Abstract
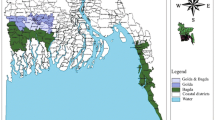
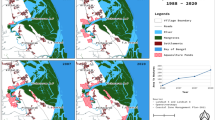
Bangladesh and India are among the world’s most populous but also most vulnerable countries to environmental risks. In addition to storms, sea-level rise, floods and droughts, local communities face a multitude of pre-existing and concomitant economic and socio-political risks. To understand these risks and how communities respond to them is critical in securing community livelihoods. We therefore ask what are the livelihood risks; how do they impact the human security of environment sensitive communities in Satkhira, Bangladesh and in Odisha, India; and, what are the responses of these communities to the livelihood risks? The communities studied in Bangladesh depend mainly on the shrimp and fish resources of the Sundarbans mangrove forest. The two communities researched at Lake Chilika in India depend on fishing and salt farming, respectively. The field research, conducted in 2012 and 2013, shows that the communities face multiple and interacting livelihood risks. While storms and floods are common environmental risks in both countries, related livelihood risks are case-specific. In Bangladesh, attacks by criminals are the major threat to human well-being, while in India, it is violent conflict between lake users. Unsustainable resource extraction is found in both study countries. In Bangladesh, shrimp farming weakens the flood protection, while in India, illegal prawn farming marginalizes poorer lake users. Accessing loans and labor migration are responses observed in both countries. We conclude that adaptation to environmental changes needs to be sensitive to the interaction between governance, local institutions and socio-economic developments.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adger, W. N. (2006). Vulnerability. Global Environmental Change, 16(3), 268–281. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2006.02.006.
Ahmed, I. (2009). Environmental refugees and environmental distress migration as a security challenge for India and Bangladesh. In H. Brauch, Ú. Spring, J. Grin, C. Mesjasz, P. Kameri-Mbote, N. Behera, et al. (Eds.), Facing Global Environmental Change (Vol. 4, pp. 295–308). Berlin: Springer. Hexagon Series on Human and Environmental Security and Peace.
Alam, S. (2003). Environmentally induced migration from Bangladesh to India. Strategic Analysis, 27(3), 422–438. doi:10.1080/09700160308450098.
Alexander, D. (2004). Review of facing up to the Storm. Disasters, 28(4), 429–430. doi:10.1111/j.0361-3666.2004.00268.x.
Ali, A. M. S. (2006). Rice to shrimp: Land use/land cover changes and soil degradation in Southwestern Bangladesh. Land Use Policy, 23(4), 421–435. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2005.02.001.
Barnett, J., Matthew, R., & O’Brian, K. (2010). Global environmental change and human security: An introduction. In R. Matthew, J. Barnett, B. McDonald, & K. O’Brian (Eds.), Global environmental change and human security (pp. 1–32). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Blaikie, P., Cannon, T., Davis, I., Wisner, B., & Cannon, T. (2003). At risk: Natural hazards, people’s vulnerability and disasters. London: Routledge.
Bogner, A., Littig, B., & Menz, W. (Eds.). (2009). Interviewing experts. London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Brahmanand, P. S., Kumar, A., Ghosh, S., Chowdhury, S. R., Singandhupe, R. B., Singh, R., et al. (2013). Challenges to food security in India. Current Science, 104(7), 841–846.
Brakenridge, G. R., Syvitski, J. P. M., Overeem, I., Higgins, S. A., Kettner, A. J., Stewart-Moore, J. A., et al. (2013). Global mapping of storm surges and the assessment of coastal vulnerability. Natural Hazards, 66(3), 1295–1312. doi:10.1007/s11069-012-0317-z.
CIA (Central Intelligence Agency). (2013a). The world factbook—Bangladesh. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/bg.html. Accessed 9 June 2013.
CIA (Central Intelligence Agency). (2013b). The world factbook—India. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/in.html. Accessed 9 June 2013.
Conroy, C., Mishra, A., & Rai, A. (2002). Learning from self-initiated community forest management in Orissa, India. Forest Policy and Economics, 4(3), 227–237. doi:10.1016/S1389-9341(01)00068-5.
