise E, Quan C, Stephan JP, Young SG, Tom J, Tsui V, Um J, Varfolomeev E, Vucic D, Wagner AJ, Wallweber HJ, Wang L, Ware J, Wen Z, Wong H, Wong JM, Wong M, Wong S, Yu R, Zobel K, Fairbrother WJ. Discovery of a potent small-molecule antagonist of inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) proteins and clinical candidate for the treatment of cancer (GDC-0152). J Med Chem. 2012;55:4101–13.
Chauhan D, Neri P, Velankar M, Podar K, Hideshima T, Fulciniti M, Tassone P, Raje N, Mitsiades C, Mitsiades N, Richardson P, Zawel L, Tran M, Munshi N, Anderson KC. Targeting mitochondrial factor Smac/DIABLO as therapy for multiple myeloma (MM). Blood. 2007;109:1220–7.
Gaither A, Porter D, Yao Y, Borawski J, Yang G, Donovan J, Sage D, Slisz J, Tran M, Straub C, Ramsey T, Iourgenko V, Huang A, Chen Y, Schlegel R, Labow M, Fawell S, Sellers WR, Zawel L. A Smac mimetic rescue screen reveals roles for inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in tumor necrosis factor-alpha signaling. Cancer Res. 2007;67:11493–8.
Li L, Thomas RM, Suzuki H, De Brabander JK, Wang X, Harran PG. A small molecule Smac mimic potentiates TRAIL- and TNFalpha-mediated cell death. Science. 2004;305:1471–4.
Petersen SL, Wang L, Yalcin-Chin A, Li L, Peyton M, Minna J, Harran P, Wang X. Autocrine TNFalpha signaling renders human cancer cells susceptible to Smac-mimetic-induced apoptosis. Canc Cell. 2007;12:445–56.
Sun H, Nikolovska-Coleska Z, Lu J, Meagher JL, Yang CY, Qiu S, Tomita Y, Ueda Y, Jiang S, Krajewski K, Roller PP, Stuckey JA, Wang S. Design, synthesis, and characterization of a potent, nonpeptide, cell-permeable, bivalent Smac mimetic that concurrently targets both the BIR2 and BIR3 domains in XIAP. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:15279–94.
Lu J, Bai L, Sun H, Nikolovska-Coleska Z, McEachern D, Qiu S, Miller RS, Yi H, Shangary S, Sun Y, Meagher JL, Stuckey JA, Wang S. SM-164: a novel, bivalent Smac mimetic that induces apoptosis and tumor regression by concurrent removal of the blockade of cIAP-1/2 and XIAP. Cancer Res. 2008;68:9384–93.
Varfolomeev E, Blankenship JW, Wayson SM, Fedorova AV, Kayagaki N, Garg P, Zobel K, Dynek JN, Elliott LO, Wallweber HJ, Flygare JA, Fairbrother WJ, Deshayes K, Dixit VM, Vucic D. IAP antagonists induce autoubiquitination of c-IAPs, NF-kappaB activation, and TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell. 2007;131:669–81.
Vince JE, Wong WW, Khan N, Feltham R, Chau D, Ahmed AU, Benetatos CA, Chunduru SK, Condon SM, McKinlay M, Brink R, Leverkus M, Tergaonkar V, Schneider P, Callus BA, Koentgen F, Vaux DL, Silke J. IAP antagonists target cIAP1 to induce TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell. 2007;131:682–93.
Dueber EC, Schoeffler AJ, Lingel A, Elliott JM, Fedorova AV, Giannetti AM, Zobel K, Maurer B, Varfolomeev E, Wu P, Wallweber HJ, Hymowitz SG, Deshayes K, Vucic D, Fairbrother WJ. Antagonists induce a conformational change in cIAP1 that promotes autoubiquitination. Science. 2011;334:376–80.
Feltham R, Bettjeman B, Budhidarmo R, Mace PD, Shirley S, Condon SM, Chunduru SK, McKinlay MA, Vaux DL, Silke J, Day CL. Smac mimetics activate the E3 ligase activity of cIAP1 protein by promoting RING domain dimerization. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:17015–28.
Cheung HH, Mahoney DJ, Lacasse EC, Korneluk RG. Down-regulation of c-FLIP Enhances death of cancer cells by smac mimetic compound. Cancer Res. 2009;69:7729–38.
Fulda S, Wick W, Weller M, Debatin KM. Smac agonists sensitize for Apo2L/TRAIL- or anticancer drug-induced apoptosis and induce regression of malignant glioma in vivo. Nat Med. 2002;8:808–15.
Arnt CR, Chiorean MV, Heldebrant MP, Gores GJ, Kaufmann SH. Synthetic Smac/DIABLO peptides enhance the effects of chemotherapeutic agents by binding XIAP and cIAP1 in situ. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:44236–43.
