Abstract
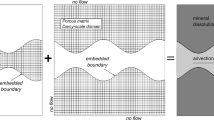
Subsurface contamination problems of metals and radionuclides are ubiquitous. Metals and radionuclides may exist in the solute phase or may be bound to soil particles and interstitial portions of the geologic matrix. Accurate tools to reliably predict the migration and transformation of these metals and radionuclides in the subsurface environment enhance the ability of environmental scientists, engineers, and decision makers to analyze their impact and to evaluate the efficacy of alternative remediation techniques prior to incurring expense in the field. A mechanistic-based numerical model could provide such a tool. This paper communicates the development and verification of a mechanistically coupled fluid-flow thermal-reactive biogeochemical-transport model where both fast and slow reactions occur in porous and fractured media. Theoretical bases, numerical implementations, and numerical experiments using the model are described. A definition of the “rates” of fast/equilibrium reactions is presented to come up with a consistent set of governing equations. Two example problems are presented. The first one is a reactive transport problem which elucidates the non-isothermal effects on heterogeneous reactions. It also demonstrates that the rates of fast/equilibrium reactions are not necessarily greater than that of slow/kinetic reactions in the context of reactive transport. The second example focuses on a complicated but realistic advective–dispersive–reactive transport problem. This example exemplifies the need for innovative numerical algorithms to solve problems involving stiff geochemical reactions. It also demonstrates that rates of all fast/equilibrium reactions are finite and definite. Furthermore, it is noted that a species-versus-time curve cannot be used to characterize the rate of homogeneous fast/equilibrium reaction in a reactive transport system even if one and only one such reaction is responsible for the production of this species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacon, D.H., White, M.D., McGrail, B.P.: Subsurface Transport Over Reactive Multiphases (STORM): A General, Coupled, Nonisothermal Multiphase Flow, Reactive Transport, and Porous Medium Alternation Simulator, Version 2, User’s Guide. PNNL-13108. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland (2000)
Cheng, H.P.: Development and application of a three-dimensional finite element model of subsurface flow, heat transfer, and reactive chemical transport. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, The Pennsylvania State University. University Park (1995)
Cheng, J.R., Strobl, R.O., Yeh, G.T., Lin, H.C., Choi, W.: Modeling of two-dimensional density-dependent flow and transport through variably saturated porous media. J. Hydrol. Eng. 3(4), 248–257 (1998). doi:10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(1998)3:4(248)
Chilakapati, A.: RAFT: A Simulator for ReActive Flow and Transport Groundwater Contaminants. Report 10636, 124 pp., PNL, Richland (1995)
Chilakapati, A., Ginn, T., Szecsody, J.: An analysis of complex reaction networks in groundwater modeling. Water Resour. Res. 34(7), 1767–1780 (1998). doi:10.1029/98WR01041
DOE: Natural and Accelerated Bioremediation Research NABIR, Program Plan, DOE/ER-0659T. US Department of Energy, Office of Energy Research, Office of Health and Environmental Research, 126 pp., Washington, DC (1995)
Dullien, F.A.L.: Porous Media. Academic, New York (1979)
Dykaar, B.D., Kitanidis, P.K.: Macrotransport of a biologically reacting solute through porous media. Water Resour. Res. 32(2), 307–320 (1996). doi:10.1029/95WR03241
Engesgaard, P., Kipp, K.L.: A geochemical transport model for redox-controlled movement of mineral fronts in groundwater flow systems: a case of nitrate removal by oxidation of pyrite. Water Resour. Res. 20(10), 2829–2843 (1992). doi:10.1029/92WR01264
