Abstract
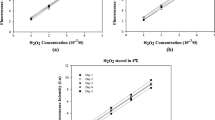
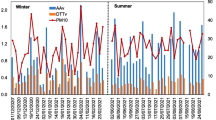
The diurnal variations in the concentrations of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in various size fractions were determined for ambient particles in Rubidoux, CA. Sampling of particles was conducted at 3 h intervals using a cascade impactor. The collected particles were reacted with dichlorofluorescin (DCFH), a non-fluorescent probe that fluoresces when oxidized. The factors affecting the diurnal variation in ROS concentration were also investigated with special emphasis on the relation between ROS concentration and the intensity of photochemical reactions where the ozone concentration was taken as an index. The intensity of photochemical reactions was found to be a moderate factor affecting the daytime ROS concentration. The concentration of ROS was found to be higher on the smaller particles of the ambient aerosol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonini, J. M., Clarke, R. W., Krishnamurthy, G. G., Sreekanthan, P., Jenkins, N., Eagar, T. W., and Brian, J. D., 1998: Freshly generated stainless steel welding fume induces greater lung inflammation in rats as compared to aged fume, Toxicol. Lett. 98, 78–86.
Cathcart, R., Schwiers, E., and Ames, B. N., 1983: Detection of picomole levels of hydroperoxides using a fluorescent dichlorofluorescin assay, Anal. Biochem. 134, 111–116.
Cerutti, P. A., 1985: Prooxidant states and tumor promotion, Science 227, 375–381.
Finlayson-Pitts, B. J. and Pitts Jr., J. N., 2000: Chemistry of the Upper and Lower Atmosphere: Theory, Experiments, and Applications, Academic Press, California.
Hung, H.-F. and Wang, C.-S., 2001: Experimental determination of reactive oxygen species in Taipei aerosols, J. Aerosol Sci. 32, 1201–1211.
Kao, M.-C. and Wang, C.-S., 2002: Reactive oxygen species in incense smoke, Aerosol Air Quality Res. 2, 61–69.
Kehrer, J. P., 1993: Free radicals as mediators of tissue injury and disease, Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 23, 21–48.
Kuo, M.-L., Jee, S.-H., Chou, M.-H., and Ueng, T.-H., 1998: Involvement of oxidative stress in motorcycle exhaust particle-induced DNA damage and inhibition of intercellular communication, Mutat. Res. 413, 143–150.
LeBel, C. P., Ischiropoulos, H., and Bondy, S. C., 1992: Evaluation of the probe 2′, 7′-dichlorofluorescin as an indicator of reactive oxygen species formation and oxidative stress, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 5, 227–231.
Marple, A. V., Rubow, L. K., and Behm, M. S., 1991: A microorifice uniform deposit impactor (MOUDI): Description, calibration, and use, Aerosol Sci. Technol. 14, 434–446.
Olszyna, K. J., Meagher, J. F., and Bailey, E. M., 1988: Gas phase, cloud and rainwater measurements of H2O2 at a high elevation site, Atmos. Environ. 22, 1699–1706.
Paulson, S. E. and Orlando, J. J., 1996: The reactions of ozone with alkenes: An important source of HO x in the boundary layer, Geophys. Res. Lett. 23, 3727–3730.
Sakugawa, H. and Kaplan, I. R., 1990: Observation of the diurnal variation of gaseous H2O2 in Los Angeles air using a cryogenic collection method, Aerosol Sci. Technol. 12, 77–85.
Seinfeld, J. H. and Pandis, S. N., 1998: Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, Wiley Publishers, New York.
Shi, X. and Dalal, N. S., 1988: ESR evidence for the hydroxyl radical formation in aqueous suspension of quartz particles and its possible significance to lipid peroxidation in silicosis, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 25, 237–245.
Tsai, W., Cohen, Y., Sakugawa, H., and Kaplan, I. R., 1991: Hydrogen peroxide levels in Los Angeles: A screening-level evaluation, Atmos. Environ. 25, 67–78.
Vallyathan, V., Shi, X., Dalal, N. S., Irr, W., and Castranova, V., 1988: Generation of free radicals from freshly fractured silica dust: Potential role in acute silica induced lung injury, Am. Rev. of Respir. Diseases 138, 1213–1219.
Vallyathan, V., Castranova, V., Pack, D., Leonard, S., Shumaker, J., Hubbs, A. F., Shoemaker, D. A., Ramsey, D. M., Pretty, J. R., McLaurin, J. L., Khan, A., and Teass, A., 1995: Freshly fractured quartz inhalation leads to enhanced lung injury and inflammation, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 152, 1003–1009.
Wayne, R. P., Barnes, I., Biggs, P., Burrows, J. P., Canosa-Mas, C. E., Hjorth, J., LeBras, G., Moortgat, G. K., Perner, D., Poulet, G., Restelli, G., and Sidebottom, H., 1991: The nitrate radical: Physics, chemistry, and the atmosphere, Atmos. Environ. 25A, 1–203.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10874-005-5013-3.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Venkatachari, P., Hopke, P.K., Grover, B.D. et al. Measurement of Particle-Bound Reactive Oxygen Species in Rubidoux Aerosols. J Atmos Chem 50, 49–58 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-005-1662-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-005-1662-z