Abstract
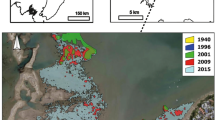
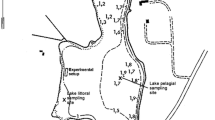
The Mondego estuary (Portugal) has suffered severe ecological stress over the last two decades, as manifested in the replacement of seagrasses by opportunistic macroalgae, degradation of water quality and increased turbidity. A restoration plan was implemented in 1998, which aimed to reverse the eutrophication effects, and especially to restore the original natural seagrass (Zostera noltii) community. This article explores the long-term changes in Ampithoe valida and Melita palmata (Amphipoda) populations in response to eutrophication (with consequent seagrass loss and macroalgal proliferation) and to the subsequent restoration plan (with progressive seagrass recovery and macroalgal biomass decline). Until the early 1990s, high densities of A. valida and M. palmata were recorded in the Mondego estuary, especially during the occurrence of the macroalgal bloom and during all the periods in which green macroalgae were available. After the implementation of the restoration plan, species abundance, biomass and production levels decreased considerably due to the progressive decline of green macroalgae. This implied the virtual disappearance of the amphipod population, mainly A. valida. Distinct behaviours displayed by the two species could be related to different food strategies and habitat preferences. Ampithoe valida showed feeding preferences for ephemeral softer, filamentous or bladed algae (e.g. Ulva sp.) due to its high caloric content, using the Z. noltii bed only as a habitat for protection against predators or shelter from wave action. On the other hand, M. palmata did not suffer a strong decline in its population density, biomass and production, which may indicate that this species is probably not a primary consumer of green macroalgae and may readily shift to alternative ecological niches.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benke, A. C., 1979. A modification of the Hynes method for estimating secondary production with particular significance for multivoltine populations. Limnology and Oceanography 24: 168–171.
Cardoso, P. G., M. A. Pardal, A. I. Lillebø, S. M. Ferreira, D. Raffaelli & J. C. Marques, 2004. Dynamic changes in seagrass assemblages under eutrophication and implications for recovery. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 302: 233–248.
Cardoso, P. G., A. Brandão, M. A. Pardal, D. Raffaelli & J. C. Marques, 2005. The resilience of Hydrobia ulvae populations to anthropogenic and natural disturbances. Marine Ecology Progress 289: 191–199.
Cardoso, P. G., D. Raffaelli & M. A. Pardal, 2008. The impact of extreme weather events on the seagrass Zostera noltii and related Hydrobia ulvae population. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56: 483–492.
Carvalho, S., A. Moura & M. Sprung, 2006. Ecological implications of removing seagrass beds (Zostera noltii) for bivalve aquaculture in southern Portugal. Cahiers de Biologie Marine 47: 321–329.
Cloern, J. E., 2001. Our evolving conceptual model of the coastal eutrophication problem. Marine Ecology Progress Series 210: 223–253.
Cruz-Rivera, E. & M. E. Hay, 2000. The effects of diet mixing on consumer fitness: macroalgae, epiphytes, and animal matter as food for marine amphipods. Oecologia 123: 252–264.
de Jonge, V. N., D. J. de Jong & M. M. Katwijk, 2000. Policy plans and management measures to restore eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) in the Dutch Wadden Sea. Helgoland Marine Research 54: 151–158.
Dolbeth, M., A. I. Lillebø, P. G. Cardoso, S. M. Ferreira & M. A. Pardal, 2005. Annual production of estuarine fauna in different environmental conditions: an evaluation of the estimation methods. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 326: 115–127.
Dolbeth, M., P. G. Cardoso, S. M. Ferreira, T. Verdelhos, D. Raffaelli & M. A. Pardal, 2007. Anthropogenic and natural disturbance effects on a macrobenthic estuarine community over a 10-year period. Marine Pollution Bulletin 54: 576–585.
Elliott, M., D. Burdon, K. L. Hemingway & S. E. Apitz, 2007. Estuarine, coastal and marine ecosystem restoration: confusing management and science – a revision of concepts. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 74: 349–366.
Flindt, M. R., L. Kamp-Nielsen, J. C. Marques, M. A. Pardal, M. Bocci, G. Bendoricchio, J. Salomonsen, S. N. Nielsen & S. E. Jørgensen, 1997. Description of the three shallow estuaries: Mondego River (Portugal), Roskilde Fjord (Denmark) and the lagoon of Venice (Italy). Ecological Modelling 102: 17–31.
Hobbs, R. J. & D. A. Norton, 1996. Towards a conceptual framework for restoration ecology. Restoration Ecology 4: 93–110.
Kennish, M. J., 2000. Anthropogenic impacts and the National Estuary Program. In Estuary Restoration and Maintenance. The National Estuary Program. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL: 9–87.
Kennish, M. J., 2002. Environmental threats and environmental futures of estuaries. Environmental Conservation 29: 78–107.
Kraufvelin, P., S. Salovius, H. Christie, F. E. Moy, R. Karez & M. F. Pedersen, 2006. Eutrophication-induced changes in benthic algae affect the behaviour and fitness of the marine amphipod Gammarus locusta. Aquatic Botany 84: 199–209.