CRED (Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters). (2013). Country profile. http://www.emdat.be/country-profile. Accessed 15 April 2013.
Dalby, S. (2009). Security and environmental change. Cambridge: Polity.
del Ninno, C., & Dorosh, P. A. (2001). Averting a food crisis: Private imports and public targeted distribution in Bangladesh after the 1998 flood. Agricultural Economics, 25(2–3), 337–346. doi:10.1016/s0169-5150(01)00090-1.
Dorosh, P. A. (2001). Trade liberalization and national food security: Rice trade between Bangladesh and India. World Development, 29(4), 673–689. doi:10.1016/S0305-750X(00)00121-2.
Few, R. (2003). Flooding, vulnerability and coping strategies: Local responses to a global threat. Progress in Development Studies, 3(1), 43–58. doi:10.1191/1464993403ps049ra.
Fischer, I., & Salehin, M. (2009). Health and poverty as challenges for human security: Two case studies on Northern Vietnam and Bangladesh. In H. Brauch, Ú. Spring, J. Grin, C. Mesjasz, P. Kameri-Mbote, N. Behera, et al. (Eds.), Facing global environmental change (Vol. 4, pp. 563–572). Berlin: Springer. Hexagon Series on Human and Environmental Security and Peace.
Ghorbani, G. (2012). The role of micro-credit in improving rural development. Life Science Journal-Acta Zhengzhou University Overseas Edition, 9(3), 2629–2632.
Gopal, B., & Chauhan, M. (2006). Biodiversity and its conservation in the Sundarban mangrove ecosystem. Aquatic Sciences, 68(3), 338–354. doi:10.1007/s00027-006-0868-8.
Government of Orissa (2011). Annual Plan 2011–2012. http://www.odisha.gov.in/p&c/Download/2011-12/Annual_Plan_2011_12_Vol_I.pdf. Accessed 13 July 2013.
Hall, D., Alam, M. G. S., & Raha, S. K. (2011). Increased food security in Bangladesh from one health and integrated agriculture. EcoHealth, 7, S154–S155. (Meeting Abstract).
Hedger, M., Singha, A., & Reddy, M. (2010). Building climate resilience at state level: Disaster risk management and rural livelihoods in Orissa. Sussex: Institute of Development Studies.
Hoque, S. (2004). Micro-credit and the reduction of poverty in Bangladesh. Journal of Contemporary Asia, 34(1), 21–32. doi:10.1080/00472330480000281.
IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). (2012). Managing the risks of extreme events and disasters to advance climate change adaptation. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). (2007). Climate Change. (2007). Climate change impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. Geneva: Cambridge University Press.
Iwasaki, S., & Shaw, R. (2009). Linking human security to natural resources: Perspective from a fishery resource allocation system in Chilika lagoon, India. Sustainability Science, 4(2), 281–292. doi:10.1007/s11625-009-0084-2.
Jayaraman, G., Rao, A. D., Dube, A., & Mohanty, P. K. (2007). Numerical simulation of circulation and salinity structure in Chilika Lagoon. Journal of Coastal Research, 861–877, doi:10.2112/04-0225r.1.
Jolly, R., & Ray, D. B. (2007). Human security—national perspectives and global agendas: Insights from national human development reports. Journal of International Development, 19(4), 457–472. doi:10.1002/jid.1382.
Kale, V. (2012). On the link between extreme floods and excess monsoon epochs in South Asia. Climate Dynamics, 39(5), 1107–1122. doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1251-6.
Karim, M. F., & Mimura, N. (2008). Impacts of climate change and sea-level rise on cyclonic storm surge floods in Bangladesh. Global Environmental Change, 18(3), 490–500. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2008.05.002.
Khagram, S., & Ali, S. (2006). Environment and security. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 31(1), 395–411. doi:10.1146/annurev.energy.31.042605.134901.
Khagram, S., Clark, W., & Raad, D. F. (2003). From the environment and human security to sustainable security and development. Journal of Human Development, 4(2), 289–313. doi:10.1080/1464988032000087604.
