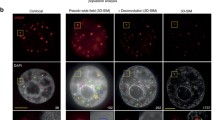
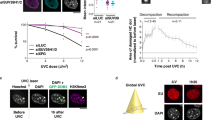
Abstract
Epigenetic alterations induced by ionizing radiation may contribute to radiation carcinogenesis. To detect relative accumulations or losses of constitutive post-translational histone modifications in chromatin regions surrounding DNA double-strand breaks (DSB), we developed a method based on ion microirradiation and correlation of the signal intensities after immunofluorescence detection of the histone modification in question and the DSB marker γ-H2AX. We observed after ionizing irradiation markers for transcriptional silencing, such as accumulation of H3K27me3 and loss of active RNA polymerase II, at chromatin regions labeled by γ-H2AX. Confocal microscopy of whole nuclei and of ultrathin nuclear sections revealed that the histone modification H3K4me3, which labels transcriptionally active regions, is underrepresented in γ-H2AX foci. While some exclusion of H3K4me3 is already evident at the earliest time amenable to this kind of analysis, the anti-correlation apparently increases with time after irradiation, suggesting an active removal process. Focal accumulation of the H3K4me3 demethylase, JARID1A, was observed at damaged regions inflicted by laser irradiation, suggesting involvement of this enzyme in the DNA damage response. Since no accumulation of the repressive mark H3K9me2 was found at damaged sites, we suggest that DSB-induced transcriptional silencing resembles polycomb-mediated silencing rather than heterochromatic silencing.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2D:
-
two-dimensional
- 3D:
-
three-dimensional
- DSB:
-
double-strand break
- ICA:
-
intensity correlation analysis
- ICQ:
-
intensity correlation quotient
- MeV:
-
Mega electron volts
- PDM:
-
product of the differences from the mean
References
Altaf M, Saksouk N, Côté J (2007) Histone modifications in response to DNA damage. Mutat Res 618:81–90
Ayoub N, Jeyasekharan AD, Bernal JA, Venkitaraman AR (2008) HP1-beta mobilization promotes chromatin changes that initiate the DNA damage response. Nature 453:682–686
Ayoub N, Jeyasekharan AD, Venkitaraman AR (2009) Mobilization and recruitment of HP1: a bimodal response to DNA breakage. Cell Cycle 8:2945–2950
Baldeyron C, Soria G, Roche D, Cook AJL, Almouzni G (2011) HP1alpha recruitment to DNA damage by p150CAF-1 promotes homologous recombination repair. J Cell Biol 193:81–95
Barcellos-Hoff MH, Nguyen DH (2009) Radiation carcinogenesis in context: how do irradiated tissues become tumors? Health Phys 97:446–457
Barlow AL, Macleod A, Noppen S, Sanderson J, Guérin CJ (2010) Colocalization analysis in fluorescence micrographs: verification of a more accurate calculation of Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Microsc Microanal 16:710–724
Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K et al (2007) High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 129:823–837
Benevolenskaya EV, Murray HL, Branton P, Young RA, Kaelin WG (2005) Binding of pRB to the PHD protein RBP2 promotes cellular differentiation. Mol Cell 18:623–635
Beshiri ML, Islam A, DeWaal DC, Richter WF, Love J, Lopez-Bigas N, Benevolenskaya EV (2010) Genome-wide analysis using ChIP to identify isoform-specific gene targets. J Vis Exp 41:2101
Binda O, LeRoy G, Bua DJ, Garcia BA, Gozani O, Richard S (2010) Trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 4 impairs methylation of histone H3 lysine 9: regulation of lysine methyltransferases by physical interaction with their substrates. Epigenetics 5:767–775
Bolte S, Cordelières FP (2006) A guided tour into subcellular colocalization analysis in light microscopy. J Microsc 224:213–232
Brookes E, Pombo A (2009) Modifications of RNA polymerase II are pivotal in regulating gene expression states. EMBO Rep 10:1213–1219
Campos EI, Reinberg D (2009) Histones: annotating chromatin. Annu Rev Genet 43:559–599
Chagraoui J, Hebert J, Girard S, Sauvageau G (2011) An anticlastogenic function for the Polycomb Group gene Bmi1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:5284–5289
