Abstract
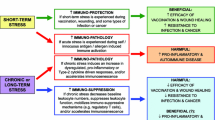
This study was designed to experimentally verify the possibility that Andrographis paniculata could be another medicinal herb potentially useful for prevention of diverse spectrums of pathologies commonly associated with chronic unavoidable environmental stress, and whether andrographolide could as well be its quantitatively major bioactive secondary metabolite. Preventive effects of 21 daily oral 50, 100 and 200 mg/kg doses of a therapeutically used extract of the plant (AP) and 30 and 60 mg/kg/day of pure andrographolide were compared in rats subjected to 1-h daily unavoidable foot-shocks. A pharmaceutically well-standardized Withania somnifera (WS) root extract was used as a reference herbal anti-stress agent in all experiments. Effects of the treatments on stress-induced alterations in body weight, gastric ulcer, adrenal and spleen weights, and depressive state and sexual behavior in male rats were quantified. Other parameters quantified were plasma cortisol levels, and expressions of the cytokines TNF-α, IL-10 and IL-1β in blood and brain. All observed stress-induced pathological changes were less pronounced or completely prevented by both AP and pure andrographolide. Even the lowest tested doses of AP (50 mg/kg/day) or of andrographolide (30 mg/kg/day) suppressed almost maximally the blood IL-1β and IL-10 as well as brain TNF-α and IL-10 expressions induced by chronic stress. Qualitatively, the observed activity profiles of both of them were similar to those of WS dose tested. These results reveal that both AP and andrographolide are pharmacologically polyvalent anti-stress agents, and that biological processes regulating corticosterone and cytokine homeostasis are involved in their modes of actions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhargava KP, Singh N (1981) Anti-stress activity of Ocimum sanctum Linn. Indian J Med Res 73:443–451
Bhattacharya SK, Muruganandam AV (2003) Adaptogenic activity of Withania somnifera: an experimental study using a rat model of chronic stress. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 75:547–555
Boonstra R (2013) Reality as the leading cause of stress: rethinking the impact of chronic stress in nature. Funct Ecol 27:11–23
Chandrasekaran CV, Thiyagarajan P, Sundarajan K, Goudar KS, Deepak M, Murali B, Allan JJ, Agarwal A (2009) Evaluation of the genotoxic potential and acute oral toxicity of standardized extract of Andrographis paniculata (KalmCold™). Food Chem Toxicol 47:1892–1902
Chandrasekaran CV, Gupta A, Agarwal A (2010) Effect of an extract of Andrographis paniculata leaves on inflammatory and allergic mediators in vitro. J Ethnopharmacol 129:203–207
Everds NE, Snyder PW, Bailey KL, Bolon B, Creasy DM, Foley GL, Rosol TJ, Sellers T (2013) Interpreting stress responses during routine toxicity studies: a review of the biology, impact, and assessment. Toxicol Pathol 41:560–614
Govindarajan R, Vijayakumar M, Pushpangadan P (2005) Antioxidant approach to disease management and the role of ‘Rasayana’ herbs of Ayurveda. J Ethnopharmacol 99:165–178
Hennessy MB, Deak T, Schiml PA (2014) Sociality and sickness: have cytokines evolved to serve social functions beyond times of pathogen exposure? Brain Behav Immun 37c:15–20
Hidalgo MA, Hanke JL, Bertoglio JC, Burgos RA (2013) Andrographolide a new potential drug for long term treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis disease. In: Matsuno H (ed) Innovative Rheumatology. InTech, Croatia, pp 247–270
Hu D, Wan L, Chen M, Caudle Y, LeSage G, Li Q, Yin D (2014) Essential role of IL-10/STAT3 in chronic stress-induced immune suppression. Brain Behav Immun 36:118–127
Hueston CM, Deak T (2014) The inflamed axis: the interaction between stress, hormones, and the expression of inflammatory-related genes within key structures comprising the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis. Physiol Behav 124:77–91
Jayakumar T, Hsieh CY, Lee JJ, Sheu JR (2013) Experimental and clinical pharmacology of Andrographis paniculata and its major bioactive phytoconstituent andrographolide. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. Article ID: 846740. doi:10.1155/2013/846740
Koolhaas JM, Bartolomucci A, Buwalda B, de Boer SF, Flügge G, Korte SM, Meerlo P, Murison R, Olivier B, Palanza P, Richter-Levin G, Sgoifo A, Steimer T, Stiedl O, van Dijk G, Wöhr M, Fuchs E (2011) Stress revisited: a critical evaluation of the stress concept. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35:1291–1301