Fang, Y., Yeh, G.T., Burgos, W.D.: A new paradigm to model reaction-based biogeochemical processes. Water Resour. Res. 39(4), 1083–1108 (2003). doi:10.1029/2002WR001694
Fang, Y.: Reactive chemical transport under multiphase system. Ph.D. Dissertation, Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA (2003)
Hunter, K.S., Wang, Y., Van Cappellen, P.: Kinetic modeling of microbially-driven redox chemistry of subsurface environments: coupling transport, microbial metabolism and geochemistry. J. Hydrol. (Amst.) 209, 53–80 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(98)00157-7
Kindred, J.S., Celia, M.A.: Contaminant transport and biodegradation 2. Conceptual model and test simulations. Water Resour. Res. 25(6), 1149–1159 (1989). doi:10.1029/WR025i006p01149
Kräutle, S., Knabner, P.: A new numerical reduction scheme for fully coupled multicomponent transport-reaction problems in porous media. Water Resour. Res. 41, W09414 (2005). doi:10.1029/2004WR003624
Kräutle, S., Knabner, P.: A reduction scheme for coupled multicomponent transport-reaction problems in porous media: generalization to problems with heterogeneous equilibrium reactions. Water Resour. Res. 43(3), W03429.1–W03429.15 (2007)
Lensing, H.J., Voyt, M., Herrling, B.: Modeling of biologically mediated redox processes in the subsurface. J. Hydrol. (Amst.) 159, 125–143 (1994). doi:10.1016/0022-1694(94)90252-6
Li, Y.: A coupled model of fluid flow, thermal transport, and reactive chemical transport through variably saturated media. M. S. Thesis, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL 32816 (2003)
Lichner, P.C., Seith, M.S.: User’s Manual for MULTIFLO: Part II MULTIFLO 1.0 and GEM 1.0, Multicomponent-multiphase Reactive Transport Model. CNWRA 96–019. Center for Nuclear Waste Regulatory Analyses, San Antonio (1996)
Lichtner, P.C.: Continuum formulation of multicomponent-multiphase reactive transport. In: Lichtner, P.C., Steefel, C.I., Oelkers, E.H. (eds.) Reactive Transport in Porous Media, Reviews in Mineralogy, vol. 34, pp. 1–79. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C. (1996)
Marzel, P., Seco, A., Ferrer, J., Gambaldón, C.: Modeling multiple reactive solute transport with adsorption under equilibrium and nonequilibrium conditions. Adv. Water Resour. 17, 363–374 (1994). doi:10.1016/0309-1708(94)90012-4
Parkhurst, D.L.: User’s Guide to PHREEQC, A Computer Model for Speciation, Reaction-Path, Advective-Dispersive Transport and Inverse Geochemical Calculations. US Geological Survey, Water Resources Investigations Report 95–4227 (1995)
Parkhurst, D.L., Appelo, C.J.: User’s guide to PHREEQC (version 2)—A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-reaction, One-dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations. US Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 99–4259 (312 pp.) (1999)
Rittmann, B.E., VanBriesen, J.M.: Microbiological processes in reactive modeling. In: Lichtner, P.C., Steefel, C.I., Oelkers, E.H. (eds.) Reactive Transport in Porous Media, Reviews in Mineralogy, vol. 34, pp. 311–334. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C. (1996)
Salvage, K.M., Yeh, G.T.: Development and application of a numerical model of kinetic and equilibrium microbiological and geochemical reactions (BIOKEMOD). J. Hydrol. (Amst.) 209, 27–52 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(98)00120-6
Singh, V.: Elementary Hydrology. Prentice Hall, New Jersey (1992)
Smith, S.L., Jaffee, P.R.: Modeling the transport and reaction of trace metals in water saturated soils and sediments. Water Resour. Res. 34(11), 3135–3147 (1998). doi:10.1029/98WR02227
Steefel, C.I., Lichtner, P.C.: Diffusion and reaction in rock matrix bordering a hyperalkaline fluid-filled fracture. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 58, 3595–3612 (1994). doi:10.1016/0016-7037(94)90152-X