Chapman RD, Heidemann M, Albert TK et al (2007) Transcribing RNA polymerase II is phosphorylated at CTD residue serine-7. Science 318:1780–1782
Chi P, Allis CD, Wang GG (2010) Covalent histone modifications—miswritten, misinterpreted and mis-erased in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 10:457–469
Chou DM, Adamson B, Dephoure NE et al (2010) A chromatin localization screen reveals poly (ADP ribose)-regulated recruitment of the repressive polycomb and NuRD complexes to sites of DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:18475–18480
Christensen J, Agger K, Cloos PAC et al (2007) RBP2 belongs to a family of demethylases, specific for tri- and dimethylated lysine 4 on histone 3. Cell 128:1063–1076
Cloos PAC, Christensen J, Agger K, Helin K (2008) Erasing the methyl mark: histone demethylases at the center of cellular differentiation and disease. Genes Dev 22:1115–1140
Costes SV, Daelemans D, Cho EH, Dobbin Z, Pavlakis G, Lockett S (2004) Automatic and quantitative measurement of protein-protein colocalization in live cells. Biophys J 86:3993–4003
Das C, Lucia MS, Hansen KC, Tyler JK (2009) CBP/p300-mediated acetylation of histone H3 on lysine 56. Nature 459:113–117
Efron B, Tibshirani R (1993) An introduction to the bootstrap. Chapman & Hall, New York
Egloff S, Murphy S (2008) Cracking the RNA polymerase II CTD code. Trends Genet 24:280–288
Faucher D, Wellinger RJ (2010) Methylated H3K4, a transcription-associated histone modification, is involved in the DNA damage response pathway. PLoS Genet 6:e1001082
French AP, Mills S, Swarup R, Bennett MJ, Pridmore TP (2008) Colocalization of fluorescent markers in confocal microscope images of plant cells. Nat Protoc 3:619–628
Frescas D, Guardavaccaro D, Bassermann F, Koyama-Nasu R, Pagano M (2007) JHDM1B/FBXL10 is a nucleolar protein that represses transcription of ribosomal RNA genes. Nature 450:309–313
Ginjala V, Nacerddine K, Kulkarni A et al (2011) BMI1 is recruited to DNA breaks and contributes to DNA damage-induced H2A ubiquitination and repair. Mol Cell Biol 31:1972–1982
Greubel C, Hable V, Drexler GA et al (2008) Competition effect in DNA damage response. Radiat Environ Biophys 47:423–429
Grigaravicius P, Greulich KO, Monajembashi S (2009) Laser microbeams and optical tweezers in ageing research. Chemphyschem 10:79–85
Hable V, Greubel C, Bergmaier A et al (2009) The live cell irradiation and observation setup at SNAKE. Nucl Instr and Meth in Phys Res B 267:2090–2097
Hauptner A, Dietzel S, Drexler GA et al (2004) Microirradiation of cells with energetic heavy ions. Radiat Environ Biophys 42:237–245
Hayakawa T, Ohtani Y, Hayakawa N et al (2007) RBP2 is an MRG15 complex component and down-regulates intragenic histone H3 lysine 4 methylation. Genes Cells 12:811–826
Iacovoni JS, Caron P, Lassadi I et al (2010) High-resolution profiling of gammaH2AX around DNA double strand breaks in the mammalian genome. EMBO J 29:1446–1457
Khanna R, Li Q, Sun L, Collins TJ, Stanley EF (2006) N type Ca2+ channels and RIM scaffold protein covary at the presynaptic transmitter release face but are components of independent protein complexes. J Neurosci 140:1201–1208
Kovalchuk O, Baulch JE (2008) Epigenetic changes and nontargeted radiation effects—is there a link? Environ Mol Mutagen 49:16–25
Kruhlak MJ, Celeste A, Dellaire G et al (2006) Changes in chromatin structure and mobility in living cells at sites of DNA double-strand breaks. J Cell Biol 172:823–834
Larsen DH, Poinsignon C, Gudjonsson T et al (2010) The chromatin-remodeling factor CHD4 coordinates signaling and repair after DNA damage. J Cell Biol 190:731–740
Li Q, Lau A, Morris TJ, Guo L, Fordyce CB, Stanley EF (2004) A syntaxin 1, Galpha(o), and N-type calcium channel complex at a presynaptic nerve terminal: analysis by quantitative immunocolocalization. J Neurosci 24:4070–4081
Loree J, Koturbash I, Kutanzi K, Baker M, Pogribny I, Kovalchuk O (2006) Radiation-induced molecular changes in rat mammary tissue: possible implications for radiation-induced carcinogenesis. Int J Radiat Biol 82:805–815
