Abstract
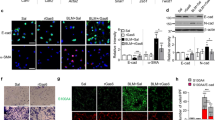
Childhood asthma, an airway inflammatory disease, is a serious threat to the child’s quality of life. Recently, TIPE2 expression was reported to be decreased in children with asthma. Therefore, additional studies focusing on TIPE2 might provide an approach for treating childhood asthma. In this study, we found that TIPE2 was poorly expressed in hyperstretched human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B). TIPE2 overexpression also significantly suppressed the stretch-induced secretion of asthma-related inflammatory factors (TNF-α, TSLP, MMP-9, and VEGF). In contrast, TIPE2 inhibition significantly promoted the secretion of TNF-α, TSLP, MMP-9, and VEGF. Furthermore, overexpression of TIPE2 remarkably inhibited the activation of Wnt/β-catenin in hyperstretched BEAS-2B cells, while siTIPE2 activated Wnt/β-catenin in hyperstretched BEAS-2B cells. Further analysis showed that the Wnt/β-catenin signal inhibitor Dkk-1 could further enhance the TIPE2-induced suppression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which also suppressed the siTIPE2-induced secretion of TNF-α, TSLP, MMP-9, and VEGF in hyperstretched BEAS-2B cells. Dkk-1 reversed the effects of siRNA-TIPE2 on Wnt/β-catenin signaling and inflammatory cytokines. In summary, we have exhibited that TIPE2 inhibited the expression of asthma-related inflammatory factors in hyperstretched BEAS-2B cells by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. TIPE2 may be involved in airway inflammation during asthma attack, and it may be used as a potential therapeutic target for bronchial epithelial inflammation in childhood asthma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mete, F., E. Ozkaya, S. Aras, V. Koksal, O. Etlik, and I. Baris. 2014. Association between gene polymorphisms in TIM1, TSLP, IL18R1 and childhood asthma in Turkish population. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 7: 1071–1077.
Elias, J.A., C.G. Lee, T. Zheng, B. Ma, R.J. Homer, and Z. Zhu. 2003. New insights into the pathogenesis of asthma. Journal of Clinical Investigation 111: 291–297.
Haj-Salem, I., R. Fakhfakh, J.C. Berube, E. Jacques, S. Plante, M.J. Simard, Y. Bosse, and J. Chakir. 2015. MicroRNA-19a enhances proliferation of bronchial epithelial cells by targeting TGFbetaR2 gene in severe asthma. Allergy 70: 212–219.
Gras, D., P. Chanez, I. Vachier, A. Petit, and A. Bourdin. 2013. Bronchial epithelium as a target for innovative treatments in asthma. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 140: 290–305.
Devries, A., and D. Vercelli. 2013. Epigenetics of human asthma and allergy: promises to keep. Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology 31: 183–189.
Zhao, G., X. Lin, M. Zhou, and J. Zhao. 2013. Association between CC10 + 38A/G polymorphism and asthma risk: a meta-analysis. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences 29: 1439–1443.
Freundt, E.C., N. Bidere, and M.J. Lenardo. 2008. A different TIPE of immune homeostasis. Cell 133: 401–402.
Sun, H., S. Gong, R.J. Carmody, A. Hilliard, L. Li, J. Sun, L. Kong, L. Xu, B. Hilliard, S. Hu, H. Shen, X. Yang, and Y.H. Chen. 2008. TIPE2, a negative regulator of innate and adaptive immunity that maintains immune homeostasis. Cell 133: 415–426.
Kong, L., K. Liu, Y.Z. Zhang, M. Jin, B.R. Wu, W.Z. Wang, W. Li, Y.M. Nan, and Y.H. Chen. 2013. Downregulation of TIPE2 mRNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology International 7: 844–849.
Ma, Y., X. Liu, Z. Wei, X. Wang, Z. Wang, W. Zhong, Y. Li, F. Zhu, C. Guo, and L. Zhang. 2013. The expression and significance of TIPE2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from asthmatic children. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology 78: 523–528.
Sun, H., G. Zhuang, L. Chai, Z. Wang, D. Johnson, Y. Ma, and Y.H. Chen. 2012. TIPE2 controls innate immunity to RNA by targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Rac pathway. Journal of Immunology 189: 2768–2773.
Zhang, G., C. Hao, Y. Lou, W. Xi, X. Wang, Y. Wang, Z. Qu, C. Guo, Y. Chen, Y. Zhang, and S. Liu. 2010. Tissue-specific expression of TIPE2 provides insights into its function. Molecular Immunology 47: 2435–2442.