Steefel, C.I., Yabusaki, S.B.: OS3D/GIMRT, Software for Modeling Multi-Component-Multidimensional Reactive Transport, User’s Manual and Programmer’s Guide, 55 pp. PNL-11166. Pacific Northwest Laboratory, Richland (1996)
Steefel, C.I.: CRUNCH. A computer program for multicomponent reactive transport in porous media. http://www-esd.lbl.gov/ESDstaff/steefel/WebCrunch.htm (2008)
Suarez, D., Šimunnek, J.: Solute transport modeling under variably saturated water flow conditions. In: Lichtner, P.C., Steefel, C.I., Oelkers, E.H. (eds.) Reactive Transport in Porous Media, Reviews in Mineralogy, vol. 34, pp. 229–268. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C. (1996)
Sun, J.: A three-dimensional model of fluid flow, thermal transport, and hydrogeochemical transport through variably saturated Conditions. M. S. Thesis, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Central Florida, Orlando 32816 (2004)
Szecsödy, J.E., Zachara, J.M., Bruckhart, P.: Adsorption-dissolution reactions affecting the distribution and stability of Co(II)-EDTA in Fe-oxide coated sand. Environ. Sci. Technol. 28, 1706–1716 (1994). doi:10.1021/es00058a024
Taylor, S.W., Jaffee, P.R.: Substrate and biomass transport in a porous medium. Water Resour. Res. 26(9), 2181–2194 (1990)
Theis, T.L., Kirkner, D.J., Jennings, A.A.: Multi-Solute Subsurface Transport Modeling for Energy Solid Wastes. Tech. Progress Rept. C00-10253-3, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Notre Dame, Norte Dame (1982)
Widdowson, M.A., Molz, F.J., Benefield, L.D.: A numerical transport model for oxygen- and nitrate-based respiration linked to substrate and nutrient availability in porous media. Water Resour. Res. 24(9), 1553–1565 (1988). doi:10.1029/WR024i009p01553
Wood, B.D., Dawson, C.N., Szecsody, J.E., Streile, G.P.: Modeling contaminant transport and biodegradation in a layered porous media system. Water Resour. Res. 30(6), 1833–1845 (1994). doi:10.1029/94WR00434
Xu, T., Sonnenthal, E., Spycher, N., Pruess, K.: TOUGHREACT user’s guide: a simulation program for non-isothermal multiphase reactive geochemical transport in variably saturated geologic media. Earth Sciences Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, University of California, Berkeley (2003)
Yang, C., Samper, J., Montenegro, L.: CORE2D V4: a code for water flow, heat and solute transport and geochemical reactions: simulations of chemical interactions of clays and concrete. International Workshop ‘Modelling Reactive Transport in Porous Media’, Strassbourg, France, 21–24 January 2008
Yeh, G.T., Luxmoore, R.J.: Modeling moisture and thermal transport in unsaturated porous media. J. Hydrol. (Amst.) 64, 299–309 (1983). doi:10.1016/0022-1694(83)90074-4
Yeh, G.T., Tripathi, V.S.: A critical evaluation of recent developments in hydrogeochemical transport models of reactive multichemical components. Water Resour. Res. 25(1), 93–108 (1989). doi:10.1029/WR025i001p00093
Yeh, G.T., Tripathi, V.S.: HYDROGEOCHEM: A Coupled Model of Hydrological Transport and Geochemical Equilibrium of Multi-component Systems. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge (1990)
Yeh, G.T., Tripathi, V.S.: A model for simulating transport of reactive multispecies components: model development and demonstration. Water Resour. Res. 27(12), 3075–3094 (1991). doi:10.1029/91WR02028
Yeh, G.T., Cheng, J.R., Cheng, H.P.: 2DFEMFAT: user’s manual of a 2-dimensional finite element model of flow and transport through saturated-unsaturated media. Course Notes on Modeling of Flow and Contaminants in the Subsoil. IGMC, Delft, The Netherlands, June 28–July 2 (1993)
Yeh, G.T., Carpenter, S.L., Hopkins, P.L., Siegel, M.D.: Users’ manual of LEGHC: a Lagrangian–Eulerian finite element model of hydrogeochemical transport through saturated-unsaturated media—version 1–0. SAND93–7081. Sandia National Laboratory, Albuquerque (1995a)
