Abstract
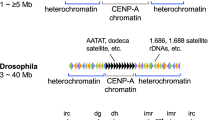
The proper functioning of centromeres requires a complex cascade of epigenetic events involving chromatin and kinetochore assembly; however, the precise mechanism by which this cascade proceeds is unknown. The pivotal event during kinetochore formation is the “loading,” or deposition, of CENP-A. This histone H3 variant is specific to centromeres and replaces conventional H3 in centromeric chromatin. Failure to load CENP-A into mammalian centromeres in late telophase/early G1 of the cell cycle leads to malsegregation and cell division defects in subsequent cell cycles. Mounting evidence supports the hypothesis that an RNA component is involved, although how RNAs participate in centromere formation in mammals has remained unknown. Using the marsupial model, the tammar wallaby, we show that centromeric retroelements produce small RNAs and that hypermorphic expression of these centromeric small RNAs results in disruption of CENP-A localization. We propose that tight regulation of the processing of this new class of small RNAs, crasiRNAs, is an integral component of the epigenetic framework necessary for centromere establishment.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CENP:
-
Centromere protein
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- RNAi:
-
RNA interference
- dsRNA:
-
Double-stranded RNA
- KERV:
-
Kangaroo endogenous retrovirus
- kLTR:
-
KERV long terminal repeat
- crasiRNA:
-
Centromere repeat-associated short interacting RNA
- H3:
-
Histone 3
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- piRNA:
-
Piwi interacting RNA
- IVT:
-
In vitro transcription
- IC:
-
Immunochemistry
- FITC:
-
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
- N.A.:
-
Numerical aperture
- FACS:
-
Fluorescence activated cell sorting
- RISC:
-
RNA-induced silencing complex
- LNA:
-
Locked nucleic acid
- miSAT:
-
Minor satellite
- LINE:
-
Long interspersed nuclear element
- HAC:
-
Human artificial chromosome
- HJURP:
-
Holliday junction recognition protein
- ACA:
-
Anti-centromere antibody
- PKR:
-
Protein kinase R
References
Allshire R, Karpen G (2008) Epigenetic regulation of centromeric chromatin: old dogs, new tricks? Nat Rev Genet 9:923–937
Alonso A, Mahmood R, Li S, Cheung F, Yoda K, Warburton PE (2003) Genomic microarray analysis reveals distinct locations for the CENP-A binding domains in three human chromosome 13q32 neocentromeres. Hum Mol Genet 12:2711–2721
Alonso A, Fritz B, Hasson D, Abrusan G, Cheung F, Yoda K, Radlwimmer B, Ladurner AG, Warburton PE (2007) Co-localization of CENP-C and CENP-H to discontinuous domains of CENP-A chromatin at human neocentromeres. Genome Biol 8:R148
Alonso A, Hasson D, Cheung F, Warburton PE (2010) A paucity of heterochromatin at functional human neocentromeres. Epigenetics Chromatin 3:6
Amaral PP, Dinger ME, Mercer TR, Mattick JS (2008) The eukaryotic genome as an RNA machine. Science 319:1787–1789
Bergmann JH, Rodriguez MG, Martins NM, Kimura H, Kelly DA, Masumoto H, Larionov V, Jansen LE, Earnshaw WC (2011) Epigenetic engineering shows H3K4me2 is required for HJURP targeting and CENP-A assembly on a synthetic human kinetochore. EMBO J 30:328–340
Bergmann JH, Jakubsche JN, Martins NM, Kagansky A, Nakano M, Kimura H, Kelly DA, Turner BM, Masumoto H, Larionov V et al (2012) Epigenetic engineering: histone H3K9 acetylation is compatible with kinetochore structure and function. J Cell Sci 125:411–421
Bouzinba-Segard H, Guais A, Francastel C (2006) Accumulation of small murine minor satellite transcripts leads to impaired centromeric architecture and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:8709–8714
Brown JD, Strbuncelj M, Giardina C, O'Neill RJ (2002) Interspecific hybridization induced amplification of Mdm2 on double minutes in a Mus hybrid. Cytogenet Genome Res 98:184–188