Korte SM, Koolhaas JM, Wingfield JC, McEwen BS (2005) The Darwinian concept of stress: benefits of allostasis and costs of allostatic load and the trade-offs in health and disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:3–38
Lim JC, Chan TK, Ng DS, Sagineedu SR, Stanslas J, Wong WS (2012) Andrographolide and its analogues: versatile bioactive molecules for combating inflammation and cancer. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 39:300–310
Lucini D, Pagani M (2012) From stress to functional syndromes: an internist’s point of view. Eur J Intern Med 23:295–301
Morishita S, Shoji M, Oguni Y, Hirai Y, Sugimoto C, Ito C (1993) Effects of crude drugs derived from animal sources on sexual and learning behaviour in chronically stressed mice. Phytother Res 7:57–63
Panossian A, Wikman G (2013) Efficacy of Andrographis paniculata in upper respiratory tract infectious diseases and the mechanism of action. In: Wagner H, Ulrich-Merzenich G (eds) Evidence and rational based research on Chinese drugs. Springer, Vienna, pp 137–179
Porsolt RD, Anton G, Blavet N, Jalfre M (1978) Behavioural despair in rats: a new model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Eur J Pharmacol 47:379–391
Reber SO (2012) Stress and animal models of inflammatory bowel disease—an update on the role of the hypothalamo–pituitary–adrenal axis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 37:1–19
Saraiva M, O’Garra A (2010) The regulation of IL-10 production by immune cells. Nat Rev Immunol 10:170–181
Saxena RC, Singh R, Kumar P, Yadav SC, Negi MP, Saxena VS, Joshua AJ, Vijayabalaji V, Goudar KS, Venkateshwarlu K, Amit A (2010) A randomized double blind placebo controlled clinical evaluation of extract of Andrographis paniculata (KalmCold™) in patients with uncomplicated upper respiratory tract infection. Phytomedicine 17:178–185
Singh B, Chandan BK, Sharma N, Singh S, Khajuria A, Gupta DK (2005) Adaptogenic activity of glyco-peptido-lipid fraction from the alcoholic extract of Trichopus zeylanicus Gaerten (part II). Phytomedicine 12:468–481
Singh GK, Rai G, Chatterjee SS, Kumar V (2012) Beneficial effects of Fumaria indica on chronic stress-induced neurobehavioral and biochemical perturbations in rats. Chin Med 3:49–60
Singh GK, Rai G, Chatterjee SS, Kumar V (2013) Effects of ethanolic extract of Fumaria indica L. on rat cognitive dysfunctions. Ayu 34:421–429
Thakur AK, Chatterjee SS, Kumar V (2014a) Neuropsychopharmacology of a therapeutically used Andrographis paniculata extract: a preclinical study. Orient Pharm Exp Med 14:181–191
Thakur AK, Chatterjee SS, Kumar V (2014b) Therapeutic potential of traditionally used medicinal plant Andrographis paniculata (Burm. F.) against diabesity: an experimental study in rats. TANG: Int J Genuine Tradit Med 4:1–8
Thakur AK, Chatterjee SS, Kumar V (2014c) Adaptogenic potential of Andrographolide: an active principle of the King of Bitters (Andrographis paniculata). J Tradit Complement Med (in press)
Thiebot MH, Martin P, Puech AJ (1992) Animal behavioural studies in the evaluation of antidepressant drugs. Br J Psychiatry Suppl 160:44–50
Valdiani A, Kadir MA, Tan SG, Talei D, Abdullah MP, Nikzad S (2012) Nain-e Havandi Andrographis paniculata present yesterday, absent today: a plenary review on underutilized herb of Iran’s pharmaceutical plants. Mol Biol Rep 39:5409–5424
Williamson EM (2002) Major herbs of Ayurveda. Churchill Livingstone, China
Acknowledgments
AKT thankfully acknowledged the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, New Delhi, for awarding INSPIRE Fellowship (IF110595). The authors would like to acknowledge Natural Remedies Pvt. Ltd., Bangalore, for providing complementary samples of standardized extract of Andrographis paniculata, standardized root extract of Withania somnifera and pure andrographolide along with HPLC fingerprints.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shyam Sunder Chatterjee is a retired Head of Pharmacology Research Laboratories, Dr. Willmar Schwabe GmbH & Co. KG, Karlsruhe, Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thakur, A.K., Soni, U.K., Rai, G. et al. Protective Effects of Andrographis paniculata Extract and Pure Andrographolide Against Chronic Stress-Triggered Pathologies in Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34, 1111–1121 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0086-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0086-1