Loyola A, Almouzni G (2007) Marking histone H3 variants: how, when and why? Trends Biochem Sci 32:425–433
Luijsterburg MS, Dinant C, Lans H et al (2009) Heterochromatin protein 1 is recruited to various types of DNA damage. J Cell Biol 185:577–586
Miller KM, Tjeertes JV, Coates J et al (2010) Human HDAC1 and HDAC2 function in the DNA-damage response to promote DNA nonhomologous end-joining. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:1144–1151
Mothersill C, Seymour C (2003) Radiation-induced bystander effects, carcinogenesis and models. Oncogene 22:7028–7033
Murr R, Loizou JI, Yang Y-G et al (2006) Histone acetylation by Trrap-Tip60 modulates loading of repair proteins and repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Nat Cell Biol 8:91–99
Nagy Z, Soutoglou E (2009) DNA repair: easy to visualize, difficult to elucidate. Trends Cell Biol 19:617–629
Nottke AC, Beese-Sims SE, Pantalena LF, Reinke V, Shi Y, Colaiácovo MP (2011) SPR-5 is a histone H3K4 demethylase with a role in meiotic double-strand break repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:12805–12810
O’Hagan HM, Mohammad HP, Baylin SB (2008) Double strand breaks can initiate gene silencing and SIRT1-dependent onset of DNA methylation in an exogenous promoter CpG island. PLoS Genet 4(8):e1000155
O’Neill LP, Spotswood HT, Fernando M, Turner BM (2008) Differential loss of histone H3 isoforms mono-, di- and tri-methylated at lysine 4 during X-inactivation in female embryonic stem cells. Biol Chem 389:365–370
Pasini D, Hansen KH, Christensen J, Agger K, Cloos PAC, Helin K (2008) Coordinated regulation of transcriptional repression by the RBP2 H3K4 demethylase and Polycomb-Repressive Complex 2. Genes Dev 22:1345–1355
Polo SE, Kaidi A, Baskcomb L, Galanty Y, Jackson SP (2010) Regulation of DNA-damage responses and cell-cycle progression by the chromatin remodelling factor CHD4. EMBO J 29:3130–3139
R Development Core Team (2010) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. http://www.R-project.org
Ronneberger O, Baddeley D, Scheipl F et al (2008) Spatial quantitative analysis of fluorescently labeled nuclear structures: problems, methods, pitfalls. Chromosome Res 16:523–562
Rouquette J, Genoud C, Vazquez-Nin GH, Kraus B, Cremer T, Fakan S (2009) Revealing the high-resolution three-dimensional network of chromatin and interchromatin space: a novel electron-microscopic approach to reconstructing nuclear architecture. Chromosome Res 17:801–810
Rouquette J, Cremer C, Cremer T, Fakan S (2010) Functional nuclear architecture studied by microscopy: present and future. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 282:1–90
Sánchez-Molina S, Mortusewicz O, Bieber B, Auer S, Eckey M, Leonhardt H, Friedl AA, Becker PB (2011) Role for hACF1 in the G2/M damage checkpoint. Nucl Acids Res. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr435
Sawarkar R, Paro R (2010) Interpretation of developmental signaling at chromatin: the Polycomb perspective. Dev Cell 19:651–661
Schmitges FW, Prusty AB, Faty M et al (2011) Histone methylation by PRC2 is inhibited by active chromatin marks. Mol Cell 42:330–341
Shanbhag NM, Rafalska-Metcalf IU, Balane-Bolivar C, Janicki SM, Greenberg RA (2010) ATM-dependent chromatin changes silence transcription in cis to DNA double-strand breaks. Cell 141:970–981
Shilatifard A (2008) Molecular implementation and physiological roles for histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methylation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20:341–348
Simon JA, Kingston RE (2009) Mechanisms of polycomb gene silencing: knowns and unknowns. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:697–708
Smeenk G, Wiegant WW, Vrolijk H, Solari AP, Pastink A, van Attikum H (2010) The NuRD chromatin-remodeling complex regulates signaling and repair of DNA damage. J Cell Biol 190:741–749
Solimando L, Luijsterburg MS, Vecchio L, Vermeulen W, van Driel R, Fakan S (2009) Spatial organization of nucleotide excision repair proteins after UV-induced DNA damage in the human cell nucleus. J Cell Sci 122:83–91