Caplen NJ, Fleenor J, Fire A, Morgan RA (2000) dsRNA-mediated gene silencing in cultured Drosophila cells: a tissue culture model for the analysis of RNA interference. Gene 252:95–105
Carone DM, Longo MS, Ferreri GC, Hall L, Harris M, Shook N, Bulazel KV, Carone BR, Obergfell C, O'Neill MJ et al (2009) A new class of retroviral and satellite encoded small RNAs emanates from mammalian centromeres. Chromosoma 118:113–125
Carroll CW, Milks KJ, Straight AF (2010) Dual recognition of CENP-A nucleosomes is required for centromere assembly. J Cell Biol 189:1143–1155
Chan FL, Wong LH (2012) Transcription in the maintenance of centromere chromatin identity. Nucleic Acids Res 40(22)
Chan FL, Marshall OJ, Saffery R, Won Kim B, Earle E, Choo KHA, Wong LH (2012) Active transcription and essential role of RNA polymerase II at the centromere during mitosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:1979–1984
Choo K (1997) The centromere. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Chueh AC, Northrop EL, Brettingham-Moore KH, Choo KH, Wong LH (2009) LINE retrotransposon RNA is an essential structural and functional epigenetic component of a core neocentromeric chromatin. PLoS Genet 5:e1000354
Clarke PA, Mathews MB (1995) Interactions between the double-stranded RNA binding motif and RNA: definition of the binding site for the interferon-induced protein kinase DAI (PKR) on adenovirus VA RNA. RNA 1:7–20
Clemens MJ (2001) Initiation factor eIF2 alpha phosphorylation in stress responses and apoptosis. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 27:57–89
du Sart D, Cancilla MR, Earle E, Mao JI, Saffery R, Tainton KM, Kalitsis P, Martyn J, Barry AE, Choo KH (1997) A functional neo-centromere formed through activation of a latent human centromere and consisting of non-alpha-satellite DNA. Nat Genet 16:144–153
Du Y, Topp CN, Dawe RK (2010) DNA binding of centromere protein C (CENPC) is stabilized by single-stranded RNA. PLoS Genet 6:e1000835
Dunleavy EM, Roche D, Tagami H, Lacoste N, Ray-Gallet D, Nakamura Y, Daigo Y, Nakatani Y, Almouzni-Pettinotti G (2009) HJURP is a cell-cycle-dependent maintenance and deposition factor of CENP-A at centromeres. Cell 137:485–497
Erhardt S, Mellone BG, Betts CM, Zhang W, Karpen G, Straight AF (2008) Genome-wide analysis reveals a cell cycle-dependent mechanism controlling centromere propagation. J Cell Biol 183:805–818
Eymery A, Horard B, El Atifi-Borel M, Fourel G, Berger F, Vitte AL, Van den Broeck A, Brambilla E, Fournier A, Callanan M et al (2009) A transcriptomic analysis of human centromeric and pericentric sequences in normal and tumor cells. Nucleic Acids Res 37:6340–6354
Ferreri GC, Liscinsky DM, Mack JA, Eldridge MD, O'Neill RJ (2005) Retention of latent centromeres in the mammalian genome. J Hered 96:217–224
Ferreri GC, Brown JD, Obergfell C, Jue N, Finn CE, O'Neill MJ, O'Neill RJ (2011) Recent amplification of the kangaroo endogenous retrovirus, KERV, limited to the centromere. J Virol 85:4761–4771
Ferri F, Bouzinba-Segard H, Velasco G, Hube F, Francastel C (2009) Non-coding murine centromeric transcripts associate with and potentiate Aurora B kinase. Nucleic Acids Res 37:5071–5080
Fishel B, Amstutz H, Baum M, Carbon J, Clarke L (1988) Structural organization and functional analysis of centromeric DNA in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol 8:754–763
Folco HD, Pidoux AL, Urano T, Allshire RC (2008) Heterochromatin and RNAi are required to establish CENP-A chromatin at centromeres. Science 319:94–97
Foltz DR, Jansen LE, Bailey AO, Yates JR 3rd, Bassett EA, Wood S, Black BE, Cleveland DW (2009) Centromere-specific assembly of CENP-a nucleosomes is mediated by HJURP. Cell 137:472–484
Fujita Y, Hayashi T, Kiyomitsu T, Toyoda Y, Kokubu A, Obuse C, Yanagida M (2007) Priming of centromere for CENP-A recruitment by human hMis18alpha, hMis18beta, and M18BP1. Dev Cell 12:17–30
Fukagawa T, Nogami M, Yoshikawa M, Ikeno M, Okazaki T, Takami Y, Nakayama T, Oshimura M (2004) Dicer is essential for formation of the heterochromatin structure in vertebrate cells. Nat Cell Biol 6:784–791