Yang L, Mashima T, Sato S, Mochizuki M, Sakamoto H, Yamori T, Oh-Hara T, Tsuruo T. Predominant suppression of apoptosome by inhibitor of apoptosis protein in non-small cell lung cancer H460 cells: therapeutic effect of a novel polyarginine-conjugated Smac peptide. Cancer Res. 2003;63:831–7.
Bockbrader KM, Tan M, Sun Y. A small molecule Smac-mimic compound induces apoptosis and sensitizes TRAIL- and etoposide-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2005;24:7381–8.
Vogler M, Walczak H, Stadel D, Haas TL, Genze F, Jovanovic M, Gschwend JE, Simmet T, Debatin KM, Fulda S. Targeting XIAP bypasses Bcl-2-mediated resistance to TRAIL and cooperates with TRAIL to suppress pancreatic cancer growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2008;68:7956–65.
Loeder S, Drensek A, Jeremias I, Debatin KM, Fulda S. Small molecule XIAP inhibitors sensitize childhood acute leukemia cells for CD95-induced apoptosis. Int J Cancer. 2010;126:2216–28.
Fakler M, Loeder S, Vogler M, Schneider K, Jeremias I, Debatin KM, Fulda S. Small molecule XIAP inhibitors cooperate with TRAIL to induce apoptosis in childhood acute leukemia cells and overcome Bcl-2-mediated resistance. Blood. 2009;113:1710–22.
Probst BL, Liu L, Ramesh V, Li L, Sun H, Minna JD, Wang L. Smac mimetics increase cancer cell response to chemotherapeutics in a TNF-alpha-dependent manner. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17:1645–54.
Bai L, McEachern D, Yang CY, Lu J, Sun H, Wang S. LRIG1 modulates cancer cell sensitivity to Smac mimetics by regulating TNFalpha expression and receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Cancer Res. 2012;72:1229–38.
Infante JR, Claire Dees EC, Burris IHA, Zawel L, Sager JA, Stevenson C, Clarke K, Dhuria S, Porter D, Sen SK, Zannou E, Sharma S, Cohen RB. A phase I study of LCL161, an oral IAP inhibitor, in patients with advanced cancer. Abstract # 2775, AACR 101st Annual Meeting 2010, April 17–21, 2010, Washington, DC; 2010.
Graham MA, Mitsuuchi Y, Burns J, Chunduru S, Benetatos C, McKinlay M, Weng D, Wick MJ, Tolcher AW, Papadopoulos K, Amaravadi R, Schilder RJ, Adjei A, LoRusso P. In Abstract A25: Phase 1 PK/PD analysis of the Smac-mimetic TL32711 demonstrates potent and sustained cIAP1 suppression in patient PBMCs and tumor biopsies, AACR-NCI-EORTC International Conference: Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics, San Francisco, CA, Nov 12–16, 2011, 2011; San Francisco, CA; 2011.
Sikic BI, Eckhardt SG, Gallant G, Burris HA, Camidge DR, Colevas AD, Jones SF, Messersmith WA, Wakelee HA, Li H, Kaminker PG, Morris S, Infante JR. In Safety, pharmacokinetics (PK), and pharmacodynamics (PD) of HGS1029, an inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) inhibitor, in patients (Pts) with advanced solid tumors: results of a phase I study, 2011 ASCO Annual Meeting 2011; 2011.
Wu YT, Wagner KW, Bursulaya B, Schultz PG, Deveraux QL. Development and characterization of nonpeptidic small molecule inhibitors of the XIAP/caspase-3 interaction. Chem Biol. 2003;10:759–67.
Schimmer AD, Welsh K, Pinilla C, Wang Z, Krajewska M, Bonneau MJ, Pedersen IM, Kitada S, Scott FL, Bailly-Maitre B, Glinsky G, Scudiero D, Sausville E, Salvesen G, Nefzi A, Ostresh JM, Houghten RA, Reed JC. Small-molecule antagonists of apoptosis suppressor XIAP exhibit broad antitumor activity. Canc Cell. 2004;5:25–35.
Nikolovska-Coleska Z, Xu L, Hu Z, Tomita Y, Li P, Roller PP, Wang R, Fang X, Guo R, Zhang M, Lippman ME, Yang D, Wang S. Discovery of embelin as a cell-permeable, small-molecular weight inhibitor of XIAP through structure-based computational screening of a traditional herbal medicine three-dimensional structure database. J Med Chem. 2004;47:2430–40.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the financial support from the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, the Prostate Cancer Foundation, the Department of Defense Prostate Cancer Program (W81XWH-04-1-0213), Ascenta Therapeutics, and the National Cancer Institute, NIH (5R01CA109025 and 5R01CA127551). We thank Dr. G.W.A. Milne for his critical reading of the manuscript and Ms. Karen Kreutzer for her excellent secretarial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Bai, L., Lu, J. et al. Targeting Inhibitors of Apoptosis Proteins (IAPs) For New Breast Cancer Therapeutics. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 17, 217–228 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-012-9265-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-012-9265-1