Abstract
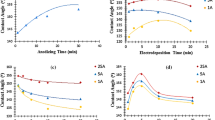
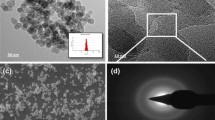
A novel method for preparing and characterizing super-hydrophobic and oleophobic surface is presented. Aluminum (Al) substrate was roughened by sandblasting and electrolytic etching to obtain micro- and nano-sized complex morphologies. Then, its substrate was covered by a chemically adsorbed monolayer (CAM) containing a fluorocarbon group. The surface of Al substrate roughened and covered with CAM was observed by scanning electron microscope and atomic force microscope. The roughnesses of the surface were ca. 100 μm and ca. 30–60 nm, respectively. The surface of the wettability was characterized by contact angle measurements and its surface indicated super-hydrophobicity and oleophobicity: the water contact angle (WCA) and oil contact angle (OCA) of hexadecane was 158.9° and 139.6°, respectively. The wettability was also characterized by solid surface energy. The solid surface energy of each solvent was obtained from the equation by Neumann et al. These values were extremely low, ranging from 0.31 to 1.29 mN/m. The total solid surface energy was obtained from the equation by Kaelble et al. The value was 0.3 mN/m. Their values indicated that the hydrophobicity and oleophobicity of our sample reached the highest level possible. In addition, our research demonstrates that it is easy to compare many different surfaces with super-hydrophobicity and oleophobicity using the solid surface energy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wenzel RN (1936) Ind Eng Chem 28:988
Ulman A (1996) Thin Solid Film 273:48
Guan K, Lu B, Yin Y (2003) Surf Coat Technol 173:219. doi:10.1016/S0257-8972(03)00521-8
Kiuru M, Alakoski E (2004) Mater Lett 58:2213. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2004.01.024
Zhu L, Feng Y, Ye X, Zhou Z (2006) Sens Actuators A 130–131:595. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2005.12.005
Zhang J, Huang W, Han Y (2006) Langmuir 22:2946. doi:10.1021/la053428q
Gao L, McCarthy TJ (2007) Langmuir 23:3762. doi:10.1021/la062634a
Qian B, Shen Z (2005) Langmuir 21:9007. doi:10.1021/la051308c
Zhang X, Jin M, Liu Z, Nishimoto S, Saito H, Murakami T, Fujishima A (2006) Langmuir 22:9477. doi:10.1021/la0618869
He B, Patankar NA, Lee J (2003) Langmuir 19:4999. doi:10.1021/la0268348
Hosono E, Fujihara S, Honma I, Zhou H (2005) J Am Chem Soc 127:13459. doi:10.1002/adma.200500275
Sagiv J (1979) Isr J Chem 18:339
Sagiv J (1980) J Am Chem Soc 102:92
Ulman A (1996) Chem Rev 96:1533
Schreiber F (2000) Prog Surf Sci 65:151. doi:10.1016/S0079-6816(00)00024-1
Tada T, Noriyasu H, Kawamura Y, Ohkubo Y, Ogawa K (2009) J Textile Eng 55:13. doi:10.4188/jte.55.13
Yamamoto H, Ohkubo Y, Ogawa K, Utsumi K (2009) Precis Eng 33:229. doi:10.1016/j.precisioneng.2008.07.006
Li D, Neumann AW (1992) J Colloid Interface Sci 148:190. doi:10.1016/0021-9797(92)90127-8
Kaelble DH, Uy KC (1970) J Adhesion 2:50. doi:10.1080/0021846708544579
Kaelble DH (1970) J Adhesion 2:66. doi:10.1080/0021846708544582
Jańczuk B, Kerkeb ML, Biatrowicz T, González-Caballero F (1992) J Colloid Interface Sci 151:333. doi:10.1016/0021-9797(92)90482-2
Shibuichi S, Yamamoto T, Onda T, Tsuji K (1998) J Colloid Interface Sci 208:287
Han D, Steckl AJ (2009) Langmuir 25:9454. doi:10.1021/la900660v
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). We gratefully thank Professor. S. Yoda and Dr. S. Matsumoto of JAXA for their helpful comments. In addition, we wish to thank Nano Science Corporation for help in AFM observation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohkubo, Y., Tsuji, I., Onishi, S. et al. Preparation and characterization of super-hydrophobic and oleophobic surface. J Mater Sci 45, 4963–4969 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4362-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4362-2