Gan L, Anton KE, Masterson BA, Vincent VA, Ye S, Gonzalez-Zulueta M (2002) Specific interference with gene expression and gene function mediated by long dsRNA in neural cells. J Neurosci Methods 121:151–157
Gent JI, Dawe RK (2012) RNA as a structural and regulatory component of the centromere. Annu Rev Genet 46:443–53
Goshima G, Wollman R, Goodwin SS, Zhang N, Scholey JM, Vale RD, Stuurman N (2007) Genes required for mitotic spindle assembly in Drosophila S2 cells. Science 316:417–421
Hall LE, Mitchell SE, O'Neill RJ (2012) Pericentric and centromeric transcription: a perfect balance required. Chromosome Res 20:535–546
Henikoff S, Ahmad K, Malik HS (2001) The centromere paradox: stable inheritance with rapidly evolving DNA. Science 293:1098–1102
Hsieh CL, Lin CL, Liu H, Chang YJ, Shih CJ, Zhong CZ, Lee SC, Tan BC (2011) WDHD1 modulates the post-transcriptional step of the centromeric silencing pathway. Nucleic Acids Res 39(10):4048–62
Jansen L, Black B, Foltz D, Cleveland D (2007) Propagation of centromeric chromatin requires exit from mitosis. J Cell Biol 176:795–805
Jin W, Lamb JC, Vega JM, Dawe RK, Birchler JA, Jiang J (2005) Molecular and functional dissection of the maize B chromosome centromere. Plant Cell 17:1412–1423
Kanellopoulou C, Muljo S, Kung A, Ganesan S, Drapkin R, Jenuwein T, Livingston D, Rajewsky K (2005) Dicer-deficient mouse embryonic stem cells are defective in differentiation and centromeric silencing. Genes Dev 19:489–501
Karpen GH, Allshire RC (1997) The case for epigenetic effects on centromere identity and function. Trends Genet 13:489–496
Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC (2009) Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:126–139
Lee HR, Neumann P, Macas J, Jiang J (2006) Transcription and evolutionary dynamics of the centromeric satellite repeat CentO in rice. Mol Biol Evol 23:2505–2520
Lindsay J, Carone D, Brown J, Hall L, Qureshi S, Mitchell S, Jannetty N, Hannon G, Renfree M, Pask A et al (2012) Unique small RNA signatures uncovered in the tammar wallaby genome. BMC Genomics (in press)
Lo AW, Magliano DJ, Sibson MC, Kalitsis P, Craig JM, Choo KH (2001) A novel chromatin immunoprecipitation and array (CIA) analysis identifies a 460-kb CENP-A-binding neocentromere DNA. Genome Res 11:448–457
May BP, Lippman ZB, Fang Y, Spector DL, Martienssen RA (2005) Differential regulation of strand-specific transcripts from Arabidopsis centromeric satellite repeats. PLoS Genet 1:e79
Mellone BG, Zhang W, Karpen GH (2009) Frodos found: behold the CENP-a "Ring" bearers. Cell 137:409–412
Metcalfe CJ, Bulazel KV, Ferreri GC, Schroeder-Reiter E, Wanner G, Rens W, Obergfell C, Eldridge MD, O'Neill RJ (2007) Genomic instability within centromeres of interspecific marsupial hybrids. Genetics 177:2507–2517
Murchison E, Partridge J, Tam O, Cheloufi S, Hannon G (2005) Characterization of Dicer-deficient murine embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:12135–12140
Nakano M, Okamoto Y, Ohzeki J, Masumoto H (2003) Epigenetic assembly of centromeric chromatin at ectopic alpha-satellite sites on human chromosomes. J Cell Sci 116:4021–4034
Nakano M, Cardinale S, Noskov VN, Gassmann R, Vagnarelli P, Kandels-Lewis S, Larionov V, Earnshaw WC, Masumoto H (2008) Inactivation of a human kinetochore by specific targeting of chromatin modifiers. Dev Cell 14:507–522
Neumann P, Yan H, Jiang J (2007) The centromeric retrotransposons of rice are transcribed and differentially processed by RNA interference. Genetics 176:749–761
Okamoto Y, Nakano M, Ohzeki J, Larionov V, Masumoto H (2007) A minimal CENP-A core is required for nucleation and maintenance of a functional human centromere. EMBO J 26:1279–1291
O'Neill RJ, O'Neill MJ, Graves JA (1998) Undermethylation associated with retroelement activation and chromosome remodelling in an interspecific mammalian hybrid. Nature 393:68–72
