Abstract
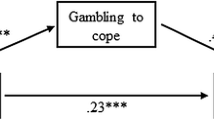
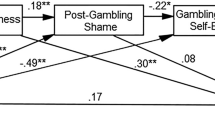
In this study we examined the relations between guilt and shame and coping strategies in response to gambling loss. Based on H.B. Lewis’s (Shame & guilt in neurosis. New York: International Universities Press, 1971) account of guilt and shame, we proposed that unlike guilt, the experience of shame involves the attribution of gambling loss to stable and global internal factors (i.e., self-devaluation). We hypothesized that problem gambling severity would be more strongly associated with the intensity of shame than with the intensity of guilt following gambling loss. Further, we hypothesized that the intensity of shame would be positively associated with the use of avoidant coping strategies following gambling loss. Finally, we hypothesized that the intensity of shame would mediate the association between problem gambling severity and the use of avoidant coping. These hypotheses were supported by a retrospective survey of recent gambling losses. Our finding suggests that the experience of shame and the use of avoidant coping strategies to deal with this emotion are central to problem gambling severity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-IV). Washington, DC.
Carver, C. S., Scheier, M. F., & Weintraub, J. K. (1989). Assessing coping strategies: A theoretically based approach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 56, 267–283.
Collins, R. L. (1993). Drinking restraint and risk for alcohol abuse. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 1, 44–54.
Dickerson, M. (1993). Internal and external determinants of persistent gambling: Problems in generalizing from one form of gambling to another. Journal of Gambling Studies, 9(3), 225–245.
Dickerson, M., & O’Connor, J. (2006). Gambling as an addictive behaviour: Imaired control, harm minimisation, treatment and prevention. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Ferris, J., & Wynne, H. (2001). The Canadian Problem Gambling Index: Final report. Canadian Centre on Substance Abuse.
Folkman, S., & Lazarus, R. (1988). The ways of coping questionnaire. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press.
Greeley, J., & Oei, T. P. S. (1999). Alcohol and tension reduction. In K. Leonard (Ed.), Psychological theories of drinking and alcoholism (2nd ed.). New York: Guilford Press.
Gupta, R., Derevensky, J., & Marget, N. (2004). Coping strategies employed by adolescents with gambling problems. Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 9, 115–120.
Hoblitzelle, W. (1987). Attempts to measure and differentiate shame and guilt: The relation between shame and depression. In H. B. Lewis (Ed.), The role of shame in symptom formation (pp. 207–235). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Holub, A., Hodgins, D. C., & Peden, N. E. (2005). Development of the temptations for gambling questionnaire: A measure of temptation in recently quit gamblers. Addiction Research & Theory, 13(2), 179–191.
Kaufman, G. (1996). The psychology of shame (2nd ed.). New York: Springer.
Klass, E. T. (1990). Guilt, shame, and embarrassment: Cognitive-behavioral approaches. In H. Leitenberg (Ed.), Handbook of social and evaluation anxiety (pp. 385–414). New York: Plenum.
Lewis, H. B. (1971). Shame & guilt in neurosis. New York: International Universities Press.
MacKinnon, D. P., Lockwood, C. M., Hoffman, J. M., West, S. G., & Sheets, V. (2002). A comparison of methods to test mediation and other intervening variable effects. Psychological Methods, 7, 83–104.
McCormick, R. A. (1994). The importance of coping skill enhancement in the treatment of the pathological gambler. Journal of Gambling Studies, 10, 77–86.
Moos, R. H. (1992). Coping responses inventory: Adult form manual. Palo Alto, CA: Center for Health Care Evaluation, Stanford University and Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Centers.
Niedenthal, P. M., Tangney, J. P., & Gavanski, I. (1994). “If only I weren’t” versus “If only I hadn’t”: Distinguishing shame and guilt in counterfactual thinking. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 67(4), 585–595.
Nower, L., Derevensky, J. L., & Gupta, R. (2004). The relationship of impulsivity, sensation seeking, coping and substance use in youth gamblers. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 18(1), 49–55.