Khandelwal, A., Mohanti, M., García-Rodríguez, F., & Scharf, B. (2008). Vegetation history and sea level variations during the last 13,500 years inferred from a pollen record at Chilika Lake, Orissa, India. Vegetation History and Archaeobotany, 17(4), 335–344. doi:10.1007/s00334-007-0127-5.
King, G., & Murray, C. J. L. (2001). Rethinking human security. Political Science Quarterly, 116(4), 585–610. doi:10.2307/798222.
Kumar, T. S., Mahendra, R. S., Nayak, S., Radhakrishnan, K., & Sahu, K. C. (2010). Coastal vulnerability assessment for Orissa State, East Coast of India. Journal of Coastal Research, 26(3), 523–534. doi:10.2112/09-1186.1.
Kumar, K., Patwardhan, S., Kulkarni, A., Kamala, K., Rao, K., & Jones, R. (2011). Simulated projections for summer monsoon climate over India by a high-resolution regional climate model (PRECIS). Current Science, 101(3), 312–326.
Lee, H. S. (2013). Estimation of extreme sea levels along the Bangladesh coast due to storm surge and sea level rise using EEMD and EVA. Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans, 118(9), 4273–4285. doi:10.1002/jgrc.20310.
Lindenberg, M. (2002). Measuring household livelihood security at the family and community level in the developing world. World Development, 30(2), 301–318. doi:10.1016/S0305-750X(01)00105-X.
Mahmud, T., & Prowse, M. (2012). Corruption in cyclone preparedness and relief efforts in coastal Bangladesh: Lessons for climate adaptation? Global Environmental Change, 22(4), 933–943. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2012.07.003.
Mallika, J. (Ed.). (2011). Human security challenges in India. New Delhi: National Bureau of Asian Research.
Mayer, B., Boas, I., Ewing, J. J., Baillat, A., & Das, U. K. (2013). Governing environmentally related migration in Bangladesh: Responsibilities, security and the causality problem. Asian and Pacific Migration Journal, 22(2), 177–198.
Mazumder, M. S. U., & Lu, W. C. (2013). Micro-credit and poverty reduction: A case of Bangladesh. Prague Economic Papers, 22(3), 403–417.
Mendola, M. (2008). Migration and technological change in rural households: Complements or substitutes? Journal of Development Economics, 85(1–2), 150–175. doi:10.1016/j.jdeveco.2006.07.003.
Milbert, I. (2009). Policy dimensions of human security and vulnerability challenges: The case of urban India (Vol. 4, facing global environmental change: Environmental, human, energy, food, health and water security concepts). Berlin: Springer.
Mohapatra, M., Mohanty, U. C., & Behera, S. (2003). Spatial variability of daily rainfall over Orissa, India, during the southwest summer monsoon season. International Journal of Climatology, 23(15), 1867–1887. doi:10.1002/joc.974.
Mohapatra, A., Mohanty, R., Mohanty, S. K., Bhatta, K. S., & Das, N. R. (2007). Fisheries enhancement and biodiversity assessment of fish, prawn and mud crab in Chilika lagoon through hydrological intervention. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 15(3), 229–251. doi:10.1007/s11273-006-9025-3.
Moses, J. W. (2009). Leaving poverty behind: A radical proposal for developing Bangladesh through emigration. Development Policy Review, 27(4), 457–479.
Muhammad, M. I. (2009). Policy-administration dichotomy in food security programs of Bangladesh: The ethico-governance perspective. In Proceedings of 2009 international conference on public administration. Chengdu: Univ Electronic Science & Technology China Press.
Mukherjee, S., Chaudhuri, A., Kundu, N., Mitra, S., & Homechaudhuri, S. (2013). Comprehensive analysis of fish assemblages in relation to seasonal environmental variables in an estuarine river of Indian Sundarbans. Estuaries and Coasts, 36(1), 192–202. doi:10.1007/s12237-012-9558-z.
Nayak, P. K., & Berkes, F. (2010). Whose marginalisation? Politics around environmental injustices in India’s Chilika lagoon. Local Environment, 15(6), 553–567. doi:10.1080/13549839.2010.487527.