Paddison PJ, Caudy AA, Hannon GJ (2002) Stable suppression of gene expression by RNAi in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:1443–1448
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Pfeffer S, Sewer A, Lagos-Quintana M, Sheridan R, Sander C, Grasser FA, van Dyk LF, Ho CK, Shuman S, Chien M et al (2005) Identification of microRNAs of the herpesvirus family. Nat Methods 2:269–276
Raefski AS, O'Neill MJ (2005) Identification of a cluster of X-linked imprinted genes in mice. Nat Genet 37:620–624
Renfree MB, Papenfuss AT, Deakin JE, Lindsay J, Heider T, Belov K, Rens W, Waters PD, Pharo EA, Shaw G et al (2011) Genome sequence of an Australian kangaroo, Macropus eugenii, provides insight into the evolution of mammalian reproduction and development. Genome Biol 12:R81
Reyes-Turcu FE, Zhang K, Zofall M, Chen E, Grewal SIS (2011) Defects in RNA quality control factors reveal RNAi-independent nucleation of heterochromatin. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18(10):1132–1138
Schueler MG, Higgins AW, Rudd MK, Gustashaw K, Willard HF (2001) Genomic and genetic definition of a functional human centromere. Science 294:109–115
Sullivan KF, Hechenberger M, Masri K (1994) Human CENP-A contains a histone H3 related histone fold domain that is required for targeting to the centromere. J Cell Biol 127:581–592
Ting DT, Lipson D, Paul S, Brannigan BW, Akhavanfard S, Coffman EJ, Contino G, Deshpande V, Iafrate AJ, Letovsky S et al (2011) Aberrant overexpression of satellite repeats in pancreatic and other epithelial cancers. Science 331:593–596
Topp CN, Zhong CX, Dawe RK (2004) Centromere-encoded RNAs are integral components of the maize kinetochore. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:15986–15991
Valgardsdottir R, Chiodi I, Giordano M, Cobianchi F, Riva S, Biamonti G (2005) Structural and functional characterization of noncoding repetitive RNAs transcribed in stressed human cells. Mol Biol Cell 16:2597–2604
Volpe T, Kidner C, Hall I, Teng G, Grewal S, Martienssen R (2002) Regulation of heterochromatic silencing and histone H3 lysine-9 methylation by RNAi. Science 297:1833–1837
Volpe T, Schramke V, Hamilton G, White S, Teng G, Martienssen R, Allshire R (2003) RNA interference is required for normal centromere function in fission yeast. Chromosome Res 11:137–146
Warburton PE, Cooke CA, Bourassa S, Vafa O, Sullivan BA, Stetten G, Gimelli G, Warburton D, Tyler-Smith C, Sullivan KF et al (1997) Immunolocalization of CENP-A suggests a distinct nucleosome structure at the inner kinetochore plate of active centromeres. Curr Biol 7:901–904
Wong LH, Brettingham-Moore KH, Chan L, Quach JM, Anderson MA, Northrop EL, Hannan R, Saffery R, Shaw ML, Williams E et al (2007) Centromere RNA is a key component for the assembly of nucleoproteins at the nucleolus and centromere. Genome Res 17:1146–1160
Zhu Q, Pao GM, Huynh AM, Suh H, Tonnu N, Nederlof PM, Gage FH, Verma IM (2011) BRCA1 tumour suppression occurs via heterochromatin-mediated silencing. Nature 477:179–184
Acknowledgments
We thank the Center for Applied Genetics and Technology for instrumentation, S. Kasowitz for xlr3b dsRNA and A. Pask and M. Renfree for tammar material. A special thanks to A. Pask and B. Mellone for helpful discussion and comments on the manuscript and B. Mellone and I. Oderberg for SoftWoRx quantification protocols. This work was supported by grants from the UCRF and NSF to RJO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Beth A. Sullivan.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 53 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carone, D.M., Zhang, C., Hall, L.E. et al. Hypermorphic expression of centromeric retroelement-encoded small RNAs impairs CENP-A loading. Chromosome Res 21, 49–62 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-013-9337-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-013-9337-0