MacDonald, B.T., K. Tamai, and X. He. 2009. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Developmental Cell 17: 9–26.
Baron, R., and M. Kneissel. 2013. WNT signaling in bone homeostasis and disease: from human mutations to treatments. Nature Medicine 19: 179–192.
Baarsma, H.A., M. Konigshoff, and R. Gosens. 2013. The WNT signaling pathway from ligand secretion to gene transcription: molecular mechanisms and pharmacological targets. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 138: 66–83.
Clevers, H., and R. Nusse. 2012. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 149: 1192–1205.
Le, P.N., J.D. McDermott, and A. Jimeno. 2015. Targeting the Wnt pathway in human cancers: therapeutic targeting with a focus on OMP-54F28. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 146: 1–11.
George, S.J. 2008. Wnt pathway: a new role in regulation of inflammation. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 28: 400–402.
Tan, R.J., D. Zhou, L. Zhou, and Y. Liu. 2014. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and kidney fibrosis. Kidney International Supplement 4: 84–90.
Guo, L., T. Wang, Y. Wu, Z. Yuan, J. Dong, X. Li, J. An, Z. Liao, X. Zhang, D. Xu, and F.Q. Wen. 2016. WNT/beta-catenin signaling regulates cigarette smoke-induced airway inflammation via the PPARdelta/p38 pathway. Laboratory Investigation; A Journal of Technical Methods and Pathology 96: 218–229.
Kwak, H.J., D.W. Park, J.Y. Seo, J.Y. Moon, T.H. Kim, J.W. Sohn, D.H. Shin, H.J. Yoon, S.S. Park, and S.H. Kim. 2015. The Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway regulates the development of airway remodeling in patients with asthma. Experimental & Molecular Medicine 47: e198.
Reuter, S., H. Martin, H. Beckert, M. Bros, E. Montermann, C. Belz, A. Heinz, S. Ohngemach, U. Sahin, M. Stassen, R. Buhl, L. Eshkind, and C. Taube. 2014. The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway attenuates experimental allergic airway disease. Journal of Immunology 193: 485–495.
Bao, Z., S. Lim, W. Liao, Y. Lin, C. Thiemermann, B.P. Leung, and W.S. Wong. 2007. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibition attenuates asthma in mice. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 176: 431–438.
Fredberg, J.J. 2000. Frozen objects: small airways, big breaths, and asthma. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 106: 615–624.
Wang, J., L. Liu, Y. Xia, and D. Wu. 2014. Silencing of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 suppresses hyperstretch-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines in vitro. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica Shanghai 46: 556–564.
Haseneen, N.A., G.G. Vaday, S. Zucker, and H.D. Foda. 2003. Mechanical stretch induces MMP-2 release and activation in lung endothelium: role of EMMPRIN. American Journal of Physiology - Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 284: L541–L547.
Thomas, R.A., J.C. Norman, T.T. Huynh, B. Williams, S.J. Bolton, and A.J. Wardlaw. 2006. Mechanical stretch has contrasting effects on mediator release from bronchial epithelial cells, with a rho-kinase-dependent component to the mechanotransduction pathway. Respiratory Medicine 100: 1588–1597.
Spiegel, A., S. Shivtiel, A. Kalinkovich, A. Ludin, N. Netzer, P. Goichberg, Y. Azaria, I. Resnick, I. Hardan, H. Ben-Hur, A. Nagler, M. Rubinstein, and T. Lapidot. 2007. Catecholaminergic neurotransmitters regulate migration and repopulation of immature human CD34+ cells through Wnt signaling. Nature Immunology 8: 1123–1131.
Reuter, S., H. Beckert, and C. Taube. 2016. Take the Wnt out of the inflammatory sails: modulatory effects of Wnt in airway diseases. Laboratory Investigation; A Journal of Technical Methods and Pathology 96: 177–185.
Chen, C.L., H. Li, X.H. Xing, H.S. Guan, J.H. Zhang, and J.W. Zhao. 2015. Effect of TRPV1 gene mutation on bronchial asthma in children before and after treatment. Allergy and Asthma Proceedings 36: e29–e36.
Ho, C.Y., C.K. Wong, F.W. Ko, C.H. Chan, A.S. Ho, D.S. Hui, and C.W. Lam. 2002. Apoptosis and B-cell lymphoma-2 of peripheral blood T lymphocytes and soluble fas in patients with allergic asthma. Chest 122: 1751–1758.