O’Brien, K., Leichenko, R., Kelkar, U., Venema, H., Aandahl, G., Tompkins, H., et al. (2004). Mapping vulnerability to multiple stressors: Climate change and globalization in India. Global Environmental Change, 14(4), 303–313. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2004.01.001.
Palakudiyil, T., & Todd, M. (2003). Facing up to the storm—how local communities can cope with disaster—lessons from Orissa and Gujarat. London: Christian Aid.
Paris, R. (2001). Human security: Paradigm shift or hot air? International Security, 26(2), 87–102.
Patton, M. Q. (2005). Qualitative Research. In B. Everitt, & D. Howell (Eds.), Encyclopedia of statistics in behavioral science (pp. 1633–1643). Chichester: Wiley.
Penning-Rowsell, E. C., Sultana, P., & Thompson, P. M. (2013). The ‘last resort’? Population movement in response to climate-related hazards in Bangladesh. Environmental Science and Policy, 27, S44–S59. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2012.03.009.
Polsky, C., Neff, R., & Yarnal, B. (2007). Building comparable global change vulnerability assessments: The vulnerability scoping diagram. Global Environmental Change, 17(3–4), 472–485. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2007.01.005.
Rahman, M. M. (2009). Temporary migration and changing family dynamics: Implications for social development. Population Space and Place, 15(2), 161–174. doi:10.1002/psp.537.
Rahman, M. M., Islam, M. N., Ahmed, A. U., & Georgi, F. (2012). Rainfall and temperature scenarios for Bangladesh for the middle of 21st century using RegCM. Journal of Earth System Science, 121(2), 287–295. doi:10.1007/s12040-012-0159-9.
Rajawat, A. S., Gupta, M., Acharya, B. C., & Nayak, S. (2007). Impact of new mouth opening on morphology and water quality of the Chilika Lagoon—a study based on Resourcesat-1 LISS-III and AWiFS and IRS-1D LISS-III data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 28(5), 905–923. doi:10.1080/01431160600904949.
Rawlani, A. K., & Sovacool, B. K. (2011). Building responsiveness to climate change through community based adaptation in Bangladesh. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 16(8), 845–863. doi:10.1007/s11027-011-9298-6.
Ray-Bennett, N. S. (2010). The role of microcredit in reducing women’s vulnerabilities to multiple disasters. Disasters, 34(1), 240–260. doi:10.1111/j.0361-3666.2009.01127.x.
Ray-Bennett, N. S., Collins, A., Bhuiya, A., Edgeworth, R., Nahar, P., & Alamgir, F. (2010). Exploring the meaning of health security for disaster resilience through people’s perspectives in Bangladesh. Health and Place, 16(3), 581–589. doi:10.1016/j.healthplace.2010.01.003.
Refliefweb (2001). India: Orissa floods appeal no. 21/2001 operations update No. 1. http://reliefweb.int/report/india/india-orissa-floods-appeal-no-212001-operations-update-no-1. Accessed 13 July 2013.
Reza, A., Feeroz, M., & Islam, M. (2002). Man-tiger interaction in the Bangladesh Sundarbans. Bangladesh Journal of Life Sciences, 14(1/2), 75–82.
Robson, J. P., & Nayak, P. K. (2010). Rural out-migration and resource-dependent communities in Mexico and India. Population and Environment, 32(2–3), 263–284. doi:10.1007/s11111-010-0121-1.
Roy, A. K. D., Alam, K., & Gow, J. (2012). A review of the role of property rights and forest policies in the management of the Sundarbans mangrove forest in Bangladesh. Forest Policy and Economics, 15, 46–53. doi:10.1016/j.forpol.2011.08.009.
Saha, S. (2012). Security implications of climate refugees in urban slums: A case study from Dhaka, Bangladesh. In J. Scheffran, M. Brzoska, H. G. Brauch, M. Link, & J. Schilling (Eds.), Climate change, human security and violent conflict: Challenges for societal stability (Vol. 8, pp. 595–611). Berlin: Springer. Hexagon Series on Human and Environment Security and Peace.
Salvi, K., Kannan, S., & Ghosh, S. (2013). High-resolution multisite daily rainfall projections in India with statistical downscaling for climate change impacts assessment. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 118(9), 3557–3578. doi:10.1002/jgrd.50280.