Parke, J., Griffiths, M. D., & Parke, A. (2007). Positive thinking among slot machine gamblers: A case of maladaptive coping? International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 5(1), 39–52.
Pattison, S. (2000). Shame: Theory, therapy, theology. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Preacher, K. J., & Hayes, A. F. (2008). Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behavior Research Methods, 40, 879–891.
Rippetoe, P. A., & Rogers, R. W. (1987). Effects of components of protection motivation theory on adaptive and maladaptive coping with a health threat. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 52, 596–604.
Ronsenthal, R., & Rugle, L. (1994). A psychodynamic approach to the treatment of pathological gambling: Part 1. Achieving abstinence. Journal of Gambling Studies, 10(1), 21–42.
Scannell, E. D., Quirk, M. M., Smith, K., Maddem, R., & Dickerson, M. (2000). Females’ coping styles and control over poker machine gambling. Journal of Gambling Studies, 16(4), 417–432.
Shepherd, L., & Dickerson, M. (2001). Situational coping with loss and control over gambling in regular poker machine players. Australian Journal of Psychology, 53(3), 160–169.
Stone, A. A., Shiffman, S. S., & DeVries, M. W. (1999). Ecological momentary assessment. In D. Kahneman, E. Diener, & N. Schwarz (Eds.), Well being: The foundations of hedonic psychology (pp. 26–39). New York: Russell Sage Foundation.
Tangney, J. P., & Dearing, R. L. (2002). Shame and guilt. New York: Guilford Press.
Tangney, J. P., Miller, R. S., Flicker, L., & Barlow, D. H. (1996). Are shame, guilt, and embarrassment distinct emotions? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 70(6), 1256–1269.
Tangney, J. P., Wagner, P., & Gramzow, R. (1992). Proneness to shame, proneness to guilt, and psychopathology. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 101(3), 469–478.
Wills, T. A., & Hirky, A. E. (1996). Coping and substance abuse: A theoretical model and review of the evidence. In M. Zeidner & N. S. Endler (Eds.), Handbook of coping: Theory, research, applications (pp. 279–302). New York: Wiley.
Wills, T. A., & Schiffman, S. (1985). Coping and substance use. In S. Shiffman & T. A. Wills (Eds.), Coping with substance use (pp. 3–24). New York: Academic Press.
Acknowledgment
This project was partially funded by the research grant of the Ontario Problem Gambling Research Centre.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: The “Coping with Gambling Loss” Scale
Appendix: The “Coping with Gambling Loss” Scale
Seeking Social Support
-
I asked people who have had similar problems what they did to deal with this problem.
-
I sought sympathy and understanding from someone.
-
I discussed my feelings with someone.
Planning to Make Up for Monetary Loss
-
I adjusted my budget to make up for the money I lost on gambling and tried to follow it.
-
I tried to earn extra income in order to make up for the money I lost.
-
I tried to cut back on other expenses in order to make up for the lost money.
Rationalization
-
I thought that at least I had good time gambling.
-
I thought that the money I lost was worth it because I enjoyed myself.
-
I told myself I deserve spending money on gambling from time to time.
-
I told myself that this gambling occasion was a treat to myself for working hard.
Wishful Thinking
-
I wished that the lost money would somehow be recovered.
-
I hoped a miracle would happen and the money I lost would come back.
-
I wished that I could start all over again and did not suffer this loss.
Non-Disclosure
-
I tried to keep my feelings to myself.
-
I kept others from knowing how bad things were.
-
I told others that I have lost less than I actually have.
-
I did not want to disclose to others how much I lost on gambling.
Distortion of Loss
-
I thought sustaining some losses is the only way to eventually win big.
-
I thought that the money I lost time was just money I had previously won from gambling.
-
I thought that eventually gains and losses balance out in my gambling.
-
I thought that the money I lost this time was not much because on average I win more than I lose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, S., Kanetkar, V. Coping with Guilt and Shame After Gambling Loss. J Gambl Stud 27, 371–387 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10899-010-9216-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10899-010-9216-y