Yeh, G.T., Carpenter, S.L., Hopkins, P.L., Siegel, M.D.: Users’ manual of LEGHC: A Lagrangian–Eulerian finite element model of hydrogeochemical transport through saturated–unsaturated media—version 1–1. SAND95–1121. Sandia National Laboratory, Albuquerque (1995b)
Yeh, G.T., Salvage, K., Choi, W.H.: Reactive multispecies-multicomponent chemical transport controlled by both equilibrium and kinetic reactions. In: Proc. XI-th Int. Conf. on Numerical Methods in Water Resources, pp. 585–592, Cancun, Mexico, 22–26 July 1996
Yeh, G.T., Salvage, K.M.: HYDROGEOCHEM 2.0: A Coupled Model of HYDROlogic Transport and Mixed GEOCHEMical Kinetic/Equilibrium Reactions in Saturated Unsaturated Media. Technical Report, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Penn State University, University Park (1997)
Yeh, G.T., Salvage, K.M.: HYDROGEOCHEM 2.1: A Coupled Model of HYDROlogic Transport and Mixed GEOCHEMical Kinetic/Equilibrium Reactions in Saturated Unsaturated Media. Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Penn State University, University Park (1997)
Yeh, G.T., Salvage, K.M., Gwo, J.P., Zachara, J.M., Szecsody, J.E.: HYDROBIOGEOCHEM: A Coupled Model of Hydrologic Transport and Mixed Biogeochemical Kinetic/Equilibrium Reactions in Saturated-Unsaturated Media. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge (1998)
Yeh, G.T., Li, M.H., Siegel, M.D.: Users’ Manual for LEHGC: A Lagrangian-Eulerian Finite Element Model of Coupled Fluid Flows and HydroGeoChemical Transport through Variably Saturated Media—version 2.0. Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Penn State University, University Park (1999)
Yeh, G.T.: Computational Subsurface Hydrology Fluid Flows. Kluwer, New York (1999)
Yeh, G.T.: Computational Subsurface Hydrology Reactions, Transport, and Fate of Chemicals and Microbes. Kluwer, New York (2000)
Yeh, G.T., Siegel, M.D., Li, M.H.: Numerical modeling of coupled fluid flows and reactive transport including fast and slow chemical reactions. J. Contam. Hydrol. 47, 379–390 (2001). doi:10.1016/S0169-7722(00)00164-9
Yeh, G.T., Sun, J.T., Jardine, P.M., Burger, W.D., Fang, Y.L., Li, M.H., Siegel, M.D.: HYDROGEOCHEM 4.0: HYDROGEOCHEM 4.0: A Coupled Model of Fluid Flow, Thermal Transport, and HYDROGEOCHEMical Transport through Saturated-unsaturated Media: Version 4.0. ORNL/TM-2004/103. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge (2004)
Yeh, G.T., Sun, J.T., Jardine, P.M., Burger, W.D., Fang, Y.L., Li, M.H., Siegel, M.D.: HYDROGEOCHEM 5.0: A Three-dimensional Model of Coupled Fluid Flow, Thermal Transport, and HYDROGEOCHEMical Transport through Variably Saturated Conditions—version 5.0. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge (2004)
Yeh, G.T., Sun, J.T., Jardine, P.M., Burger, W.D., Fang, Y.L., Li, M.H., Siegel, M.D.: HYDROGEOCHEM 5.1: A Three Dimensional Model of Coupled Fluid Flow, Thermal Transport, and HYDROGEOCHEMical Transport through Variably Saturated Conditions Version 5.1. Dept. of Civil and Environ. Engineering, University of Central Florida, Orlando (2007)
Yeh, G.T., Li, Y., Jardine, P.M., Burger, W.D., Fang, Y.L., Li, M.H., Siegel, M.D.: HYDROGEOCHEM 4.1: A Coupled Model of Fluid Flow, Thermal Transport, and HYDROGEOCHEMical Transport through Saturated Unsaturated Media Version 4.1. Dept. of Civil and Environ. Engineering, University of Central Florida, Orlando (2007)
Zhang, F., Yeh, G.T., Parker, J.C., Brooks, S.C., Pace, M.N., Kim, Y.J., Jardine, P.M.: A reaction-based paradigm to model three-dimensional reactive chemical transport in groundwater. J. Contam. Hydrol. 93, 10–32 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2006.11.007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeh, GT., Fang, Y., Zhang, F. et al. Numerical modeling of coupled fluid flow and thermal and reactive biogeochemical transport in porous and fractured media. Comput Geosci 14, 149–170 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-009-9140-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-009-9140-3