Lillebø, A. I., J. M. Neto, I. Martins, T. Verdelhos, S. Leston, P. G. Cardoso, S. M. Ferreira, J. C. Marques & M. A. Pardal, 2005. Management of a shallow temperate estuary to control eutrophication: the effect of hydrodynamics on the system’s nutrient loading. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 65: 697–707.
Limnologisk Metodik, 1992. Ferskvandsbiologisk Laboratorium University of Copenhagen. Akademisk Forlag, Copenhagen (Nitrogen method pp. 28–29 and 36–37; Phosphorus method pp. 40–41 and, 106–107).
Lopes, R. J., M. A. Pardal & J. C. Marques, 2000. Impact of macroalgal blooms and wader predation on intertidal macroinvertebrates: experimental evidence from the Mondego estuary (Portugal). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 249: 165–179.
Marques, J. C., M. A. Pardal, S. N. Nielsen & S. E. Jørgensen, 1997. Analysis of the properties of energy and biodiversity along an estuarine gradient of eutrophication. Ecological Modelling 102: 155–167.
Martins, I., M. A. Pardal, A. I. Lillebø, M. R. Flindt & J. C. Marques, 2001. Hydrodynamics as a major factor controlling the occurrence of green macroalgal blooms in a eutrophic estuary: a case study on the influence of precipitation and river management. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 52: 165–177.
Nicotri, M. E., 1980. Factors involved in herbivore food preference. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 42: 13–26.
Obenat, S., E. Spivak & L. Garrido, 2006. Life history and reproductive biology of the invasive amphipod Melita palmata (Amphipoda: Melitidae) in the Mar Chiquita coastal lagoon, Argentina. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 86: 1381–1387.
Pardal, M. A., J. C. Marques, I. Metelo, A. I. Lillebø & M. R. Flindt, 2000. Impact of eutrophication on the life cycle, population dynamics and production of Ampithoe valida (Amphipoda) along an estuarine spatial gradient (Mondego estuary, Portugal). Marine Ecology Progress Series 196: 207–219.
Pardal, M. A., J. C. Marques, I. Metelo, A. I. Lillebø & M. R. Flindt, 2002. Impact of eutrophication on amphipods Melita palmata and Ampithoe valida in the Mondego estuary. In Pardal, M. A., J. C. Marques & M. A. Graça (eds), Aquatic Ecology of the Mondego River Basin. Global Importance of Local Experience. Imprensa da Universidade de Coimbra, Coimbra: 457–472.
Pardal, M. A., P. G. Cardoso, J. P. Sousa, J. C. Marques & D. Raffaelli, 2004. Assessing environmental quality: a novel approach. Marine Ecology Progress Series 267: 1–8.
Peterson, C. H. & R. N. Lipcius, 2003. Conceptual progress towards predicting quantitative ecosystem benefits of ecological restorations. Marine Ecology Progress Series 264: 297–307.
Philippart, C. J. M., J. J. Beukema, G. C. Cadée, R. Dekker, P. W. Goedhart, J. M. VanIperen, M. F. Leopold & P. M. J. Herman, 2007. Impacts of nutrient reduction on coastal communities. Ecosystems (in press). doi:10.1007/s10021-006-9006-7.
Poore, A. G. B. & N. A. Hill, 2006. Sources of variation in herbivore preference: among-individual and past diet effects on amphipod host choice. Marine Biology 149: 1403–1410.
Poore, A. G. B., N. A. Hill & E. E. Sotka, 2008. Phylogenetic and geographic variation in host breadth and composition by herbivorous amphipods in the family Ampithoidae. Evolution 62: 21–38.
Raffaelli, D. G., J. A. Raven & L. J. Poole, 1998. Ecological impact of green macroalgal blooms. Oceanography Marine Biology 36: 97–125.
Sánchez-Jerez, P., C. Barberá-Cebrian & A. A. Ramos-Esplá, 2000. Influence of the structure of Posidonia oceanica meadows modified by bottom trawling on crustacean assemblages: comparison of amphipods and decapods. Scientia Marina 64: 319–326.
Schramm, W. & P. H. Nienhuis (eds), 1996. Marine Benthic Vegetation. Recent Changes and the Effects of Eutrohication. Springer, Berlin: 465 pp.
Strickland, J. D. M. & T. R. Parsons, 1972. A Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysis (Bulletin 167), 2nd ed. Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Ottawa: 71–80.
Valiela, I., J. Malelland, J. Hauxwell, P. J. Behr, D. Hersh & K. Foreman, 1997. Macroalgal blooms in shallow estuaries: controls and ecophysiological and ecosystem consequences. Limnology Oceanography 42: 1105–1118.
Verdelhos, T., J. M. Neto, J. C. Marques & M. A. Pardal, 2005. The effect of eutrophication abatement on the bivalve Scrobicularia plana. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 63: 261–268.
Zar, J., 1996. Biostatistical Analysis, 3rd ed. Prentice-Hall International, Upper Saddle River, NJ: 662 pp.
Zedler, J. B., 2001. Handbook for Restoring Tidal Wetlands. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL: 439 pp.
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to all the colleagues from IMAR-Coimbra, who assisted in the field and laboratory work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: P. Viaroli
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grilo, T.F., Cardoso, P.G., Dolbeth, M. et al. Long-term changes in amphipod population dynamics in a temperate estuary following ecosystem restoration. Hydrobiologia 630, 91–104 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-9782-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-9782-0