Solovjeva LV, Svetlova MP, Chagin VO, Tomilin NV (2007) Inhibition of transcription at radiation-induced nuclear foci of phosphorylated histone H2AX in mammalian cells. Chromosome Res 15:787–797
Splinter J, Jakob B, Lang M, Yano K, Engelhardt J, Hell SW, Chen DJ, Durante M, Taucher-Scholz G (2010) Biological dose estimation of UVA laser microirradiation utilizing charged particle-induced protein foci. Mutagenesis 25:289–297
Stante M, Minopoli G, Passaro F, Raia M, Vecchio LD, Russo T (2009) Fe65 is required for Tip60-directed histone H4 acetylation at DNA strand breaks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:5093–5098
Streffer C (2010) Strong association between cancer and genomic instability. Radiat Environ Biophys 49:125–131
Sun Y, Jiang X, Chen S, Fernandes N, Price BD (2005) A role for the Tip60 histone acetyltransferase in the acetylation and activation of ATM. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13182–13187
Suzuki K, Yamauchi M, Oka Y, Suzuki M, Yamashita S (2011) Creating localized DNA double-strand breaks with microirradiation. Nat Protoc 6:134–139
Tang J-B, Greenberg RA (2010) Connecting the dots: interplay between ubiquitylation and SUMOylation at DNA double strand breaks. Genes Cancer 1:787–796
Tjeertes JV, Miller K, Jackson SP (2009) Screen for DNA-damage-responsive histone modifications identifies H3K9Ac and H3K56Ac in human cells. EMBO J 28:1878–1889
van Attikum H, Gasser SM (2009) Crosstalk between histone modifications during the DNA damage response. Trends Cell Biol 19:207–217
Wang GG, Song J, Wang Z, Dormann HL, Casadio F, Li H, Luo JL, Patel DJ, Allis CD (2009) Haematopoietic malignancies caused by dysregulation of a chromatin-binding PHD finger. Nature 459:847–851
Yang B, Zwaans BMM, Eckersdorff M, Lombard DB (2009) The sirtuin SIRT6 deacetylates H3 K56Ac in vivo to promote genomic stability. Cell Cycle 8:2662–2663
Zarebski M, Wiernasz E, Dobrucki JW (2009) Recruitment of heterochromatin protein 1 to DNA repair sites. Cytometry A 75:619–625
Zinner R, Albiez H, Walter J, Peters AHFM, Cremer T, Cremer M (2006) Histone lysine methylation patterns in human cell types are arranged in distinct three-dimensional nuclear zones. Histochem Cell Biol 125:3–19
Zinner R, Teller K, Versteeg R, Cremer T, Cremer M (2007) Biochemistry meets nuclear architecture: multicolor immuno-FISH for co-localization analysis of chromosome segments and differentially expressed gene loci with various histone methylations. Adv Enzyme Regul 47:223–241
Ziv Y, Bielopolski D, Galanty Y et al (2006) Chromatin relaxation in response to DNA double-strand breaks is modulated by a novel ATM- and KAP-1 dependent pathway. Nat Cell Biol 8:870–876
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff of the Maier-Leibnitz-Laboratorium for operating the accelerator facility; K. Pfleghaar and K. Schneider for their help with laser microirradiation; B. Scholz for the help with RT-PCR; H. Hofmann, D. Wieland, and S. Lindemaier for excellent technical assistance, and S. Auer for managing the beam time. Anti-polymerase II Ser5-P and Ser2-P monoclonal antibodies as well as antibody Pol3/3 were a kind gift of D. Eick, anti-JARID1A a kind gift of E. Benevolenskaya, and anti-H3K27me3 a kind gift of T.E. Schmid. Parts of this work were supported by grants of the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (02S8457 and 03NUK007), the DFG Cluster of Excellence Munich Centre for Advanced Photonics, and the LMU innovative project Biomed-S.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Beth A. Sullivan.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
MOESM 1
(PDF 5231 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seiler, D.M., Rouquette, J., Schmid, V.J. et al. Double-strand break-induced transcriptional silencing is associated with loss of tri-methylation at H3K4. Chromosome Res 19, 883–899 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-011-9244-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-011-9244-1