Scheffran, J., Link, P. M., & Schilling, J. (2012). Theories and models of climate-security interaction: Framework and application to a climate hot spot in North Africa. In J. Scheffran, M. Brzoska, H. G. Brauch, P. M. Link, & J. Schilling (Eds.), Climate change, human security and violent conflict: Challenges for societal stability (Vol. 8, pp. 91–131). Berlin: Springer. Hexagon Series on Human and Environment Security and Peace.
Schilling, J., Freier, K. P., Hertig, E., & Scheffran, J. (2012). Climate change, vulnerability and adaptation in North Africa with focus on Morocco. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 156, 12–26. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2012.04.021.
Schilling, J., Vivekananda, J., Nisha, P., & Khan, M. A. (2013). Vulnerability to environmental risks and effects on community resilience in mid-west Nepal and south-east Pakistan. Environment and Natural Resources Research, 3(4), 1–19.
Schmidhuber, J., & Tubiello, F. (2007). Global food security under climate change. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the United States of America, 104(50), 19703–19708. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701976104.
Sharmin, S., & Naznin, R. (2013). Impacts of cyclone Aila on educational institutions: A study of south-western Bangladesh. In W. Leal Filho (Ed.), Climate change and disaster risk management (pp. 237-256, Climate Change Management): Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Shibayama, T., Tajima, Y., Kakinuma, T., Nobuoka, H., Yasuda, T., Ahsan, R., et al. (2009). Field survey of storm surge disaster due to Cyclone Sidr in Bangladesh. In Proceedings of coastal dynamics 2009. Singapore: World Scientific Publ Co Pte Ltd.
Sinha, P. C., Jain, I., Bhardwaj, N., Rao, A. D., & Dube, S. K. (2008). Numerical modeling of tide-surge interaction along Orissa coast of India. Natural Hazards, 45(3), 413–427. doi:10.1007/s11069-007-9176-4.
Taylor, M. (2013). Climate change, relational vulnerability and human security: Rethinking sustainable adaptation in agrarian environments. Climate and Development, 5(4), 318–327. doi:10.1080/17565529.2013.830954.
Thomalla, F., & Schmuck, H. (2004). ‘We all knew that a cyclone was coming’: Disaster preparedness and the cyclone of 1999 in Orissa, India. Disasters, 28(4), 373–387. doi:10.1111/j.0361-3666.2004.00264.x.
UNDP (United Nations Development Programme). (2002). Human security in Bangladesh. Dhaka: UNDP.
UNDP (United Nations Development Programme). (2009). Field visit report on selected Aila affected areas. http://cccm.iom.org.bd/file/pdf/34.pdf. Accessed 13 July 2013.
University of Oxford (2013). Oxford dictionary—livelihood. http://oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/livelihood. Accessed 9 June 2013.
Acknowledgments
This paper would not have been possible without the generous contributions of time, energy and insight from community respondents. Sincere thanks and appreciation are due to Sujan Saha, Moustafa Bawali, SK Mosharaf Hossain, Abdullah Saleh, Navarun Varma, Dr. Arabinda Mishra, Sri Rakesh Mohapatra, Rinchen Lama and colleagues at Institute for Research, Advocacy and Development (IRADA) for supporting the field research and providing helpful comments. Thanks also go to Sora Chung for detailed secondary research and to Mandana Hendessi, Major General Muniruzzaman, Phil Vernon and Lydia Powell for helpful comments and feedback. International Alert is grateful for the support from our strategic donors: the UK Department for International Development (DFID) and the support of the American People through the United States Agency for International Development (USAID). The paper is a result of the collaboration with the South Asia Network on Security and Climate change (SANSaC). The paper is also part of United States Agency for International Development (USAID) and International Alert’s ongoing work to better understand the dimensions of community resilience in South Asia. We thank the two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vivekananda, J., Schilling, J., Mitra, S. et al. On shrimp, salt and security: livelihood risks and responses in South Bangladesh and East India. Environ Dev Sustain 16, 1141–1161 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-014-9517-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-014-9517-x