Liu, Z., X. Liu, L. Sang, H. Liu, and Q. Xu. 2015. Boswellic acid attenuates asthma phenotypes by downregulation of GATA3 via pSTAT6 inhibition in a murine model of asthma. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology 8: 236–243.
Xiao, C., S.M. Puddicombe, S. Field, J. Haywood, V. Broughton-Head, I. Puxeddu, H.M. Haitchi, E. Vernon-Wilson, D. Sammut, N. Bedke, C. Cremin, J. Sones, R. Djukanovic, P.H. Howarth, J.E. Collins, S.T. Holgate, P. Monk, and D.E. Davies. 2011. Defective epithelial barrier function in asthma. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 128(549–556): e541–e512.
Georas, S.N., and F. Rezaee. 2014. Epithelial barrier function: at the front line of asthma immunology and allergic airway inflammation. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 134: 509–520.
Penberthy, K.K., I.J. Juncadella, and K.S. Ravichandran. 2014. Apoptosis and engulfment by bronchial epithelial cells. Implications for allergic airway inflammation. Annals of the American Thoracic Society 11(Suppl 5): S259–S262.
Copland, I.B., and M. Post. 2007. Stretch-activated signaling pathways responsible for early response gene expression in fetal lung epithelial cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology 210: 133–143.
Uglietta, J.P., W.W. Woodruff, E.L. Effmann, and B.A. Carroll. 1989. Duplex Doppler ultrasound evaluation of calcified inferior vena cava thrombosis. Pediatric Radiology 19: 250–252.
Xi, W., Y. Hu, Y. Liu, J. Zhang, L. Wang, Y. Lou, Z. Qu, J. Cui, G. Zhang, X. Liang, C. Ma, C. Gao, Y. Chen, and S. Liu. 2011. Roles of TIPE2 in hepatitis B virus-induced hepatic inflammation in humans and mice. Molecular Immunology 48: 1203–1208.
Popa, C., M.G. Netea, P.L. van Riel, J.W. van der Meer, and A.F. Stalenhoef. 2007. The role of TNF-alpha in chronic inflammatory conditions, intermediary metabolism, and cardiovascular risk. Journal of Lipid Research 48: 751–762.
Ying, S., B. O’Connor, J. Ratoff, Q. Meng, C. Fang, D. Cousins, G. Zhang, S. Gu, Z. Gao, B. Shamji, M.J. Edwards, T.H. Lee, and C.J. Corrigan. 2008. Expression and cellular provenance of thymic stromal lymphopoietin and chemokines in patients with severe asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Journal of Immunology 181: 2790–2798.
Biagini Myers, J.M., L.J. Martin, M.B. Kovacic, T.B. Mersha, H. He, V. Pilipenko, M.A. Lindsey, M.B. Ericksen, D.I. Bernstein, G.K. LeMasters, J.E. Lockey, and G.K. Khurana Hershey. 2014. Epistasis between serine protease inhibitor Kazal-type 5 (SPINK5) and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) genes contributes to childhood asthma. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 134(891–899): e893.
Wang, I.J., L.S. Wu, G.A. Lockett, and W.J. Karmaus. 2016. TSLP polymorphisms, allergen exposures, and the risk of atopic disorders in children. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology 116(139–145): e131.
Han, Z., Junxu, and N. Zhong. 2003. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-9 within the airways in asthma. Respiratory Medicine 97: 563–567.
Asai, K., H. Kanazawa, H. Kamoi, S. Shiraishi, K. Hirata, and J. Yoshikawa. 2003. Increased levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in induced sputum in asthmatic patients. Clinical and Experimental Allergy 33: 595–599.
Neumann, J., K. Schaale, K. Farhat, T. Endermann, A.J. Ulmer, S. Ehlers, and N. Reiling. 2010. Frizzled1 is a marker of inflammatory macrophages, and its ligand Wnt3a is involved in reprogramming Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages. FASEB journal: Official Publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 24: 4599–4612.
Zhang, J., X. Wen, X.Y. Ren, Y.Q. Li, X.R. Tang, Y.Q. Wang, Q.M. He, X.J. Yang, Y. Sun, N. Liu, and J. Ma. 2016. YPEL3 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research: CR 35: 109.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Chen, L. & Yan, W. TIPE2 Inhibits the Expression of Asthma-Related Inflammatory Factors in Hyperstretched Bronchial Epithelial Cells Through the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Inflammation 40, 770–777 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0521-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0521-9